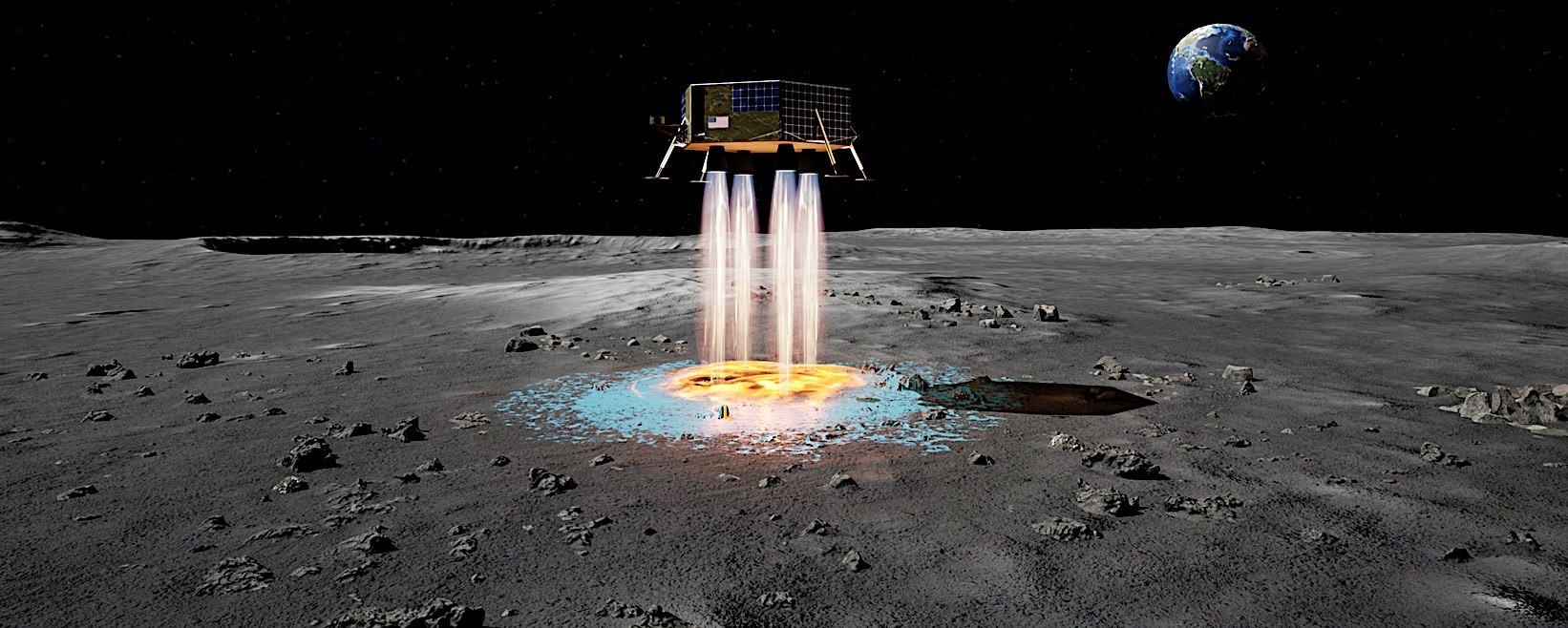
The Moon’s surface, a desolate expanse cloaked in a thick layer of abrasive lunar dust, poses a significant challenge to future lunar missions. This fine-grained regolith, the product of countless cosmic impacts, becomes a formidable obstacle when spacecraft descend upon the lunar world.
Powerful rocket engines, necessary to slow the descent of larger, heavier spacecraft like those planned for the Artemis missions, stir up this dusty mantle, creating a high-speed cloud of abrasive particles.
This plume-surface interaction can scour equipment, obscure visibility, and alter the landing site, jeopardizing mission success. As NASA prepares for these ambitious endeavors, mitigating the effects of this lunar dust is a critical priority.

The quest to safely land spacecraft on extraterrestrial bodies has spurred innovation across various sectors, including academia. The Human Lander Challenge (HuLC), a 2023 competition, sought fresh perspectives from undergraduate and graduate students to tackle this complex problem. Following our exploration of SOLACE, another groundbreaking concept emerges: PARSEC.
This ingenious idea, conceived by Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University and co-winner of the HuLC’s Excellence in Systems Engineering Award, proposes a radical solution. By harnessing the intense heat of rocket engines and introducing a specialized additive, PARSEC aims to transform the lunar surface into a solid landing pad on demand, mitigating the challenges of regolith displacement and crater formation during descent.
The PARSEC concept centers on an innovative approach to lunar landings. By injecting a granular additive into the rocket exhaust during descent, this system aims to create a solidified landing pad upon contact with the lunar surface. This method holds the promise of mitigating the impact of landings, reducing lunar surface disturbances, and providing a stable platform for spacecraft operations.
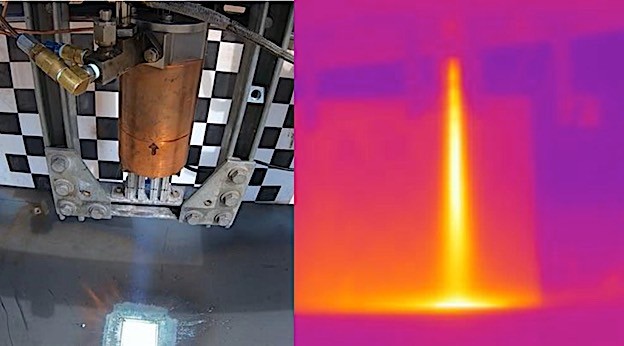
While initial tests have shown encouraging results, forming conglomerated surface material from various additives, significant research remains to optimize the system for practical application.
Key challenges include developing efficient additive storage and delivery mechanisms, selecting the most suitable additive from a range of potential materials, and conducting comprehensive testing under simulated lunar conditions.
The potential of such a solution has garnered attention, as evidenced by NASA’s recent award to the Embry-Riddle team behind PARSEC. This technology could offer a vital contribution to future lunar missions, including the Artemis program, by addressing the persistent issue of powdery lunar regolith.

