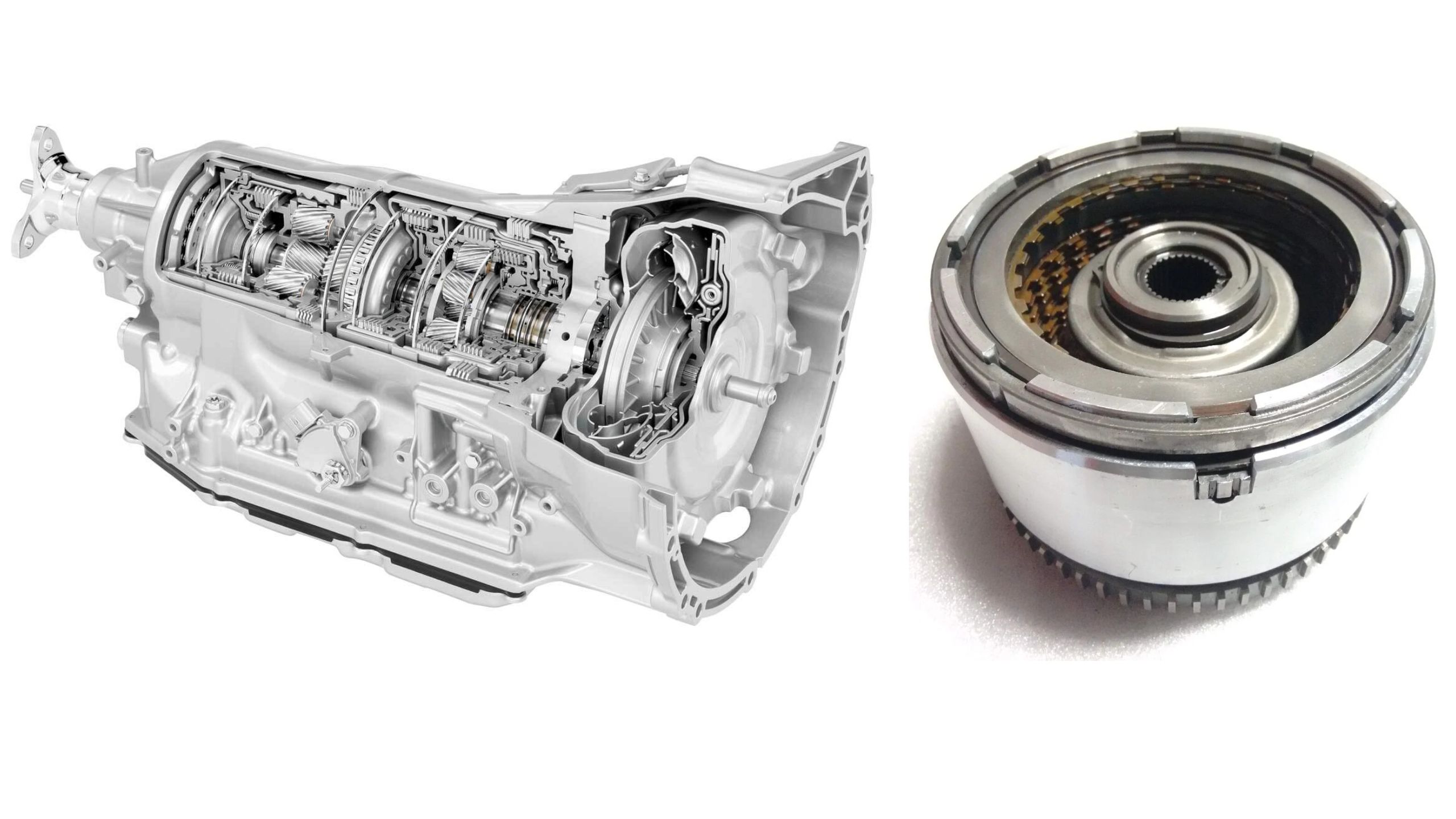
The automotive transmission represents one of the most complex and critical components in any vehicle, serving as the crucial link between engine power and wheel movement.
Over decades of automotive evolution, certain transmissions have earned legendary status for their bulletproof reliability and ability to withstand extreme abuse, while others have become notorious for premature failures, particularly involving torque converter issues that plague owners with costly repairs and unexpected breakdowns.
