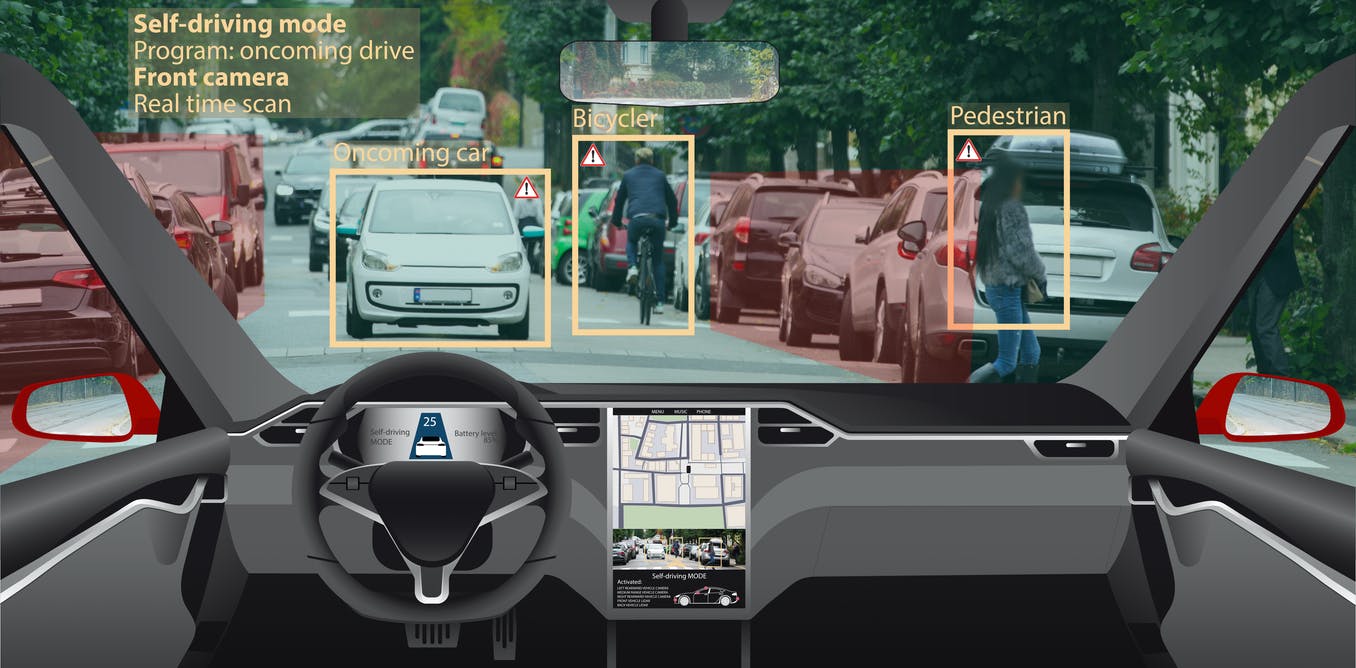
The emergence of self-driving cars is revolutionizing the automotive industry, promising enhanced safety, convenience, and efficiency. However, with this technological advancement comes a complex and pressing issue: liability in the event of an accident. Traditional accidents involving human drivers are typically resolved by determining fault based on human error or negligence.
However, in the case of self-driving cars, the question of liability becomes more intricate as the human element is minimized or removed entirely. The determination of liability in accidents involving autonomous vehicles can involve multiple parties, including the vehicle owner, the manufacturer, the software developer, and even the entity responsible for maintaining the vehicle’s technology.
