Engines are the heart of any vehicle, but not all are created equal. Some power plants are built to take abuse daily, handling neglect, heavy loads, and even modifications without skipping a beat.
Others, though promising on paper, reveal hidden flaws that lead to early failure and massive repair bills. In this comparison, we highlight five legendary engines known for their durability and toughness alongside five engines infamous for reliability issues and engineering missteps.
Whether you’re choosing a vehicle to modify, tow, or daily drive, knowing which engines can take a beating—and which ones quit under pressure—could save you thousands.
Engines That Handle Daily Abuse
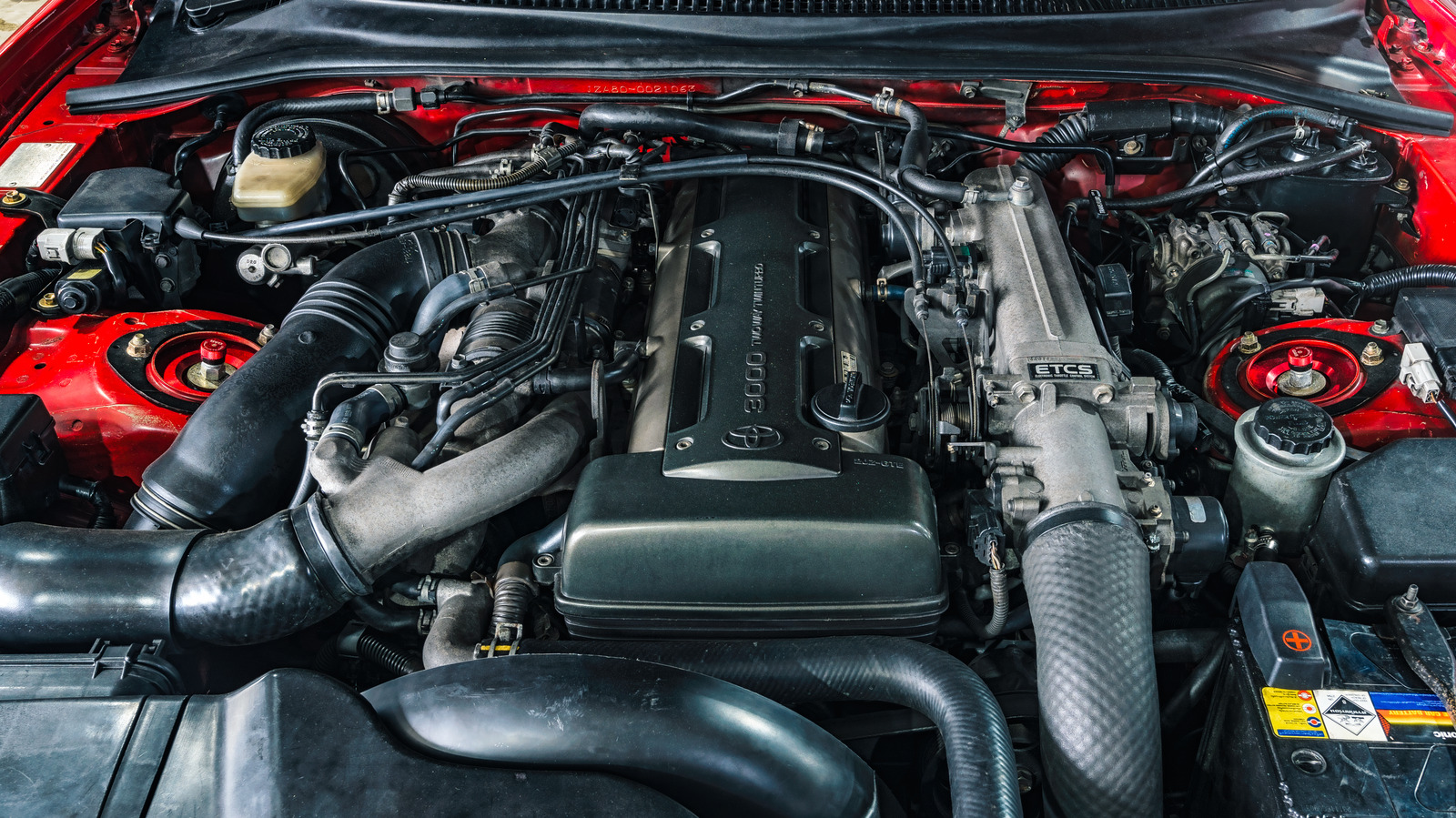
1. Toyota 2JZ-GTE (3.0L Inline-6 Turbo)
The Toyota 2JZ-GTE, found in the MK4 Supra and Toyota Aristo, is revered for its robust engineering. Featuring a cast-iron block, forged internals, and dual overhead cams, it thrives under high stress and horsepower.
