Electric vehicles (EVs) have emerged as a promising solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. Central to the operation of EVs are their batteries, which store and provide the energy needed to power the vehicle.
While EVs offer numerous environmental benefits, the production and disposal of EV batteries have raised concerns about their impact on the environment. The cost of EV batteries, both financially and ecologically, is a topic of ongoing debate. On one hand, EV batteries are seen as an environmental savior, helping to decrease reliance on fossil fuels and reduce carbon emissions.
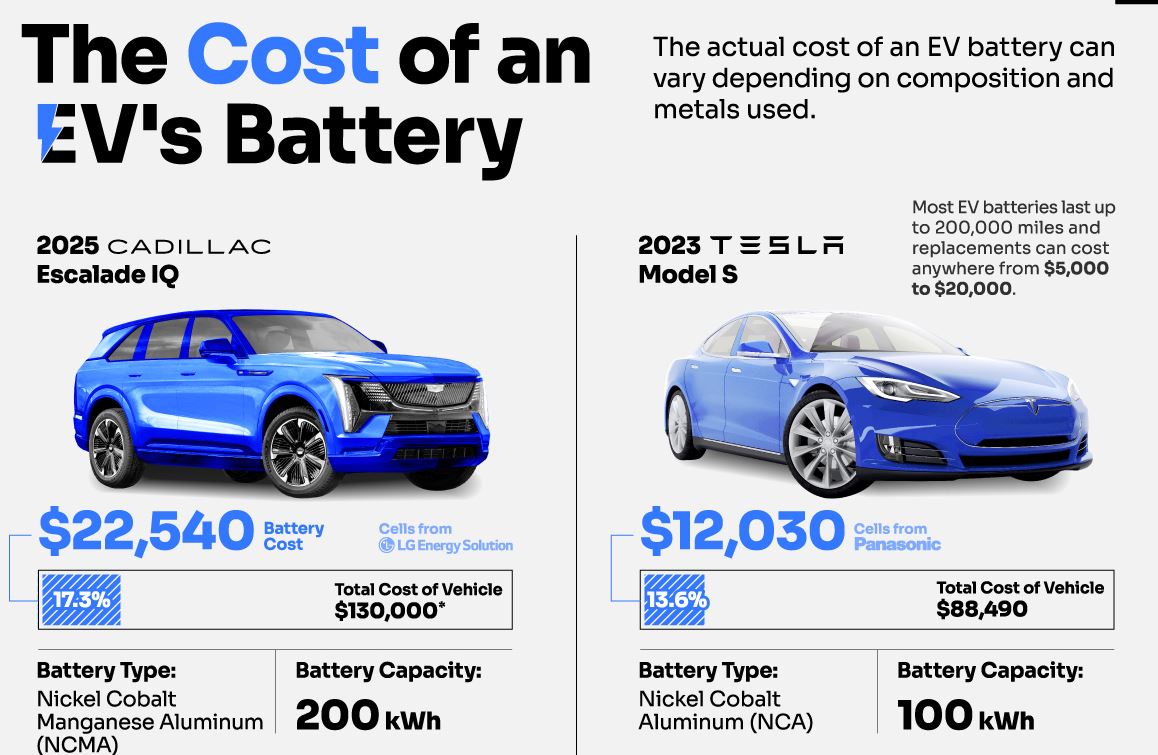
They enable the transition to cleaner energy sources and contribute to improved air quality, especially in urban areas. On the other hand, the extraction and processing of raw materials used in EV batteries, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, have significant environmental and social implications.
The mining processes can lead to habitat destruction, water pollution, and human rights abuses. In this article, we will explore both sides of the debate. First, we will examine the environmental benefits of EV batteries and their role in promoting sustainable transportation.
Then, we will look into the environmental and resource challenges associated with their production and disposal. Through this balanced analysis, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of whether EV batteries are truly an environmental savior or a resource drain.
Environmental Benefits of EV Batteries
The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and their batteries offers several significant environmental benefits, primarily centered around reducing greenhouse gas emissions, decreasing reliance on fossil fuels, and improving air quality. One of the most notable advantages of EV batteries is their potential to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, a major contributor to climate change. Unlike internal combustion engine vehicles, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning they do not release CO2, nitrogen oxides, or particulate matter into the atmosphere. This reduction in emissions is especially beneficial in urban areas, where traffic congestion and pollution levels are often high.
