A car battery is essential for powering your vehicle’s electrical systems and providing the energy needed to start the engine. It converts stored chemical energy into electrical energy, ensuring the vehicle’s components operate smoothly. During engine operation, the alternator recharges the battery, preparing it for subsequent starts and powering accessories like lights, radios, and air conditioning when the car is stationary. Without a functioning battery, your car cannot operate reliably.
Battery failures can occur for various reasons, often leaving drivers stranded unexpectedly. Understanding the causes of these failures is crucial for maintaining vehicle reliability and avoiding inconvenient breakdowns. Proactive measures, such as regular maintenance and timely diagnostics, can help identify and resolve potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
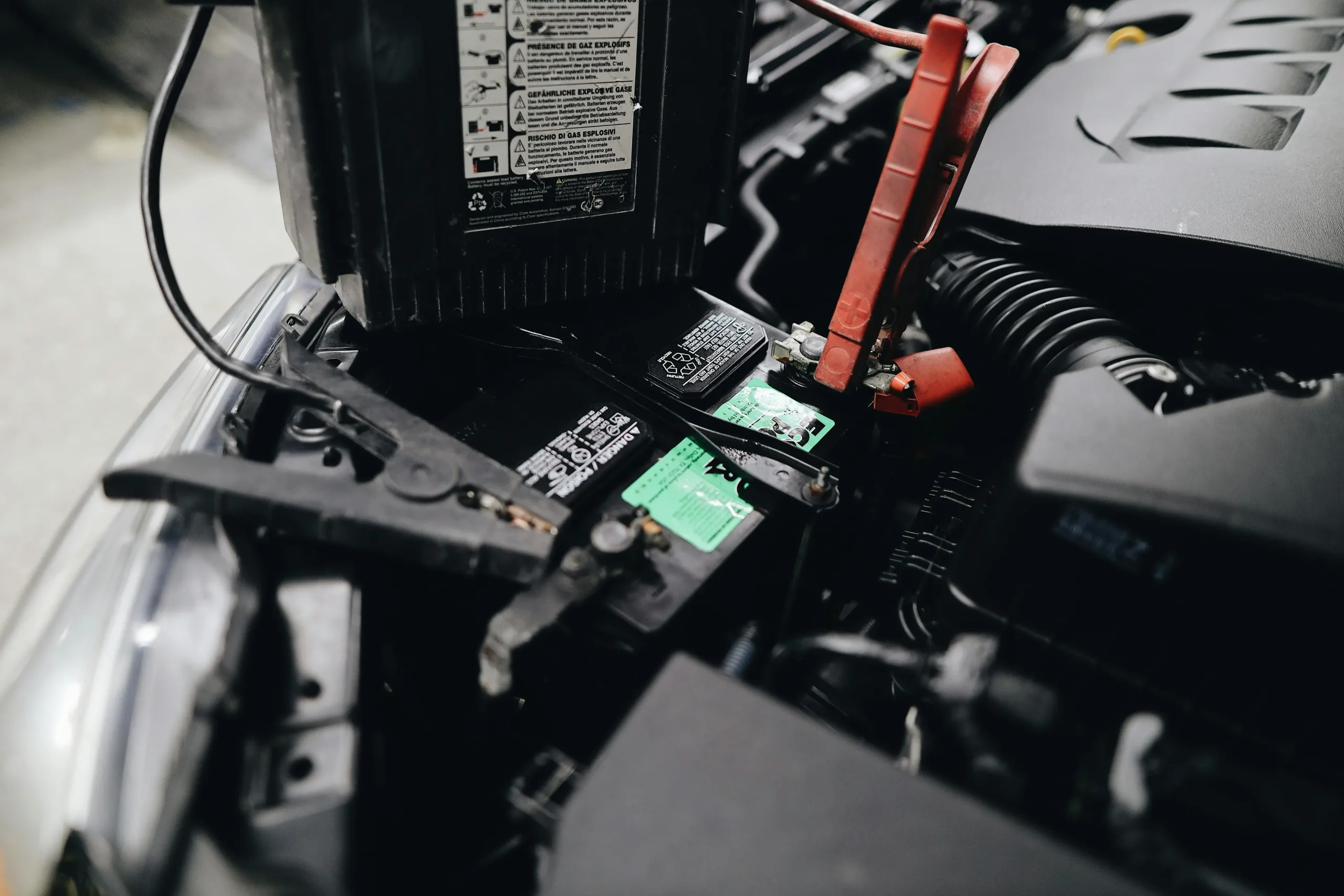
A faulty charging system is a common reason for battery failure. Components like the alternator and voltage regulator play a key role in recharging the battery while the car is in use. When these parts malfunction, the battery may not receive adequate charging. Corrosion or loose connections at the battery terminals further disrupt the flow of electrical current, reducing charging efficiency and accelerating battery depletion.