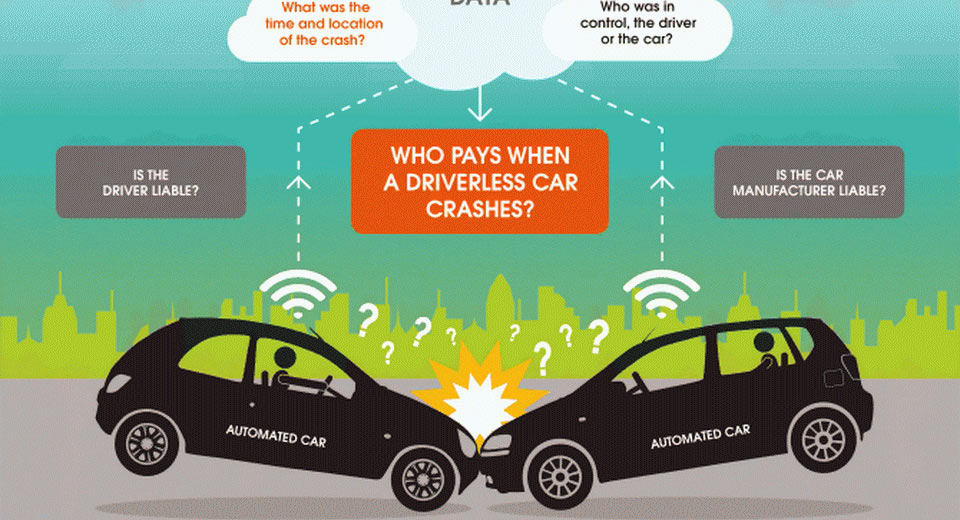
This complexity raises significant legal and ethical questions about accountability and responsibility. As self-driving technology continues to evolve, establishing clear liability frameworks is essential for ensuring public trust and the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles.
In this article, we will explore the intricacies of liability in accidents involving self-driving cars. First, we will examine the traditional liability framework for accidents and how it applies to autonomous vehicles. Then, we will delve into the emerging legal and ethical challenges specific to self-driving technology. Through this balanced analysis, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current landscape and future considerations for liability in the age of autonomous vehicles.
Traditional Liability Framework for Accidents and Its Application to Autonomous Vehicles
In traditional traffic accidents, liability is typically determined by identifying the party at fault based on human error, negligence, or intentional misconduct. Factors such as speeding, distracted driving, failure to obey traffic signals, and driving under the influence are common grounds for establishing fault. The responsible party is held accountable for damages, which may include property damage, medical expenses, and other associated costs. Insurance companies play a crucial role in the process, of assessing claims and providing compensation based on the determined liability.
With the advent of self-driving cars, the traditional liability framework faces new challenges. Autonomous vehicles operate based on complex algorithms, sensors, and artificial intelligence, reducing or eliminating the need for human intervention. This shift raises questions about who should be held accountable in the event of an accident involving a self-driving car. Should the vehicle owner be responsible, even if they were not actively driving? Or should liability rest with the manufacturer or software developer responsible for the vehicle’s technology?
One approach is to apply existing product liability principles to self-driving cars. Under product liability law, manufacturers can be held liable for defects in their products that cause harm. In the context of autonomous vehicles, if an accident is determined to be caused by a malfunction or defect in the vehicle’s software or hardware, the manufacturer or developer could be held responsible. This approach aligns with the notion that companies should ensure the safety and reliability of their products before releasing them to the market.
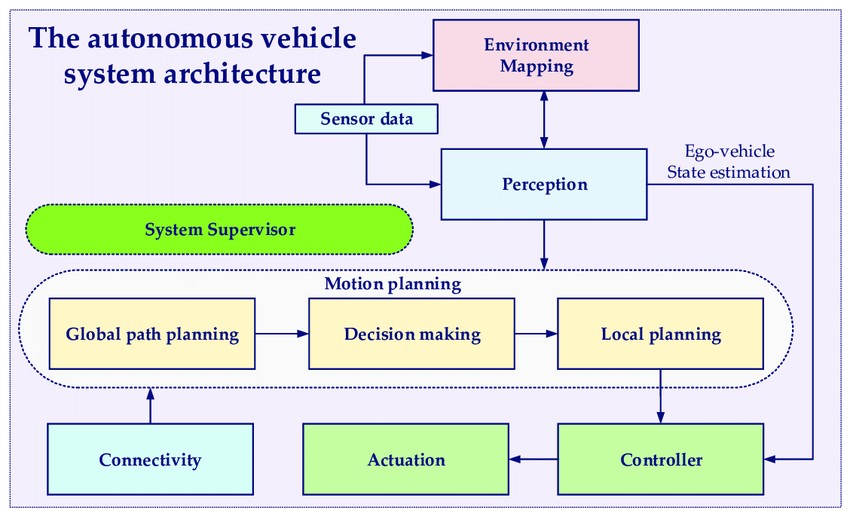
Another consideration is the role of the vehicle owner. Even with self-driving technology, owners have a responsibility to maintain their vehicles and ensure they are in proper working condition. Failure to perform necessary maintenance or ignoring recalls and updates could potentially implicate the owner in the event of an accident. Additionally, some self-driving systems still require human supervision, and the driver may be expected to take control in certain situations. In such cases, the owner’s actions (or inactions) could influence liability determinations.
