Diesel engines have played a crucial role in building and powering America, from farms and construction sites to highways and emergency services. Beyond U.S. borders, diesel engines dominate the workload in mechanized industries worldwide.
While all engine manufacturers strive for excellence, certain diesel powerplants stand out due to their durability, mechanical simplicity, and horsepower potential. These exceptional engines have earned a reputation for reliability and performance, making them some of the best ever built.
Many of the engines on this list come from an era before stringent emissions regulations introduced complexities that affected reliability. During that time, diesel engines were built with fewer restrictions, leading to robust and dependable machines.
The list includes legendary names like Cummins, International, Caterpillar, Detroit, John Deere, GM, and Mack—brands that have left a lasting impact on the industry. Although many of these engines are no longer in production, they remain highly respected and sought after by enthusiasts and professionals alike.
This carefully selected compilation highlights ten of the greatest diesel engines ever made. These powerhouses represent the best compression-ignition technology and continue to be celebrated for their performance and longevity. With that in mind, and without ranking them in any specific order, the following pages present the ultimate list of legendary diesel engines.
1. International DT466
The International DT466 is one of the most widely used and recognized diesel engines, powering school buses, box trucks, farm tractors, and small bulldozers. As the largest engine in International Harvester’s 400 series, it shared a block with the smaller 414 and 436 cubic-inch models.
Built for durability, the DT466 featured a deep-skirt cast-iron crankcase, a forged-steel crankshaft with seven main bearings, and ductile-iron wet cylinder liners. Its 4.30-inch bore and 5.35-inch stroke contributed to its torque-heavy performance, making it a reliable choice for various demanding applications.
One of the DT466’s standout characteristics is its ability to handle extreme levels of stress in stock form. Thanks to its sturdy rotating assembly and six head bolts per cylinder, it can withstand up to 1,200 horsepower before the factory head gasket becomes a concern.
According to Hypermax Engineering, this means that enthusiasts can push the engine to its limits by adding more fuel and air without needing major internal upgrades. Its robustness and resilience have made it a favorite among those who demand high power output without compromising reliability.

Beyond its use in medium-duty trucks, the DT466 has become a legend in tractor-pulling. Decades of innovation have led to extreme modifications, including replica blocks, billet crankshafts, stronger rods, and solid heads.
When paired with high-performance components like Sigma injection pumps, triple-feed injectors, and multiple turbochargers, DT466-based engines can withstand 300 psi of boost and produce over 4,000 horsepower. This remarkable versatility and strength ensure that the DT466 remains an icon in both work and competition settings.
2. 6BT Cummins
The 5.9L Cummins, specifically the 6BT, revolutionized the diesel pickup truck industry and played a significant role in the growth of the diesel aftermarket. Introduced in 1988, this 12-valve inline-six brought direct injection and turbocharging to the ¾-ton and larger truck market, setting a new standard for performance and durability.
Its arrival forced competitors like Ford and GM to step up their diesel offerings, but the Chrysler-Cummins partnership had already set the benchmark. The widespread success of the 6BT helped fuel the expansion of the diesel industry, contributing to the creation of publications like Diesel World and a booming aftermarket scene.
One of the reasons for the 6BT’s legendary reputation is its incredibly strong internal components. Its forged-steel I-beam connecting rods, each with its own rod bearing journal, can handle extreme power levels—especially when upgraded with shot peening, micro-polishing, and ARP rod bolts.
The engine’s forged-steel crankshaft is induction-hardened and held in place with 14mm main cap bolts, while the cylinder head is secured with six bolts per cylinder for extra durability.

This overbuilt design allows the engine to last a million miles in stock form or survive four-digit horsepower in modified applications. Even though the newer 6.7L Cummins block is preferred for extreme horsepower builds, the 5.9L remains a viable option for high-performance diesel enthusiasts.
The 6BT’s 12-valve crossflow cylinder head, made from gray iron, was built with longevity in mind. It features induction-hardened valve seats and durable ductile iron intake and exhaust valve rockers, making it one of the toughest cylinder heads in diesel history.
In motorsports, the 12-valve head remains a top choice, with aftermarket variants capable of extreme airflow improvements. When extensively ported and equipped with oversized valves, it can achieve airflow rates of over 300 cubic feet per minute (cfm) per cylinder—more than double the stock capability.
This combination of simplicity, strength, and performance potential cements the 5.9L Cummins as one of the most influential diesel engines ever produced.
