The debate over the future of transportation often focuses on electric vehicles, but hydrogen cars are emerging as a strong contender. Toyota, a pioneer in automotive innovation, is betting big on hydrogen fuel cell technology.
The Japanese automaker believes hydrogen has the potential to revolutionize the way we travel, offering a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional fossil fuels and even battery electric vehicles. With significant investments in research and development, Toyota is working to overcome the challenges associated with hydrogen production, storage, and distribution.
Their vision extends beyond passenger cars to include commercial vehicles, buses, and even stationary power generators. As the world seeks greener and more sustainable energy solutions, hydrogen cars could play a crucial role in reducing emissions and dependency on fossil fuels. In this article, we explore Toyota’s commitment to hydrogen technology and the potential of hydrogen cars to shape the future of transportation.
The Technology Behind Hydrogen Cars
Hydrogen cars, also known as fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), operate by converting hydrogen gas into electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen in a fuel cell. This process produces only water vapor and heat as byproducts, making FCEVs environmentally friendly. The key advantage of hydrogen technology lies in its high energy density and rapid refueling capabilities. Unlike battery electric vehicles (BEVs), which can take hours to recharge, hydrogen cars can be refueled in minutes, offering a driving experience similar to that of traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
Toyota’s flagship hydrogen vehicle, the Mirai, exemplifies the potential of this technology. Launched in 2014, the Mirai has undergone continuous improvements, with the latest generation offering a driving range of over 400 miles on a single tank of hydrogen. The vehicle’s fuel cell stack is more compact and efficient, allowing for better performance and increased interior space. The Mirai’s design also incorporates advanced aerodynamics to reduce drag and improve efficiency.
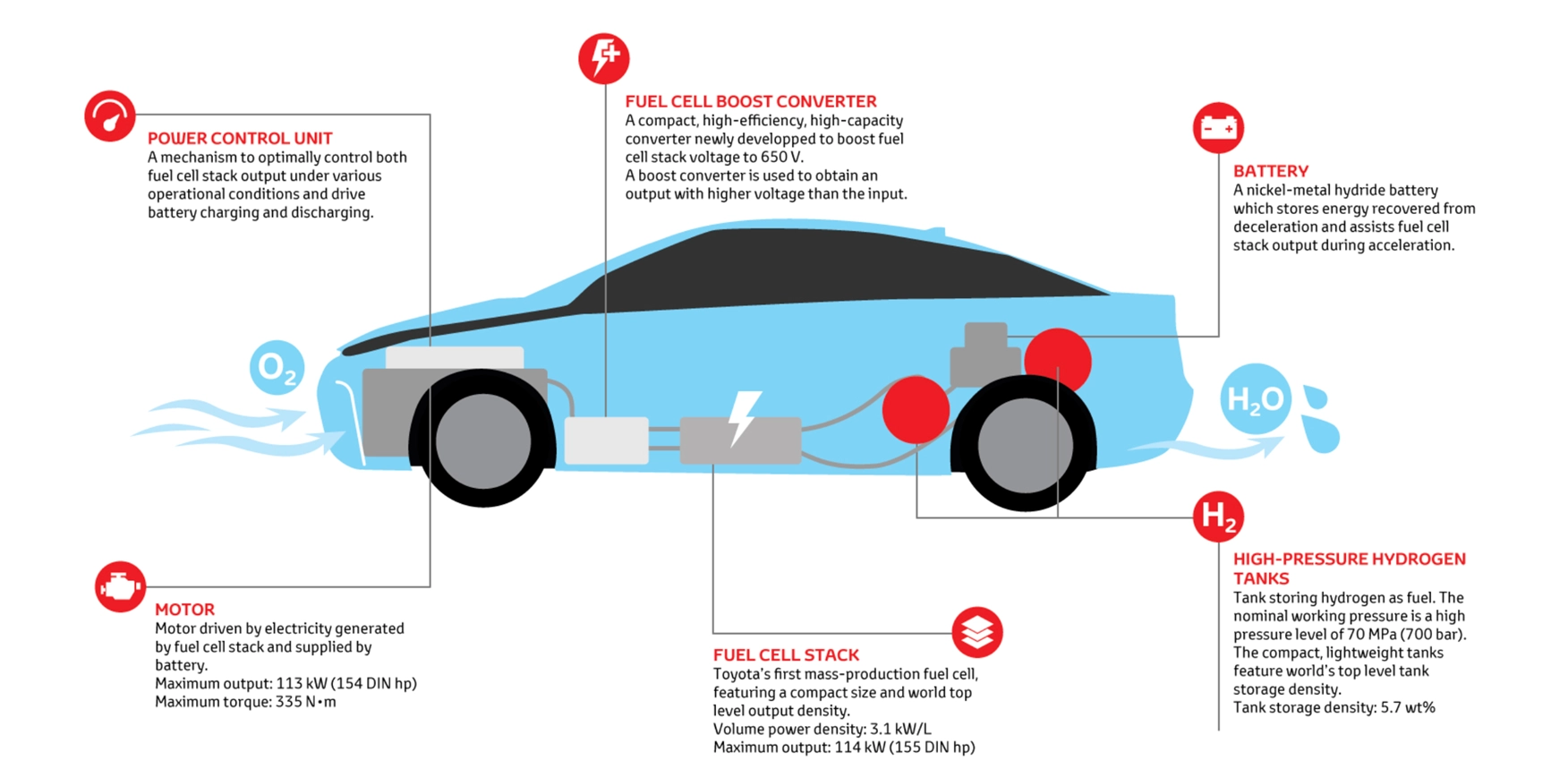
One of the main challenges facing hydrogen technology is the production of hydrogen itself. Currently, most hydrogen is produced from natural gas, which still involves carbon emissions. However, Toyota and other industry players are investing in research to develop green hydrogen production methods using renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydropower. These methods could make hydrogen a truly zero-emission fuel, further enhancing its environmental benefits.