EV batteries also play a crucial role in decreasing reliance on fossil fuels. Traditional vehicles rely on gasoline and diesel, both of which are derived from finite resources and contribute to environmental degradation through their extraction and combustion processes. By contrast, EVs can be powered by electricity generated from renewable sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower. As the electricity grid becomes greener, the environmental benefits of EVs will continue to grow, further reducing their carbon footprint.
Another significant benefit of EV batteries is their potential to improve air quality. In many cities around the world, air pollution from vehicle emissions is a major public health concern, contributing to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. By eliminating tailpipe emissions, EVs help to improve air quality, leading to better health outcomes for urban populations. This is particularly important in densely populated areas where traffic-related pollution is a leading cause of health problems.

EV batteries also support the integration of renewable energy sources into the electricity grid. Energy storage solutions, such as EV batteries, can help to balance supply and demand by storing excess energy generated from renewable sources and releasing it when needed. This capability enhances the stability and reliability of the grid, facilitating the transition to a more sustainable energy system. Additionally, the use of second-life EV batteries for energy storage applications can extend their useful life and provide additional environmental benefits.
Furthermore, the development and deployment of EV batteries drive technological innovation and economic growth. The research and development of advanced battery technologies have led to significant improvements in energy density, charging speed, and performance. These advancements not only benefit the automotive industry but also have broader applications in sectors such as renewable energy, consumer electronics, and grid storage. The growth of the EV battery industry creates high-quality jobs, stimulates investment in research and development, and contributes to economic development.
EV batteries offer substantial environmental benefits by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, decreasing reliance on fossil fuels, improving air quality, and supporting the integration of renewable energy sources. Their role in promoting sustainable transportation and driving technological innovation underscores their potential as an environmental savior.
Environmental and Resource Challenges of EV Batteries
While electric vehicle (EV) batteries provide significant environmental benefits, their production and disposal pose several environmental and resource challenges. One of the primary concerns is the extraction and processing of raw materials used in EV batteries, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. These materials are essential for the production of high-performance batteries but are often sourced through mining practices that have substantial environmental and social impacts.
The mining of lithium, for example, involves extracting lithium-rich brine from underground reservoirs, a process that requires large amounts of water. In regions where water is already scarce, such as parts of South America’s lithium triangle, this can lead to water depletion and competition with local communities for water resources. Additionally, the extraction process can result in habitat destruction, soil degradation, and contamination of water sources with harmful chemicals.
Cobalt mining, primarily concentrated in the Democratic Republic of Congo, presents significant social and environmental challenges. Artisanal and small-scale mining, which accounts for a substantial portion of cobalt production, is often associated with unsafe working conditions, child labor, and human rights abuses. Environmentally, cobalt mining can lead to deforestation, soil erosion, and the release of toxic substances into the environment.

The recycling and disposal of EV batteries also present significant challenges. Batteries contain hazardous materials that can pose risks to human health and the environment if not handled properly. Improper disposal can lead to soil and water contamination, while inadequate recycling processes can result in the loss of valuable materials. Developing efficient and sustainable recycling methods is essential to minimize the environmental impact of battery disposal and recover valuable resources.
The energy-intensive production of EV batteries is another challenge. The manufacturing process involves high energy consumption and significant greenhouse gas emissions. While efforts are being made to reduce the carbon footprint of battery production through the use of renewable energy and more efficient processes, the current production methods still contribute to environmental degradation.
Moreover, the increasing demand for EV batteries raises concerns about resource availability and sustainability. The finite nature of critical materials such as lithium and cobalt means that the continued growth of the EV industry could lead to resource depletion and supply chain constraints. Developing alternative battery chemistries that rely on more abundant and sustainable materials is crucial to address these concerns.
While EV batteries offer substantial environmental benefits, their production and disposal pose significant environmental and resource challenges. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach, including sustainable mining practices, efficient recycling methods, and the development of alternative battery technologies. By balancing the benefits and challenges, society can work towards a more sustainable and responsible approach to EV battery production and use.