3. 3406 CAT
The Caterpillar 3406 is a legendary engine in the Class 8 trucking world, powering thousands of over-the-road trucks across America with unmatched reliability. Available in multiple versions—A, B, C, and the highly regarded E model—the 3406 featured a 5.40-inch bore, a 6.50-inch stroke, and a displacement of 14.6 liters (893 cubic inches).
Depending on the model, it produced between 375 and 465 horsepower, with factory torque ratings reaching up to 1,850 lb-ft. Its durability and performance have made it a favorite among truck owners who swear by CAT power for long-haul efficiency.
The 3406E, the most revered version, marked Caterpillar’s transition to full electronic control. While earlier models were mechanical (A and B) or a mix of mechanical and electronic (C), the E model introduced a fully electronic unit injection system around 1993.

This advancement allowed tuners to recalibrate the engine control module (ECM) for significant horsepower gains, making 550-600hp setups common. The ability to unlock extra power so easily contributed to the 3406E’s cult-like following, cementing its reputation as a powerhouse in both stock and modified forms.
Beyond highway use, the 3406 has proven itself in extreme-performance applications like sled pulling, particularly in the 20,000-pound semi category.
Championship-winning drivers like Jerry and Jeremy Walker have relied on heavily modified 3406 engines in their competition trucks, pushing displacement beyond 1,000 cubic inches and using massive single turbos with inlets exceeding 5 inches. Whether on the road or the track, the 3406 remains one of Caterpillar’s most iconic and respected diesel engines.
4. 7.3L Power Stroke
The 7.3L Power Stroke may not be known for high horsepower or quick cold starts, but it is legendary for its reliability. As the largest diesel engine ever offered in a pickup, the Navistar-built 444 cubic-inch V8 debuted in 1994 with 210 horsepower and 425 lb-ft of torque.
It introduced hydraulically actuated electronically controlled unit injector (HEUI) technology, developed by Caterpillar and licensed to International to meet emissions regulations. Designed for direct injection and built around a turbocharger, it was Ford’s first serious response to the 5.9L Cummins-powered Dodge Rams, setting a new standard in the diesel pickup market.
Built with durability in mind, the 7.3L Power Stroke featured a forged-steel crankshaft and connecting rods (though powdered-metal rods appeared after 2000), along with cast-aluminum pistons and a simple yet strong valvetrain.
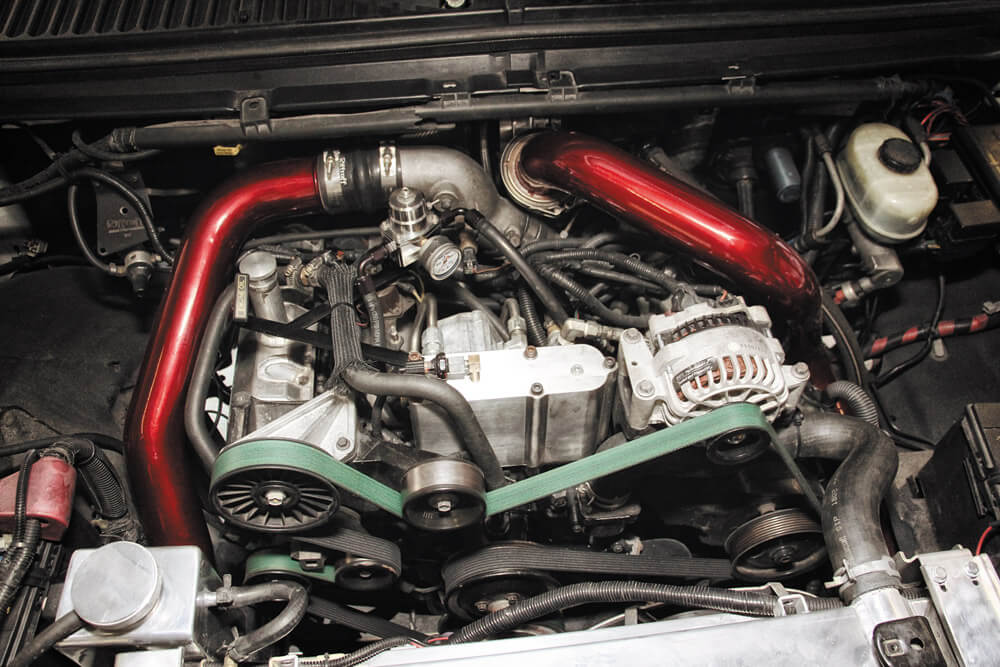

The cast-iron cylinder heads had two valves per cylinder and were secured with six head bolts per cylinder (with sharing). A single camshaft and hydraulic lifters eliminated the need for periodic valve adjustments. While it lacked the power of modern diesel, its robust design allowed it to withstand years of hard use with minimal issues.
