With the rapid expansion of the global new energy vehicle market, power battery technology (learn more about the top 10 installed capacity of power battery manufacturers worldwide) continues to evolve.
New materials, innovative processes, and integrated management methods are constantly emerging, driving advancements in the electric vehicle industry.
This article provides an in-depth analysis and comparison of the top 10 EV battery technologies currently available. It explores their fundamental principles, technological breakthroughs, and market adaptability, offering industry professionals and consumers a well-rounded perspective.
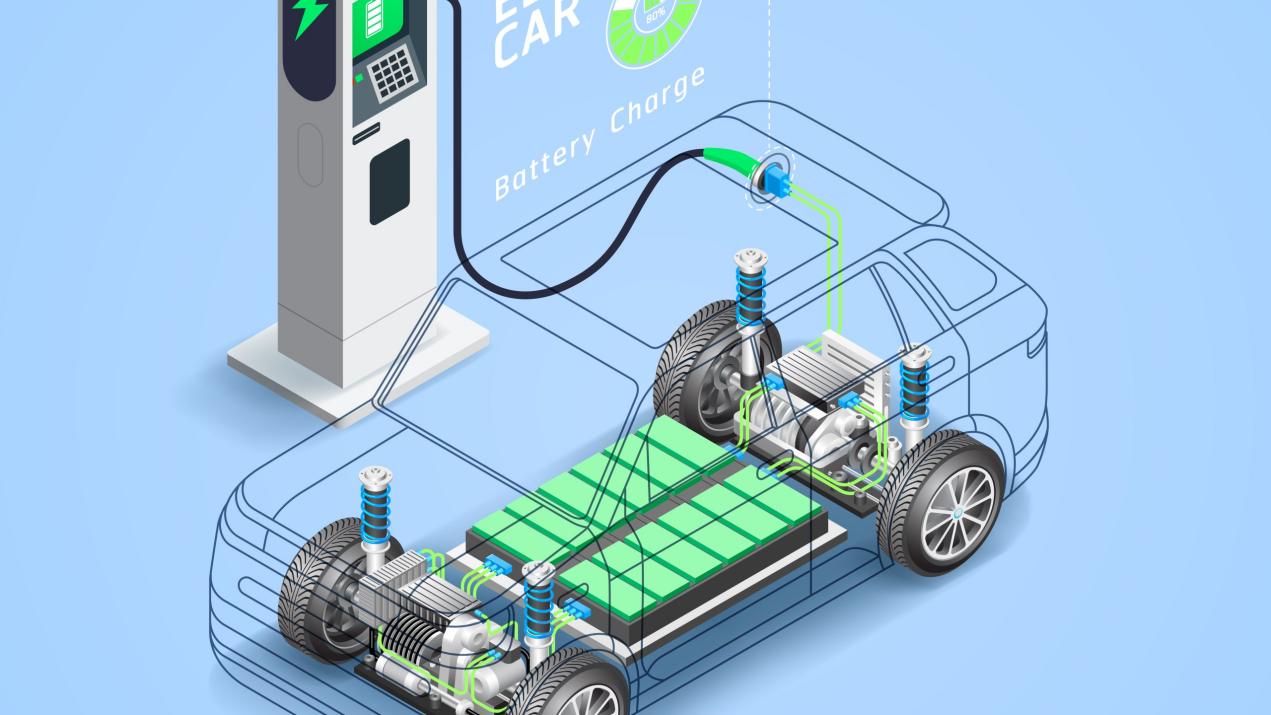
CTM (Cell To Module)
CTM is one of the earliest battery pack integration technologies. In this method, multiple EV battery cells are first connected in series and parallel to form a module.
These modules are then assembled into a battery pack, which is subsequently integrated into the vehicle chassis.
During the initial adoption of power batteries in new energy vehicles, the absence of a unified standard resulted in a wide variety of battery, module, and pack sizes.
This led to high development costs and made battery replacement and maintenance more challenging.
Over time, it was observed that vehicles shared common spatial dimensions. By analyzing these dimensions, standard module size ranges were established, leading to greater uniformity in battery cell sizes.
Since Volkswagen aggressively pursued electrification in 2008, CTM technology has undergone multiple refinements. The introduction of the 355 module (with a length of 355mm) enabled three battery modules per pack, significantly enhancing range and component reduction.
Volkswagen later introduced the longer 390 module and the more compact 590 module, further optimizing module integration efficiency.
Although CTM offers structural protection, its space utilization is becoming a limiting factor, with an overall efficiency of only 40%. This does not align with the increasing demands of the EV market.
As new energy vehicles become more widespread and lithium-ion battery performance reaches new heights, improving battery pack integration efficiency is now a pressing challenge.
Technologies such as large modularization, de-modularization, and vehicle body integration have become mainstream solutions.