Tuners regularly push this engine beyond 1,000 hp without altering the block. From 1991 to 2005, it evolved from sequential twin turbos to the addition of VVT-i. Differences between the 2JZ-GE and GTE include oil squirters and lower compression pistons.
Export versions offered larger injectors and different turbos. Even with stock internals, it offers a foundation for extreme performance and longevity, making it a tuning icon.
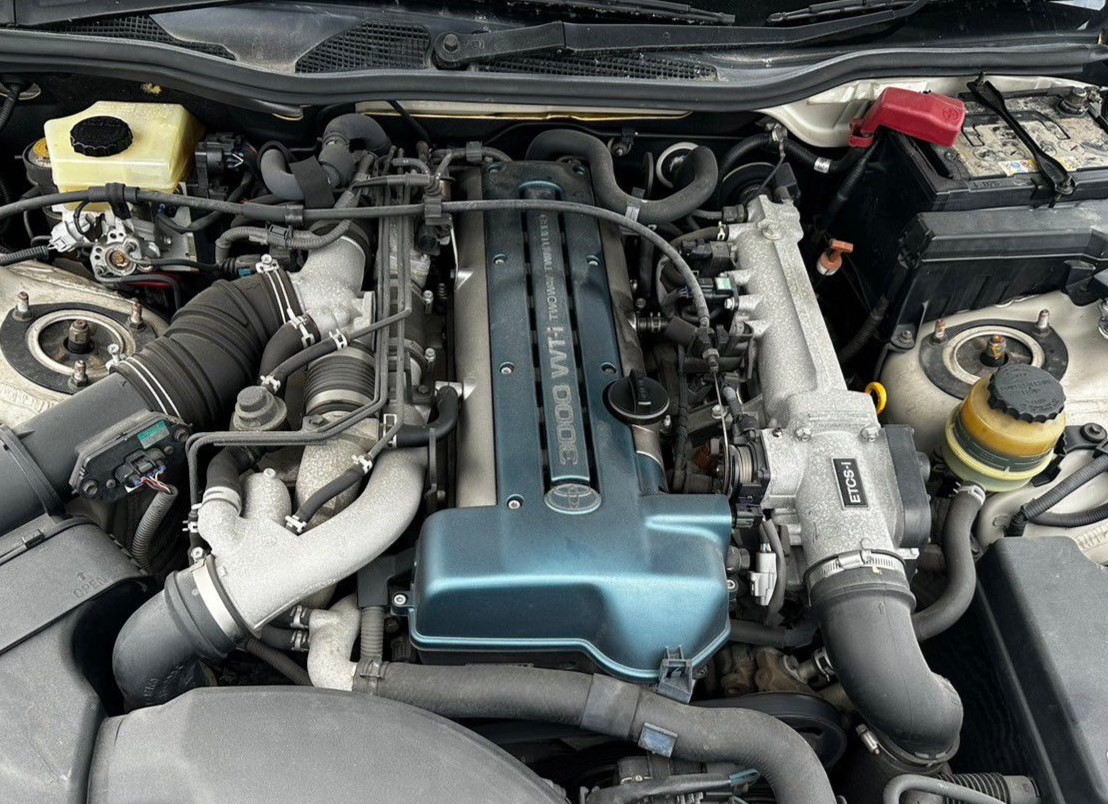

2. Cummins 6BT (5.9L Inline-6 Diesel)
Originally designed for industrial use, the Cummins 6BT debuted in the Dodge Ram in 1989. With a mechanical injection system and a cast-iron build, it’s nearly indestructible. Known as the “12-valve,” this inline-six diesel can handle low-grade fuel, poor maintenance, and heavy loads over hundreds of thousands of miles.