The 7.3L’s long lifespan is a result of its low engine speed, heavy-duty construction, and relatively modest power output, with its most powerful version producing just 275 horsepower and 525 lb-ft of torque in 2001.
While the HEUI injection system is sometimes criticized, it proved highly reliable in the 7.3L, with properly maintained injectors lasting over 200,000 miles. Nearly two decades after production ended, original injectors are still being found in running engines, a testament to the Power Stroke’s durability and its enduring legacy in the diesel world.
5. Cummins 855 Big Cam
The Cummins 855 Big Cam was introduced to meet the emissions regulations of the Clean Air Act of 1976 and quickly became one of the most fuel-efficient, durable, and powerful engines in the Class 8 truck market.
Dominating the late 1970s and early 1980s, this 14.0L (855 cubic inch) engine featured a 5.50-inch bore and a 5.98-inch stroke, with power ratings ranging from 250 to 400 horsepower in most versions. However, in generator-set applications, some models reached as high as 605 horsepower, solidifying its reputation as a powerhouse on the road and beyond.
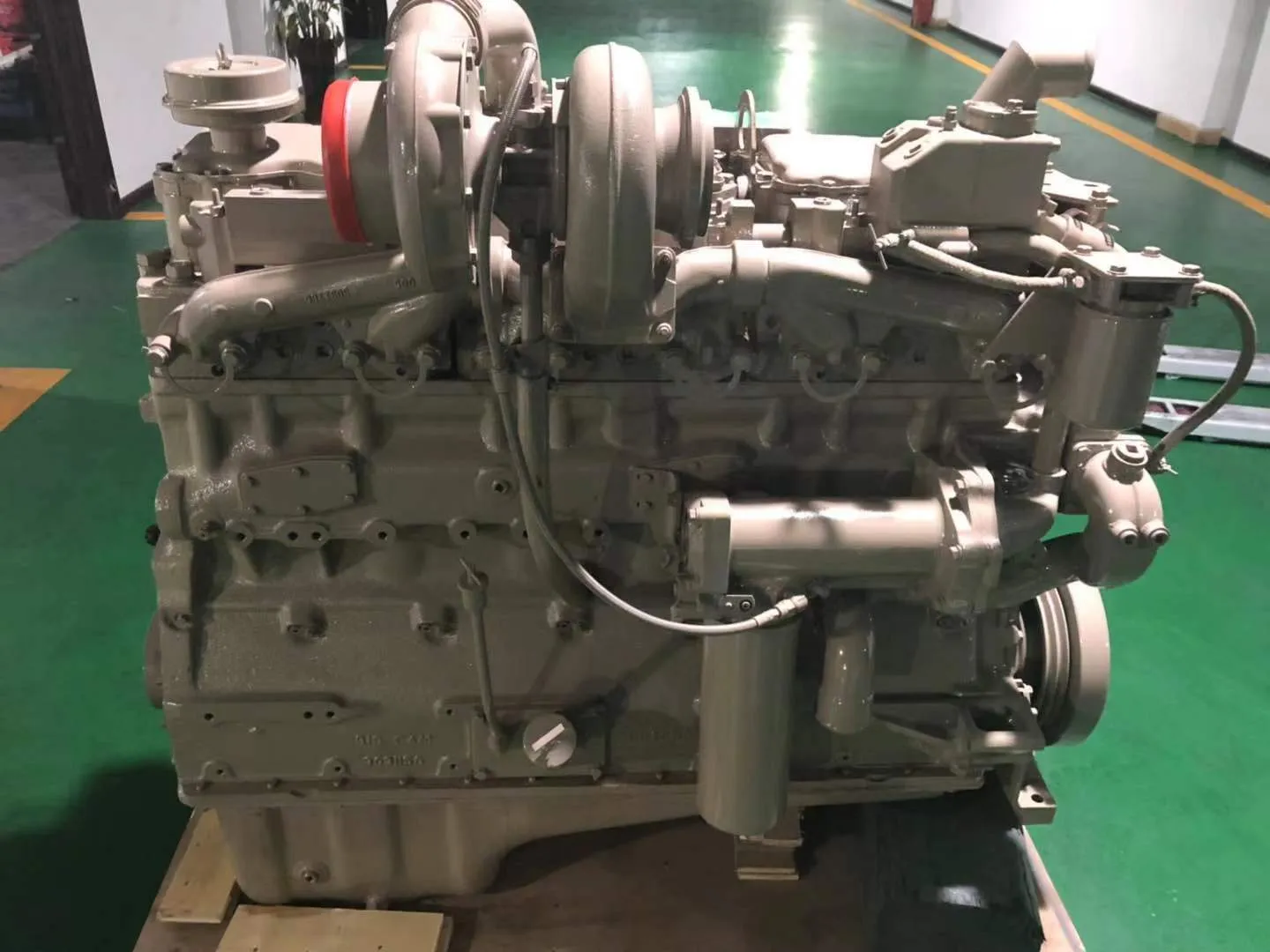

Throughout its production run, the 855 Big Cam underwent significant improvements across four versions. The first three models—Big Cam I, II, and III—used Cummins’ PT (pressure-time) fuel system, allowing for mechanically variable timing, while the Big Cam IV, introduced in 1985, incorporated electronic controls before being replaced by the N14.