CATL’s CTP (Cell To Pack)
In 2019, CATL introduced the world’s first CTP battery pack, which integrates battery cells directly into the pack itself, eliminating the need for modules.
This innovation led to the emergence of CTP technology, marking a significant leap in battery design and manufacturing by overcoming many limitations of traditional CTM technology.
CTP technology offers several key advantages. Compared to conventional battery packs, CTP packs achieve a 15-20% increase in volume utilization, a 40% reduction in component count, and a 50% boost in production efficiency.
These enhancements provide electric vehicles with greater design flexibility, enabling longer driving ranges. The energy density of CTP battery packs can reach up to 200Wh/kg, representing a more than 30% increase over traditional structures.
CTP implementation follows two main approaches: large modularization and non-modularization. CATL’s CTP technology follows the large modularization path, increasing the capacity of individual battery cells while stacking multiple cells to form a larger module.
This strategy reduces the number of modules and lowers production costs. Additionally, optimizing the connection structure between modules further simplifies assembly.
Although CTP battery packs offer high space efficiency, low costs, and improved heat dissipation, they are subject to the “wooden barrel effect,” where the weakest battery cell determines overall performance.
As a result, CTP demands high consistency among battery cells. Furthermore, maintenance and replacement costs can be higher in the event of battery failure.

Tesla’s CTC (Cell To Chassis)
At Tesla’s 2020 “Battery Day,” the company introduced CTC (Cell To Chassis) technology. CTC integrates the battery pack directly into the vehicle chassis, eliminating both the module and pack assembly steps.
This streamlined approach reduces components, lowers production costs, and decreases vehicle weight, ultimately improving driving range.
The innovation of CTC lies in integrating the upper shell of the battery pack with the vehicle’s floor, making the battery a structural part of the vehicle.
Tesla enhances safety by filling the battery pack with adhesive material to prevent heat transfer into the cabin and reinforce protection against side collisions.
CTC technology offers superior space utilization, lower production costs, and reduced vehicle weight compared to traditional integration methods.
However, it also requires higher battery cell consistency. Since the battery is integrated into the chassis, maintenance is less convenient, and battery replacement costs are significantly higher, limiting CTC’s broader application.
Also Read: Top Compact Refrigerators For Vehicles For Camping and Adventure Trips
Gotion High-Tech’s JTM (Jelly Roll To Module)
On January 8, 2021, Gotion High-Tech hosted its Tenth Science and Technology Conference in Hefei, where it introduced a 210Wh/kg lithium iron phosphate soft package cell alongside its JTM (Jelly Roll To Module) battery technology.
This innovation aims to enhance battery module integration efficiency while improving safety.
The primary distinction of JTM compared to other cell integration methods lies in its use of the jelly roll as the smallest functional unit. Within each cell, JTM connects multiple units both in parallel and series, similar to the structure of blade batteries. However, its unique design allows each unit to function independently, significantly boosting safety performance.
JTM batteries enable module formation efficiency to exceed 90%. When paired with high specific energy lithium iron phosphate batteries, the system’s energy density surpasses that of the NCM622 ternary system, making it an attractive option for high-end passenger vehicles.
Furthermore, JTM’s design effectively mitigates risks associated with thermal runaway, thereby improving battery safety.
Despite its strong advantages in integration efficiency and safety, JTM’s long-term market acceptance and practical application in automotive use still require validation to ensure its stability and reliability over extended periods.
Also Read: 10 Affordable Lightweight Battery Upgrades For High-Performance Cars
Aion’s Cassette Battery
On March 10, 2021, GAC Aion introduced the world’s first cassette battery system safety technology. The battery’s structure resembles a safety chamber similar to a cassette, hence the name “cassette battery.”
This innovation marked a major industry milestone, as it allowed ternary lithium battery packs to withstand puncturing without catching fire, thereby redefining active safety standards for ternary lithium batteries.
By optimizing design and manufacturing processes, the system’s volume energy density increased by 9.4% (302Wh/L), while its mass energy density rose by 5.7% (185Wh/kg). Additionally, production costs were reduced by 10%.
GAC Aion’s cassette battery technology revolves around three key principles: preventing internal short circuits in battery cells, preventing thermal runaway following a short circuit, and preventing thermal propagation after thermal runaway.
To achieve this, the system incorporates four core technologies, including ultra-high heat-resistant battery cells, high-strength insulated battery safety chambers, and rapid cooling systems.
The introduction of cassette battery technology addresses the safety challenges associated with ternary lithium batteries under extreme conditions such as thermal abuse and puncturing.
With volume and mass energy densities increasing by 9.4% and 5.7%, respectively, this development is expected to bolster consumer confidence in ternary lithium batteries, thereby promoting their adoption in new energy vehicles.
Despite these advancements, the complexity and production costs of the cassette battery have also risen, which may pose challenges for large-scale production and market penetration. Striking a balance between maintaining high safety standards and reducing costs remains a critical issue.