Insurance companies are also adapting to the changing landscape. Some insurers are developing specialized policies for autonomous vehicles, which may include different coverage options and liability considerations. As technology and legal frameworks evolve, insurance companies will play a critical role in shaping how liability is addressed in the context of self-driving cars.
The traditional liability framework for accidents faces new challenges with the rise of autonomous vehicles. Determining fault in accidents involving self-driving cars requires careful consideration of multiple factors, including product defects, owner responsibilities, and the evolving role of insurance companies. Applying existing principles of product liability and adapting insurance policies are potential approaches to addressing these challenges.
Emerging Legal and Ethical Challenges of Self-Driving Technology
The widespread adoption of self-driving cars presents several emerging legal and ethical challenges, particularly concerning liability and accountability. One of the primary legal challenges is establishing clear and consistent liability frameworks that address the complexities of autonomous technology. Traditional liability models may not adequately capture the nuances of self-driving systems, necessitating the development of new legal standards and regulations.
One approach to addressing these challenges is the concept of “strict liability,” where manufacturers are held liable for any harm caused by their products, regardless of fault. In the context of self-driving cars, this would mean that automakers and technology developers bear the responsibility for accidents resulting from their autonomous systems. While this approach simplifies the determination of liability, it may also place significant financial and legal burdens on manufacturers, potentially stifling innovation and growth in the industry.
Another legal consideration is the allocation of liability among multiple parties involved in the development and operation of autonomous vehicles. Self-driving cars rely on a complex ecosystem of components, including sensors, software, and communication systems, often developed by different companies. In the event of an accident, determining which party’s contribution led to the failure can be challenging. Establishing clear contractual agreements and regulatory standards can help delineate the responsibilities and liabilities of each stakeholder.
Ethical challenges also arise in the context of self-driving technology. One major ethical dilemma is the programming of autonomous systems to make decisions in critical situations. For example, how should a self-driving car prioritize the safety of its passengers versus the safety of pedestrians in the event of an unavoidable collision? These moral decisions, often referred to as the “trolley problem” in ethics, require careful consideration and transparent communication to gain public trust.
Privacy and data security are additional ethical concerns. Self-driving cars collect vast amounts of data on driving behavior, location, and vehicle performance. Ensuring that this data is protected from unauthorized access and misuse is crucial for maintaining consumer trust. Moreover, transparent data collection practices and informed consent are essential to address privacy concerns and uphold ethical standards.
Government and regulatory bodies play a critical role in addressing these legal and ethical challenges. Policymakers must develop comprehensive regulations that balance innovation with public safety and accountability. This includes establishing standards for testing and deploying autonomous vehicles, setting guidelines for data privacy and security, and creating frameworks for liability and compensation.
The rise of self-driving technology presents significant legal and ethical challenges related to liability, accountability, decision-making, and data privacy. Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort among manufacturers, technology developers, regulators, and policymakers. By developing clear and consistent legal frameworks and upholding ethical standards, society can navigate the complexities of autonomous vehicles and realize their full potential in transforming transportation.