Notable upgrades included the demand-flow cooling system and pulse exhaust manifold in the Big Cam II (1979), a pressed-steel oil pan and Holset HT3B turbocharger in the Big Cam III (1983), and a revised cylinder head and improved exhaust manifold in the Big Cam IV (1985), ensuring the engine remained competitive throughout its lifespan.
Also Read: 10 Best Electric Cars with the Longest Range in 2025 for Maximum Driving Distance
6. John Deere 50 Series 6-619
The 619 cubic-inch (10.0L) 50 Series John Deere engine is a powerhouse both on the farm and in tractor-pulling competitions, making it one of the best diesel engines ever built.
Often used as a swap-in replacement for the original 531 ci engines in models like the 5010, 5020, and 6030, the 619 has proven itself in both agricultural and motorsports settings. In tractor pulling, it frequently goes head-to-head with—and often outperforms—the International DT466, securing its reputation as a dominant force in the sport.
Built for durability and power, the 619 features a 5.125-inch bore, a 5.00-inch stroke, cylinder liners, and six head bolts per cylinder. One of its key advantages over earlier John Deere engines is its crank-driven oil pump, which eliminates the excessive cam wear issues that plagued the 30 and 40 Series engines.
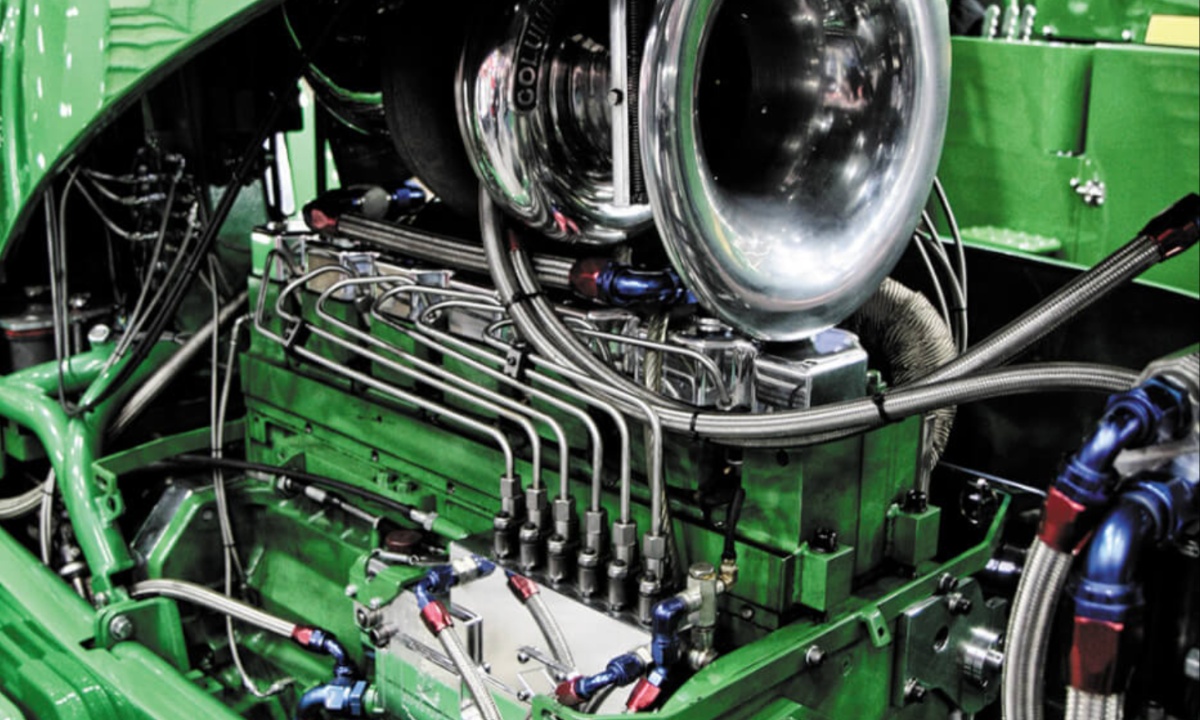
This reliability, combined with its ability to generate substantial horsepower, has made it a popular upgrade option for farmers and a formidable contender in competitive pulling.