Dongfeng’s “Three No” Battery
In 2021, Dongfeng Motor’s Lantu brand introduced the “Three No” battery, representing a significant innovation aimed at enhancing the safety of ternary lithium batteries. The power system of the Lantu FREE electric vehicle utilizes ternary lithium batteries, achieving the notable safety standard of “no smoke, no fire, and no explosion.”
Lantu FREE incorporates a three-dimensional insulation wall design for individual battery cells, along with an advanced battery monitoring and early warning system.
This approach significantly elevates the safety of ternary lithium batteries, ensuring stability during usage while alleviating consumer concerns regarding electric vehicle safety.

Great Wall Motors’ Dayu Battery
On June 29, 2021, Great Wall Motors introduced the “Dayu Battery,” which has garnered significant attention for its exceptional safety performance, ensuring that it “never catches fire and never explodes.”
Reports indicate that the name “Dayu” reflects its safety assurance principle, inspired by the “turning blockage into penetration” concept derived from Dayu’s river management techniques.
The Dayu Battery incorporates multi-level current exchange, rapid extreme cooling suppression, and multi-stage directional explosion discharge systems, utilizing high-nickel 811 ternary battery materials.
This design enhances energy density while maintaining stability even under high temperatures.
The core concept of “turning blockage into penetration” is applied to improve the overall safety of ternary lithium battery packs through eight key aspects:
Thermal source isolation, bidirectional current exchange, thermal flow distribution, directional explosion discharge, high-temperature insulation, automatic fire extinguishing, positive pressure oxygen resistance, and intelligent cooling.
Leap Motor’s MTC (Module To Chassis)
In 2022, Leap Motor officially introduced MTC technology (precisely named Module To Chassis), designed to improve battery utilization efficiency by integrating the battery modules directly into the vehicle’s chassis.
The key innovation of MTC technology lies in eliminating traditional independent battery packs and instead incorporating the modules into the chassis itself.
This integration reduces the number of components required and lowers overall production costs. As a result, Leap Motor achieves better battery layout efficiency and improved structural strength within a limited space.
Unlike Tesla’s CTC design, Leap Motor’s MTC technology retains modular components, simplifying maintenance. If a battery module malfunctions, users can replace the defective unit without needing to disassemble the entire chassis.
However, while this design enhances load-bearing capacity, it also introduces challenges in terms of integration and safety, particularly in mitigating risks associated with thermal runaway.
BYD’s CTB (Cell To Body)
In 2022, BYD officially launched its CTB (Cell To Body) integrated body technology, a breakthrough aimed at maximizing energy conversion and utilization efficiency in electric vehicles.
This technology merges the battery pack with the vehicle floor, forming an integrated structural design.
As a result of this integration, BYD’s new model “Seagull” has achieved a 66% increase in power battery system utilization, along with a 10% boost in system energy density, enabling a driving range of 700 kilometers.
CTB technology excels in enhancing battery safety, structural integrity, and overall utilization efficiency.
The battery pack design features a blade battery array layout, which significantly improves safety performance. This effective combination strengthens BYD’s focus on high-strength, lightweight vehicle design.
Despite these advancements, when compared to Tesla’s CTC technology, CTB still has room for improvement in terms of overall integration. Moving forward, BYD may further refine this technology to strengthen the bond between the battery and the vehicle structure.
Also Read: Top 10 Biggest Recalls That Affected Millions of Users – All Time
SAIC’s ONE PACK
On June 13, 2022, SAIC Motor’s MG brand revealed the “Magic Cube Battery” and introduced the first vehicle equipped with this technology—the MG MULAN.
The Magic Cube Battery features a standardized battery pack with a length of 1690mm, width of 1300mm, and adjustable heights of 110mm, 125mm, and 137mm.
While the battery pack maintains a fixed length and width, its adaptable height allows it to cater to different driving range needs.
Since the length and width remain unchanged, the Magic Cube Battery incorporates a uniform cell fixing position, a standardized quick-change cooling interface, and consistent high- and low-pressure connections, enabling battery swapping functionality (China already has the top 10 EV battery swapping companies).
The most notable feature of the Magic Cube Battery is its horizontal cell arrangement. While conventional battery packs are arranged vertically or sideways, the Magic Cube Battery adopts a “lying flat” layout.
This design optimizes the battery’s placement within the vehicle, extending cycle life and enhancing overall safety. Each electric vehicle battery technology presents unique advantages.
Beyond the technologies discussed above, CATL’s 3.0 Kirin battery is also a noteworthy development. The ongoing evolution of battery innovations continues to propel the new energy vehicle industry forward.
From traditional CTM designs to advanced CTP and CTC solutions, every iteration strives for higher energy density, improved safety, and cost reduction.
As battery technology advances, it will play a crucial role in shaping the future of the electric vehicle market.