Producing up to 215 hp and 440 lb-ft of torque, it evolved through Bosch VE and P7100 injection systems before being replaced in 1998. Simple wiring and robust design make it a favorite for swaps. The 6BT’s legacy lies in its durability, simplicity, and ability to outperform many gas engines in towing.

3. Honda K20/K24 (2.0L/2.4L Inline-4)
Honda’s K-series engines—especially the K20 and K24—balance high-revving performance with everyday reliability. Found in vehicles like the Civic Si, Accord, and Acura RSX, these engines feature forged crankshafts and intelligent VTEC timing.
The K20 is ideal for racing with its higher rev limit and smoother power band, while the K24 offers more torque for daily driving. Though the K24 has more displacement and low-end power, enthusiasts often prefer the K20 for track builds.
Swapping between them is common, but the K24 requires more work. Both remain icons in the tuning world for their balance of power, efficiency, and reliability.
4. Chevrolet LS (All-Gen Small Block V8s)
Chevrolet’s LS engine family is a cornerstone of modern performance. Found in everything from Corvettes to Camaros and Silverados, LS engines are compact, powerful, and affordable.
Thanks to strong internals and abundant aftermarket support, they’re often turbocharged or supercharged and swapped into drift cars, muscle cars, and even imports.
Variants range from 4.8L to 7.0L, and their pushrod V8 design keeps them simple and lightweight. Events like LS Fest highlight their cult status. Whether it’s a junkyard 5.3L or a built 6.0L, the LS platform remains a go-to for reliable horsepower, making it one of the most swapped engines worldwide.
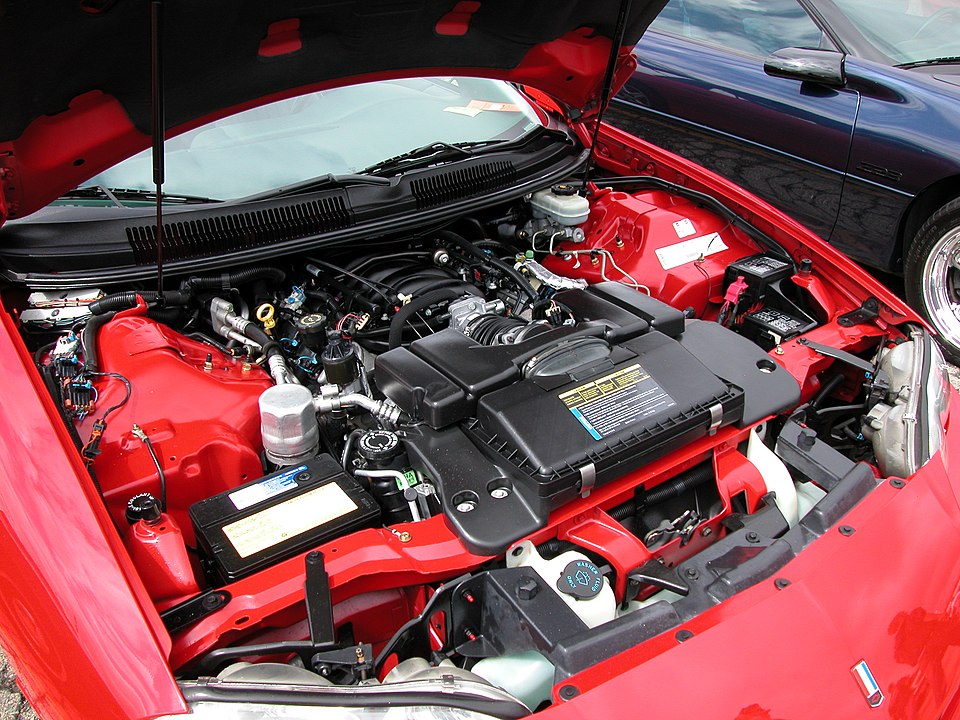

5. Mercedes-Benz OM617 (3.0L Inline-5 Diesel)
The Mercedes-Benz OM617 is a legend in diesel durability. Built between 1974 and 1990, this 3.0L inline-five powered the W123, W126, and early G-Wagen models. Its cast-iron construction and pre-chamber injection allowed it to tolerate abuse, bad fuel, and long service intervals.