In Pro Stock tractor pulling, the factory-based 619 John Deere is heavily modified for extreme performance. While the block may remain stock or be a factory replica, internal components like the crank, rods, pistons, and cylinder head are billet, and a girdle and thick deck plate reinforce the top end.
Many 619-based engines are expanded to the class maximum of 680 cubic inches and are paired with billet Sigma injection pumps and turbochargers with massive 5.5-inch inducers. Capable of spinning up to 6,000 rpm and producing around 4,200 horsepower, these highly tuned engines showcase the full potential of the legendary John Deere 619.
7. Mack E7
The Mack E7 diesel engine, introduced in 1988, became a staple in the trucking industry thanks to its durability and immense torque. Spanning over two decades of production, the E7 came in 16 different versions, with power ratings ranging from 250 to 460 horsepower.
Its 728 cubic-inch (12.0L) displacement and low-end torque, particularly the 460hp model producing 1,660 lb-ft at just 1,200 rpm, made it a powerhouse on the road. True to Mack’s reputation, the E7 delivered torque levels that rival larger engines from competitors, embodying the company’s iconic bulldog logo with its rugged, heavy-duty performance.
Initially, the E7 featured a fully mechanical design, but the early 1990s brought electronic advancements like Mack’s V-MAC (Vehicle Management and Control), which introduced sensors and actuators for improved fuel control.
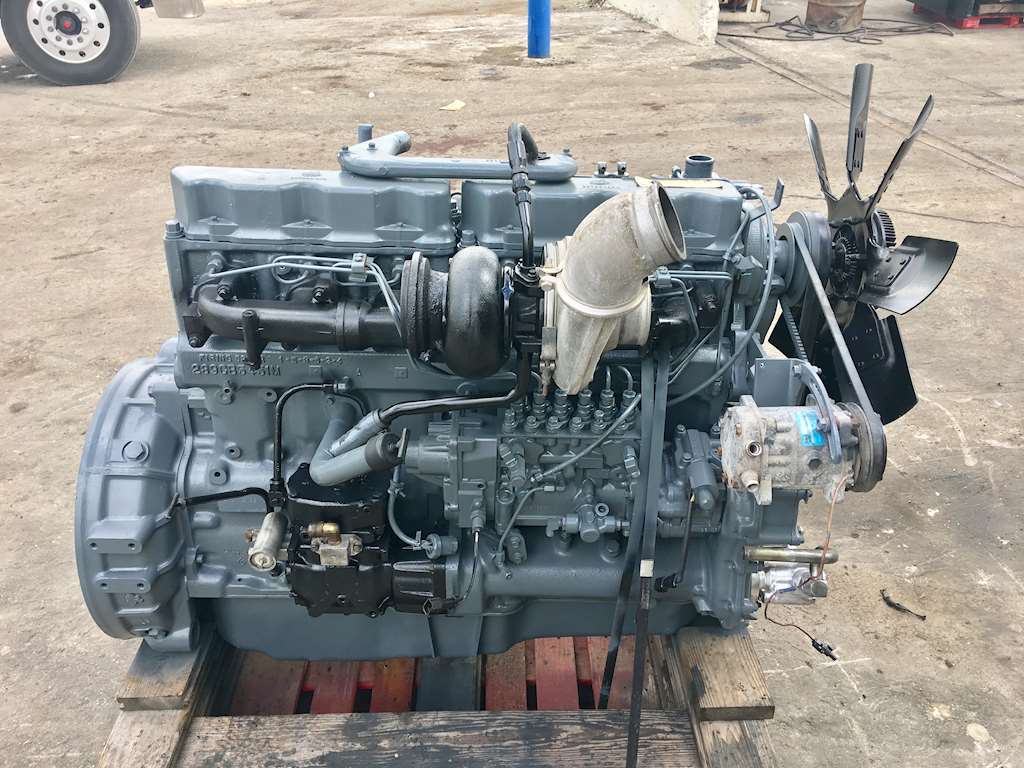

Additional refinements included the Econovance system for variable mechanical timing and, by 1998, the shift to an electronically controlled unit pump (EUP) for more precise fuel injection.
