Governments around the world are introducing incentives to promote the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) as part of their efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
These incentives come in various forms, including tax credits, rebates, grants, and infrastructure investments. While these measures aim to accelerate the transition to cleaner transportation, the question remains: who really benefits from government incentives for EVs?
Consumers
One of the primary beneficiaries of government incentives for EVs is the consumers. Tax credits and rebates can significantly reduce the upfront cost of purchasing an EV, making them more affordable for a broader range of buyers.
For example, in the United States, the federal government offers a tax credit of up to $7,500 for eligible EV purchases. Similarly, many countries in Europe offer generous subsidies and incentives to encourage EV adoption.
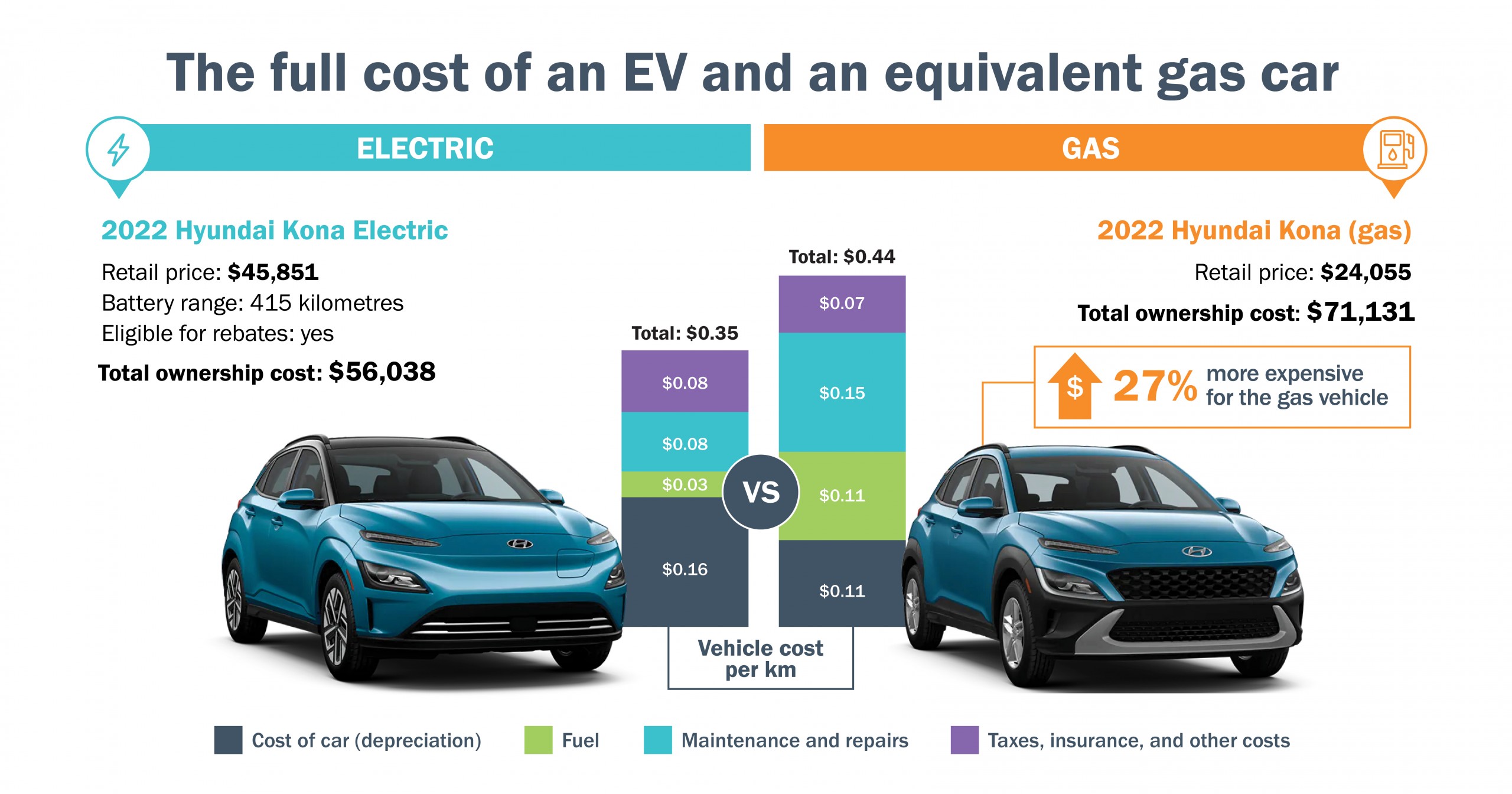
These financial incentives help bridge the price gap between EVs and conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, which are often cheaper. By making EVs more accessible, government incentives can accelerate their adoption and contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector.
Automakers
Automakers also benefit from government incentives for EVs. As demand for EVs increases, manufacturers can scale up production, leading to economies of scale and reduced costs. Government incentives can help create a stable market environment, encouraging automakers to invest in EV development and production.
Additionally, some governments offer incentives directly to automakers, such as grants for research and development or subsidies for building EV manufacturing facilities. These incentives can help automakers offset the high costs associated with developing new technologies and transitioning to electric mobility.
Environmental Impact
The environment is another key beneficiary of government incentives for EVs. By promoting the adoption of EVs, governments aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, which can significantly reduce the levels of harmful pollutants in urban areas.
Moreover, as the electricity grid becomes increasingly powered by renewable energy sources, the carbon footprint of EVs decreases. Government incentives can help accelerate this transition by encouraging both the adoption of EVs and the development of renewable energy infrastructure.
Energy Security
Government incentives for EVs can also contribute to enhanced energy security. By reducing dependence on imported oil and promoting the use of domestically produced electricity, countries can improve their energy independence and resilience. This shift can also reduce the economic and geopolitical risks associated with oil price volatility and supply disruptions.
Challenges and Criticisms
While government incentives for EVs offer numerous benefits, they are not without challenges and criticisms. One concern is that the benefits of incentives may disproportionately favor higher-income individuals who can afford the upfront cost of an EV, even with subsidies. Critics argue that more needs to be done to make EVs accessible to low- and middle-income households.
Additionally, there are concerns about the long-term sustainability of incentives. As EV adoption grows, the financial burden on governments may increase, potentially leading to a reduction or elimination of incentives. Policymakers must find a balance between promoting EV adoption and ensuring the fiscal sustainability of incentive programs.
Government incentives for EVs play a crucial role in accelerating the transition to cleaner transportation and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. While consumers, automakers, the environment, and energy security all benefit from these incentives, it is essential to address challenges and ensure that the benefits are distributed equitably. By doing so, governments can foster a sustainable and inclusive transition to electric mobility, ultimately benefiting society as a whole.
Also Read: Performance Cars and Street Racing, Do High-Power Vehicles Encourage Illegal Behavior?