Early naturally aspirated versions made around 80 hp, but later turbocharged variants reached up to 125 hp and 250 Nm of torque. Known for lasting over 1,000,000 km, the OM617 was Mercedes’ solution to U.S. fuel economy demands, appearing in models like the 300 SD. Though slow, it remains revered for unmatched reliability and mechanical simplicity.

Also Read: 5 Cars With the Most Favorable Financing Rates and 5 With the Steepest APRs
Engines That Quit Under Pressure
1. Chrysler 2.7L V6 – A Disaster by Design
The Chrysler 2.7L V6, common in Dodge Intrepid and Chrysler Concorde models, became synonymous with premature failure. It’s poorly designed internal water pump often leaked coolant into the oil, causing internal corrosion and bearing damage.
Compounded by an inadequate crankcase ventilation system and narrow oil passages, sludge buildup was nearly unavoidable, even with regular maintenance. Timing chain tensioners and plastic components frequently failed, adding to the chaos.
Many engines didn’t survive past 100,000 miles, and repairs often cost more than replacement. Its reputation remains one of the worst in American engine design, with widespread failure across thousands of units.

2. Volkswagen 3.6L VR6 FSI – Over-Engineered to Fail
Volkswagen’s 3.6L VR6 FSI, found in models like the Passat and Touareg, proved problematic despite its performance. The use of direct fuel injection led to rapid carbon buildup on intake valves, while a poorly placed timing chain—tucked against the firewall—made maintenance expensive and labor-intensive.
Timing chain tensioner failures were common and often catastrophic. Excessive oil consumption and valve deposits further damaged long-term reliability.