However, by 2003, emissions regulations required the integration of EGR (exhaust gas recirculation), which, along with other modern emissions technology, gradually diminished the engine’s legendary reliability. Despite these later changes, the E7 remains one of Mack’s most respected and long-lasting diesel engines.
8. Detroit Diesel 60 Series
The Detroit Diesel Series 60 engine line played a pivotal role in revitalizing the company during the 1980s when it was struggling to maintain market share. At a time when electronic control was still emerging, Detroit took a bold step by designing the 11.1L and 12.7L engines with fully electronic unit injection systems, which proved to be highly reliable.
Their durability was so impressive that initial overhaul recommendations were extended from 500,000 to 750,000 miles. These advancements helped establish Detroit Diesel as a leader in the industry, setting new standards for electronically controlled diesel engines.
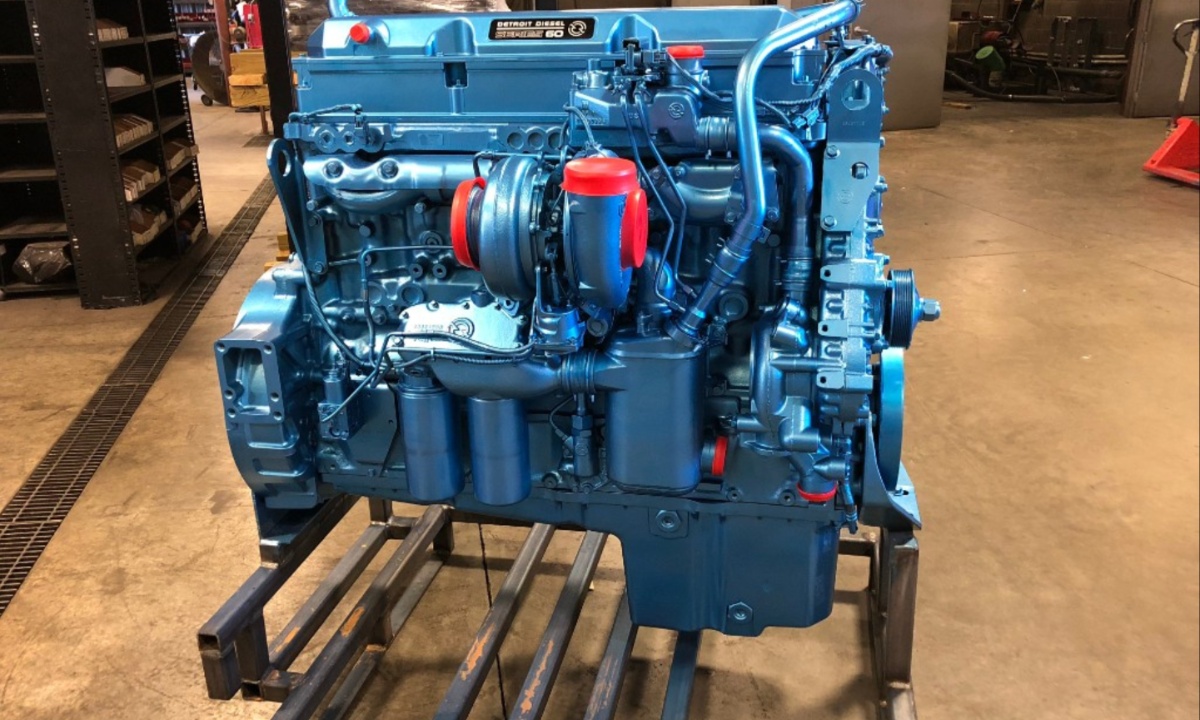
In developing the Series 60, Detroit Diesel—then owned by GM—sought assistance from John Deere to overhaul its struggling engine program. The result was a breakthrough design that addressed previous issues from the 50 Series and became a staple in the trucking industry.