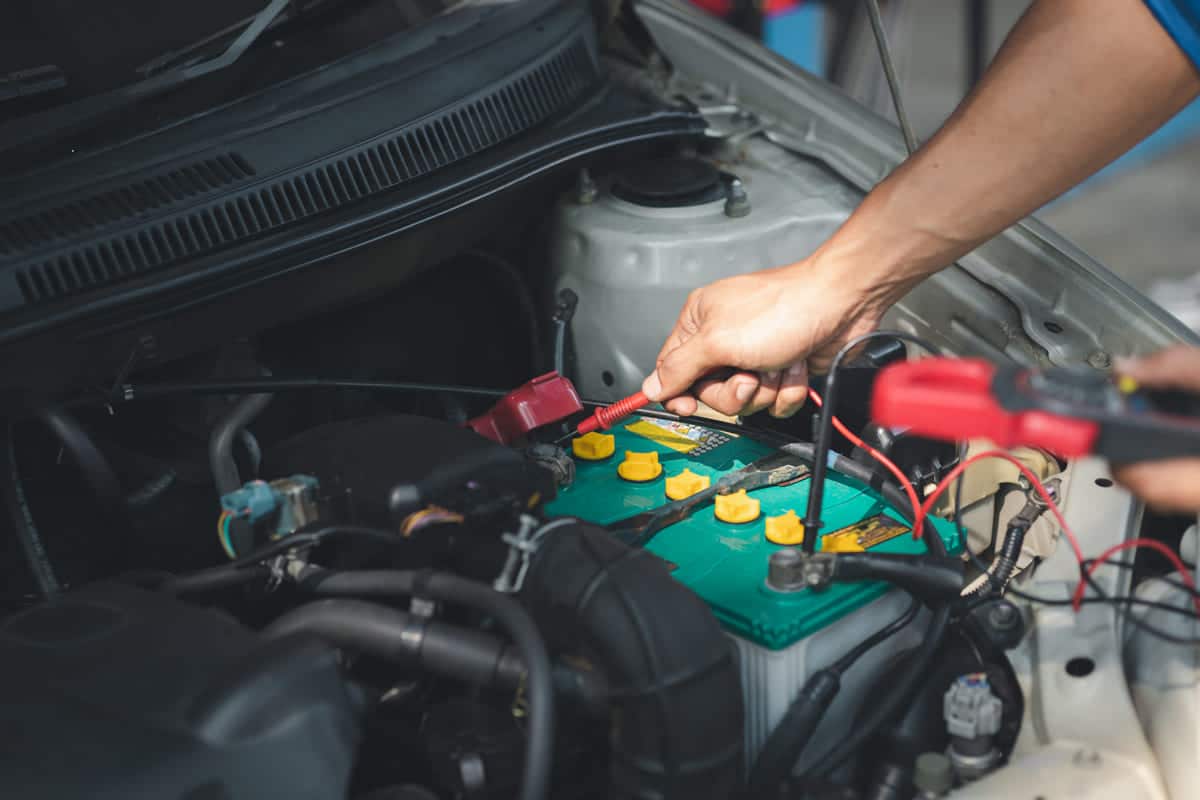

Parasitic drain is another issue that contributes to battery problems. Electrical components like malfunctioning interior lights, faulty wiring, or software glitches can draw power even when the car is turned off. While minimal power draw is normal in modern vehicles, excessive drain can prematurely deplete the battery. Regular inspections and addressing abnormal power consumption can mitigate these risks.
Frequent short trips are particularly detrimental to car batteries. Starting the engine requires a significant energy burst, which the alternator needs time to replenish. Short trips often fail to give the alternator enough time to recharge the battery fully, leading to incomplete recharge cycles. Over time, this pattern diminishes the battery’s performance and overall lifespan.
Low electrolyte levels also affect battery functionality. Heat under the hood accelerates the evaporation of the electrolyte solution, while internal leakage reduces the chemical balance needed for efficient energy storage and delivery. Aging batteries, too, experience chemical degradation over time. Sulfation and increased internal resistance weaken their capacity to hold a charge, making replacement necessary after a certain period.
Extreme temperatures compound battery issues. Cold weather increases internal resistance and makes it harder for the battery to deliver power during startups, while hot weather speeds up internal chemical reactions, causing water loss and corrosion. Both conditions reduce the battery’s efficiency and longevity, requiring extra care and maintenance in harsh climates.
When faced with a dead battery, it is important to remain calm and follow appropriate steps. Turn off all electrical components, inspect for corrosion or loose cables, and attempt a jump start if possible. Portable battery chargers are also useful in emergencies. If the battery continues to fail despite these efforts, it might be time for a replacement, especially if it has reached the end of its expected lifespan.
Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your car battery in good condition. This includes checking fluid levels, cleaning terminals to prevent corrosion, securing the battery to minimize vibrations, and conducting periodic performance tests. Professional servicing ensures comprehensive care, addressing underlying issues that may lead to premature failure. Taking these measures helps extend your battery’s life and keeps your vehicle running smoothly.