Hydrogen cars also benefit from advances in storage and distribution technology. Hydrogen is a highly volatile gas that requires special handling and infrastructure. Toyota is working on solutions such as high-pressure storage tanks and innovative refueling stations to address these challenges. By collaborating with governments, energy companies, and other stakeholders, Toyota aims to build a comprehensive hydrogen infrastructure that supports the widespread adoption of FCEVs.
Toyota’s Commitment to Hydrogen
Toyota’s dedication to hydrogen technology is evident through its substantial investments in research, development, and commercialization of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. The company’s flagship hydrogen-powered vehicle, the Mirai, has been a testament to Toyota’s commitment to innovation and sustainability. Launched in 2014, the Mirai marked Toyota’s bold entry into the hydrogen vehicle market, and the subsequent generations of the Mirai have seen significant advancements in performance, efficiency, and design.
In addition to the Mirai, Toyota is actively exploring the application of hydrogen fuel cells in various sectors beyond passenger vehicles. The company is developing hydrogen-powered commercial vehicles, buses, and even stationary power generators. These efforts demonstrate Toyota’s vision of a hydrogen-based ecosystem that extends across multiple industries, reducing carbon emissions and promoting clean energy solutions.
Toyota’s collaboration with governments, energy companies, and other stakeholders is crucial to building the necessary infrastructure for hydrogen mobility. The company has been instrumental in establishing hydrogen refueling stations in key markets, addressing one of the primary challenges to the widespread adoption of hydrogen vehicles. By fostering partnerships and investing in infrastructure, Toyota aims to create a sustainable and efficient hydrogen refueling network.
Furthermore, Toyota is investing in the development of green hydrogen production methods. Traditional hydrogen production relies on natural gas, which still involves carbon emissions. However, Toyota is committed to advancing technologies that utilize renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower to produce hydrogen. These green hydrogen production methods have the potential to make hydrogen a truly zero-emission fuel, enhancing its environmental benefits.
Toyota’s commitment to hydrogen extends beyond its own products. The company is actively involved in initiatives and collaborations aimed at promoting hydrogen technology on a global scale. Toyota is a founding member of the Hydrogen Council, a global coalition of leading energy, transport, and industry companies working to accelerate the adoption of hydrogen technology. Through its participation in such initiatives, Toyota is driving the development of a hydrogen economy that supports sustainable energy solutions.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the promising potential of hydrogen technology, several challenges must be addressed to realize its widespread adoption. One of the primary challenges is the production of hydrogen. Currently, the majority of hydrogen is produced from natural gas through a process called steam methane reforming, which still involves carbon emissions. To achieve true sustainability, the industry must transition to green hydrogen production methods that utilize renewable energy sources.
Green hydrogen production involves electrolysis, where water is split into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity generated from renewable sources such as solar, wind, or hydropower. While this method holds great promise, it is currently more expensive than traditional hydrogen production methods. Continued research and development efforts are essential to making green hydrogen production economically viable on a large scale.
Another significant challenge is the development of a comprehensive hydrogen infrastructure. Hydrogen is a highly volatile gas that requires specialized handling, storage, and distribution systems. Building and maintaining hydrogen refueling stations, especially in areas with low population density, can be cost-prohibitive. Collaborative efforts between governments, industry stakeholders, and energy companies are crucial to overcoming these infrastructure challenges.
Public perception and awareness also play a role in the adoption of hydrogen vehicles. While there is growing interest in sustainable transportation solutions, many consumers remain unfamiliar with hydrogen technology and its benefits. Public education and awareness campaigns are necessary to inform consumers about the advantages of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, such as their long driving range, quick refueling times, and zero emissions.

Despite these challenges, the future prospects for hydrogen technology are promising. Governments around the world are recognizing the potential of hydrogen as a clean energy solution and are implementing policies and incentives to support its development. Several countries, including Japan, South Korea, and Germany, have announced ambitious hydrogen strategies and investments in hydrogen infrastructure.
Automakers like Toyota are leading the way in hydrogen vehicle development and are continually advancing the technology. With ongoing research, collaboration, and investment, the barriers to hydrogen adoption can be addressed, paving the way for a sustainable and hydrogen-powered future.
Toyota’s unwavering belief in hydrogen technology is driving significant advancements in the field. The company’s commitment to research, development, and collaboration is paving the way for hydrogen fuel cell vehicles to become a viable and sustainable transportation solution. While challenges remain, the potential benefits of hydrogen cars, including long driving ranges, quick refueling times, and zero emissions, make them a promising alternative to traditional fossil fuels and battery electric vehicles.
As the world seeks greener and more sustainable energy solutions, hydrogen cars have the potential to play a crucial role in reducing emissions and transforming the automotive world. Toyota’s dedication to innovation and sustainability positions them as a leader in the hydrogen revolution, and their efforts could shape the future of transportation.