Building on this success, Detroit later introduced a 14.0L version in 2001, featuring a 6.62-inch stroke and 5.24-inch bore. This engine delivered an impressive 1,650 lb-ft of torque at 1,200 rpm and 515 horsepower at 1,800 rpm, further solidifying the Series 60’s reputation as one of the most reliable and long-lasting diesel engines ever produced.
9. KTA Cummins
The KTA Cummins was the largest Class 8 engine ever to run on American highways, boasting a massive 1,150 cubic inches (19.0L) of displacement. Designed originally for industrial applications, it eventually found its way into over-the-road trucks, delivering an impressive 600 horsepower and 1,650 lb-ft of torque in its single-turbo configuration.
However, torque delivery was intentionally limited at low RPM to preserve the lifespan of transmissions like the Eaton Fuller 8- or 13-speed. During the late 1970s and 1980s, these power figures were groundbreaking, making the KTA a legendary engine in the trucking world.
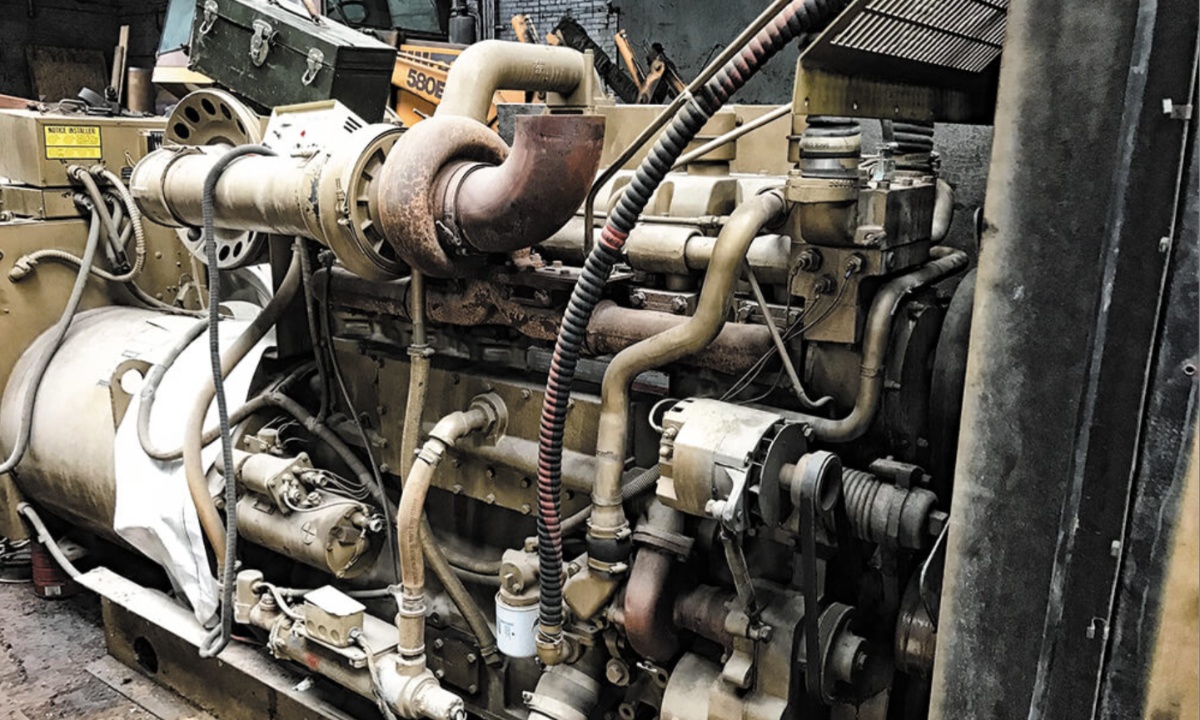
Equipped with Cummins’ PT (pressure-time) fuel system, the KTA could achieve four-digit horsepower figures with minor fueling and turbo upgrades, all while remaining a workhorse. Its massive displacement and durability made it a dominant force in truck pulling competitions, where it consistently outperformed smaller Class 8 engines.
For even more power, Cummins developed the KTTA variant, which featured twin turbochargers and was primarily used in industrial and generator applications. Whether on the road or the track, the KTA cemented its reputation as one of the most powerful and reliable diesel engines ever built.
