In the ever-evolving world of hybrid cars, buyers need to grasp how these vehicles operate under the hood to make informed decisions. As electric vehicles (EVs) gain ground, understanding the distinctions between hybrid types becomes increasingly crucial.
The upcoming Ram 1500 Ramcharger serves as a prime example, uniquely blending electric and gasoline power. Unlike traditional hybrids, such as the Prius, the Ram 1500 Ramcharger is not a mechanical hybrid.
Instead, it adopts a series hybrid configuration, where a V-6 “generator” under the hood charges the battery, providing energy for electric driving. This setup enables the Ramcharger to function as an EV for urban commutes while incorporating a generator for extended trips and demanding tasks.
Series hybrids, tracing back to early 20th-century designs, operate on electricity from the battery until the gasoline engine engages to power a generator, replenishing the battery’s charge.
Notably, the forthcoming Ramcharger joins a select few modern series-hybrid vehicles, following in the footsteps of the BMW i3 REx and the Fisker Karma. This layout, proven in diesel-electric locomotives, offers efficiency across a range of power demands.
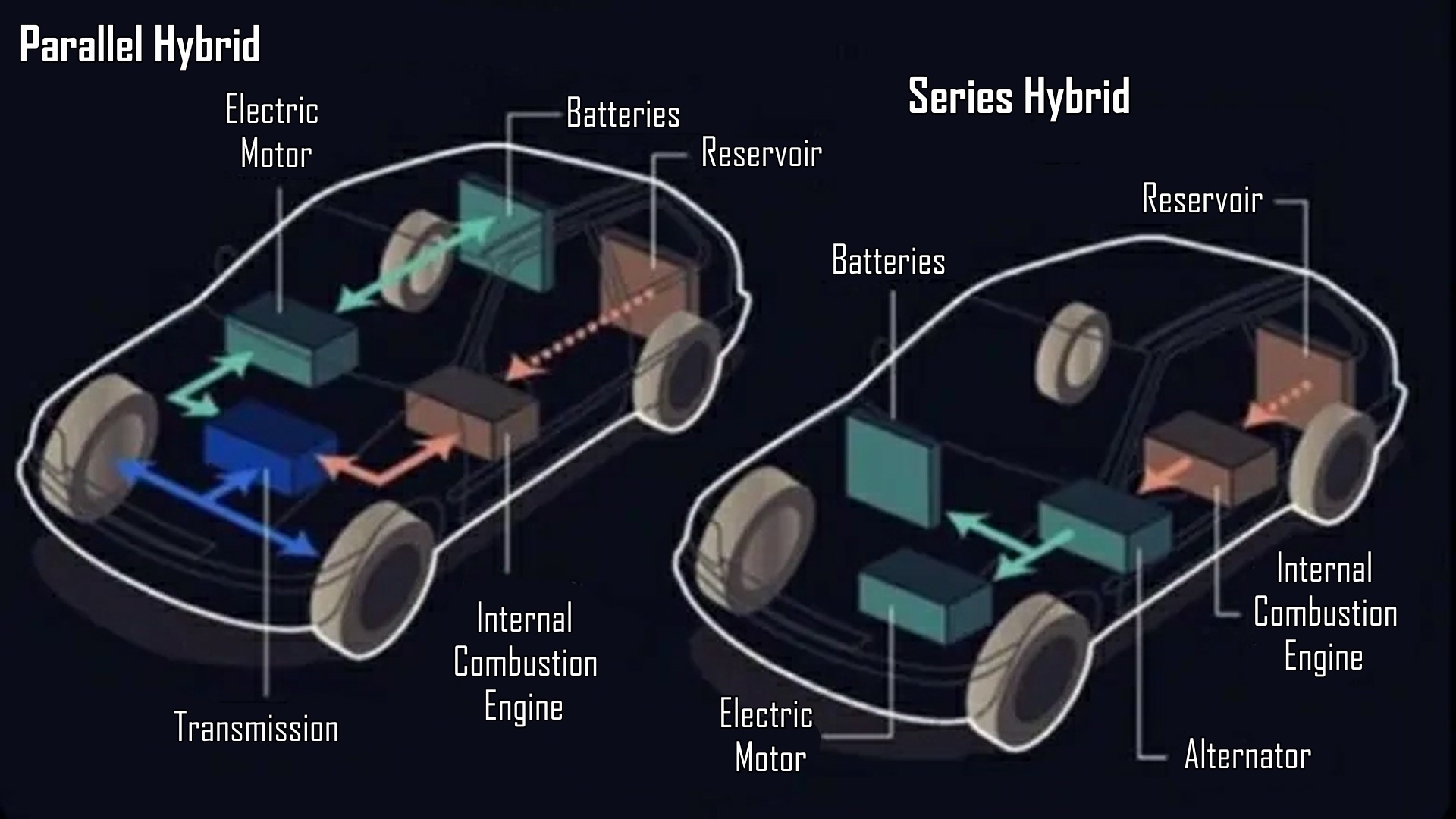
In contrast, parallel hybrid systems, exemplified by Toyota’s Hybrid Synergy Drive, employ both the engine and electric motors to drive the wheels simultaneously or independently.
Toyota’s pioneering system, introduced in the Prius, features two motors linked to the engine via a planetary gearset. It seamlessly transitions between electric and gasoline power, maximizing efficiency and regenerating energy during braking.
Hybrid systems leverage sophisticated software algorithms to optimize power distribution, balancing engine output, electric motor assistance, and regenerative braking.
Toyota’s system, doubling as a transmission, enhances flexibility and efficiency, capturing up to 30% of wasted energy during deceleration. While parallel hybrids offer simplicity and adaptability, series hybrids excel in steady power delivery and urban driving scenarios.
As the automotive industry advances, hybrid technology continues to evolve, offering consumers a spectrum of options.
Understanding the distinctions between series and parallel hybrids empowers buyers to choose vehicles that align with their driving needs and environmental goals.
Whether embracing the innovative series-hybrid approach of the Ramcharger or the proven parallel hybrid systems of Toyota, each represents a step forward in the pursuit of efficient and sustainable transportation.