Though the engine had a unique sound and decent power delivery, owners were plagued by costly upkeep. This overcomplicated design marked a sharp decline in trust toward VW’s once-respected VR6 series, especially in North America.
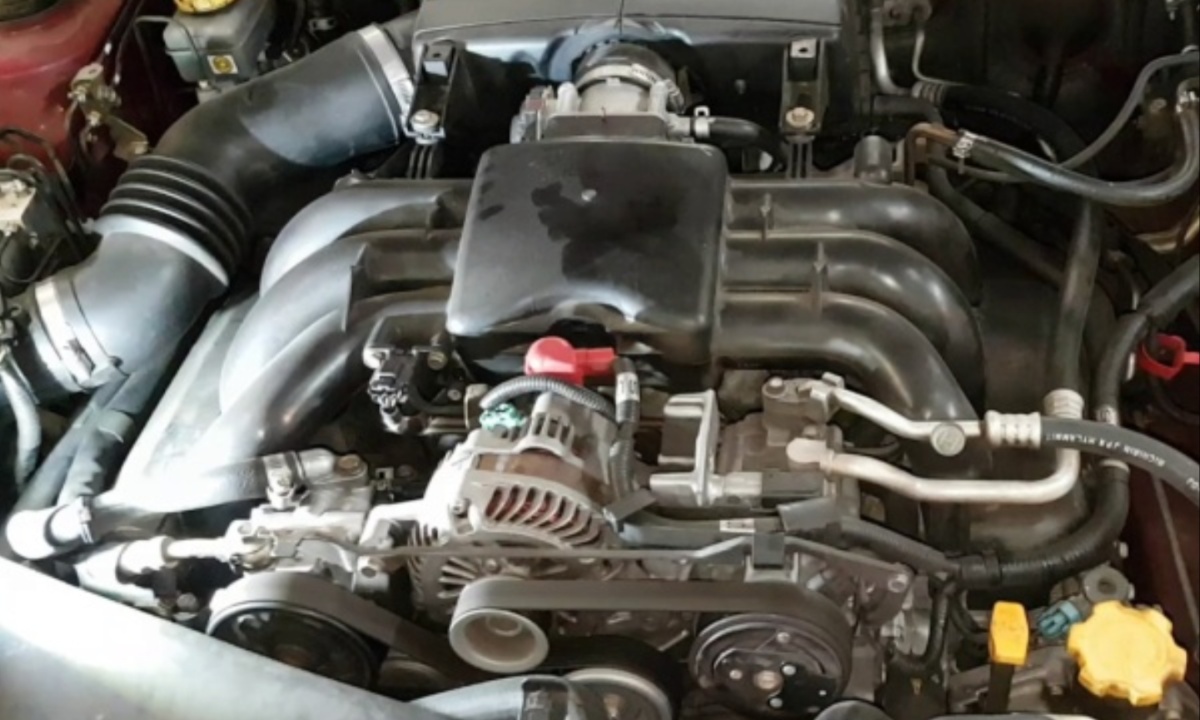
3. Subaru EZ30 / EZ36 – More Cylinders, More Problems
Subaru’s EZ30 and EZ36 flat-six engines, used in models like the Legacy 3.0R and Tribeca, expanded Subaru’s boxer lineup but introduced more trouble than benefit. Known for oil consumption, timing chain tensioner failure, and overheating, these engines suffered from poor heat distribution within the flat-six layout.
Tight engine compartments made repairs time-consuming, and frequent head gasket failures remained a legacy issue. The added weight and complexity brought only slight gains in refinement, while reliability dropped.
Subaru fans who embraced the EZ engines often found themselves saddled with unexpected maintenance costs and diminishing returns over the boxer-four alternatives.

4. Ford 3.0L Duratec V6 – A Wolf in Cheap Clothing
The Ford 3.0L Duratec V6 was featured in vehicles across Ford, Mazda, and Jaguar lineups. While its specs and aluminum construction seemed modern, serious internal flaws became apparent over time.
Its internally mounted water pump, driven by the timing chain, could fail and mix coolant with oil, usually leading to engine failure. Timing chain tensioner wear and poor gasket material further undermined reliability.
Owners often encountered oil leaks and overheating. While some engines did reach high mileage, many failed early, and repair costs were steep. The Duratec’s sleek performance masked a fragile core, tarnishing its long-term dependability.