10. 6.6L Duramax
The 6.6L Duramax (LB7) debuted in 2001, bringing groundbreaking advancements to the diesel pickup market. With 300 horsepower and 520 lb-ft of torque, it set new performance benchmarks while also introducing common-rail injection, improved refinement, and aluminum cylinder heads—features that made it the quietest and cleanest diesel pickup engine of its time.
As one of only two V-8s on the list, it stood apart from competitors by combining power with efficiency, making it a game-changer in GM’s heavy-duty truck lineup.
Beyond its impressive debut, the LB7 Duramax was built for durability, featuring a 4340 forged-steel crankshaft, forged-steel cracked cap rods, and induction-hardened cylinder walls. Remarkably, its core architecture has remained largely unchanged for over two decades, still relying on a deep-skirt, cast-iron block while other manufacturers have moved to CGI.
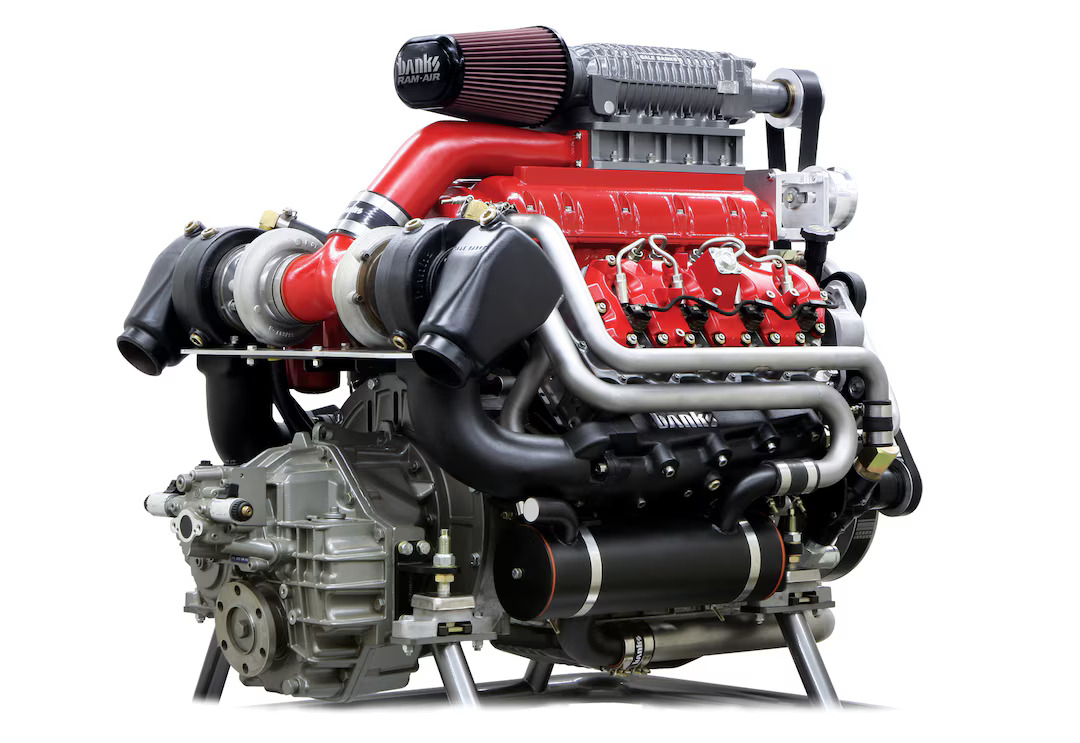

Despite its complexity, the Duramax has proven its longevity, with many examples surpassing 500,000 miles and even some LMM models exceeding 750,000 miles, solidifying its reputation as a dependable and long-lasting diesel powerhouse.
These ten diesel engines have made a lasting impact on the industry, showcasing exceptional durability, power, and innovation. From the dependable International DT466 to the formidable KTA Cummins, each engine on this list has played a crucial role in shaping the future of diesel technology.
Whether through groundbreaking technology, sheer reliability, or legendary performance, these engines have proven themselves time and time again in both work and competition settings. Their influence extends beyond their original applications, as many remain sought after by enthusiasts and professionals who recognize their enduring value.
While advancements in emissions technology and efficiency continue to push diesel engines forward, these legendary powerplants serve as a testament to an era of uncompromising strength and dependability.
Whether still in service or remembered for their contributions to the industry, these engines represent the pinnacle of compression-ignition engineering. Their legacy continues to inspire new generations of diesel enthusiasts, ensuring that their impact will be felt for years to come.
Also Read: 10 Best European Sports Cars That Rival High Performance Supercars