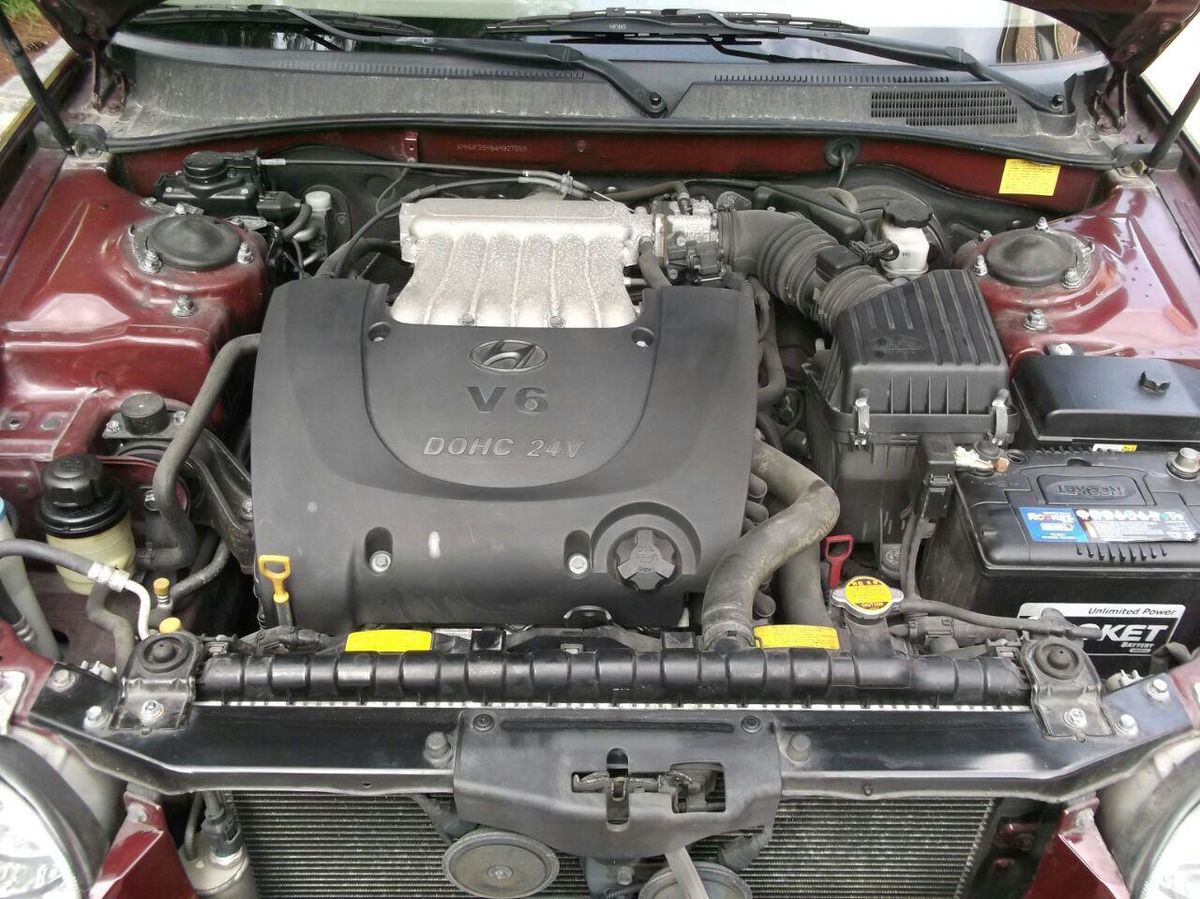
5. Hyundai/Kia 2.7L V6 Delta – An Engine That Aged Too Quickly
Hyundai and Kia’s 2.7L Delta V6, intended as a smooth and budget-friendly engine, ended up suffering from premature wear. It struggled with sludge buildup due to a weak PCV system and narrow oil passages.
Gasket failures, worn valve lifters, and failing crank pulleys were common by mid-life. A critical weak point was its timing belt: if it snapped—a frequent occurrence—valves and pistons would collide, often totaling the engine.
Though the Delta engine saw use across many models, its short lifespan and expensive repairs made it a poor long-term investment. Many owners regretted trusting its promise of refinement and value.

Whether you’re a gearhead, a daily commuter, or a weekend warrior, choosing the right engine is critical to long-term satisfaction and savings. Engines like the Toyota 2JZ-GTE, Cummins 6BT, and Chevy LS have earned cult status for surviving extreme conditions and modifications with grace.
In contrast, models like Chrysler’s 2.7L V6 or VW’s VR6 FSI are cautionary tales of poor engineering and high repair bills. This list highlights the importance of understanding what lies beneath the hood, because reliability isn’t just about reputation, it’s about proven endurance. A well-built engine isn’t just mechanical; it’s peace of mind on every drive.
Also Read: 5 Cars With Best Fuel-Cost Calculators and 5 With Misleading Displays