The distinction between these two categories often comes down to fundamental engineering philosophy, manufacturing quality, design complexity, and real-world testing.
Bulletproof transmissions typically feature robust internal components, simplified designs that prioritize durability over cutting-edge efficiency, and extensive real-world validation.
This analysis examines five transmissions renowned for their exceptional durability against five units known for early torque converter failures and related issues.
5 Transmissions Built for Abuse
These exceptionally engineered automatic transmissions feature oversized torque converters with reinforced stator assemblies and heavy-duty lockup clutches that maintain fluid coupling integrity through extreme loading conditions, including towing, racing, and commercial applications.
Their robust internal architecture includes hardened planetary gear sets, extra-capacity oil pumps, and advanced valve body designs with enlarged fluid passages that prevent the hydraulic pressure drops typically associated with high-demand operations and sustained heavy throttle applications.
Performance enthusiasts report that these legendary powertrains become stronger with proper break-in, often handling power levels far exceeding factory specifications while maintaining smooth operation and quick shift response, proving their worth through consistent performance under the most demanding conditions.
1. Toyota A750/A760 Series
The Toyota A750 and its successor, A760, represent the pinnacle of transmission engineering for heavy-duty applications, earning their reputation through decades of service in some of the world’s most demanding environments.
These five-speed automatic transmissions are found in Toyota’s Land Cruiser, Tundra, and Sequoia, where they’re designed to handle extreme conditions, and heavy-duty construction makes them ideal for off-road and high-mileage applications.
The A750’s legendary status stems from its deliberately conservative design philosophy that prioritizes reliability over cutting-edge efficiency. The transmission’s robust construction begins with its cast-aluminum case, which provides superior strength while maintaining reasonable weight.
Internal components feature oversized clutch packs with multiple friction plates, allowing for better heat dissipation and extended service life under heavy loads.
The planetary gear sets utilize hardened steel components with precise machining tolerances that ensure smooth operation even after hundreds of thousands of miles. Many Toyota Sequoias with 300k+ miles continue operating with no maintenance, demonstrating the unit’s exceptional durability.
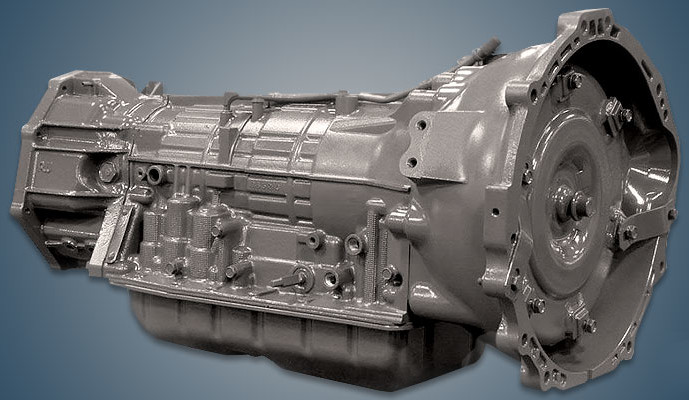
The A750’s torque converter employs a lock-up clutch system that engages smoothly across multiple gears, reducing heat generation and improving fuel economy without compromising reliability. The transmission’s valve body features simplified hydraulic circuits that minimize potential failure points while providing precise shift control.
Advanced cooling systems, including large external coolers and internal cooling circuits, help maintain optimal operating temperatures even during sustained heavy-duty operation such as towing or off-road driving.
What sets the A750 apart is Toyota’s extensive real-world testing program, which subjects these transmissions to millions of miles of abuse in various climates and operating conditions before production approval.
The unit’s electronic control module incorporates conservative shift strategies that prioritize component longevity over aggressive performance, resulting in smooth, predictable operation that extends transmission life.
Regular maintenance intervals are generous, with Toyota’s recommended fluid changes occurring at reasonable intervals that most owners can easily maintain.
The A750’s service record in commercial and fleet applications speaks volumes about its reliability. Many taxi fleets, delivery services, and construction companies report multiple vehicles exceeding 400,000 miles with original transmissions still operating smoothly.
Even when repairs become necessary, the A750’s straightforward design allows for cost-effective rebuilds using readily available parts, making it an economical long-term choice for high-mileage applications.
2. General Motors 4L80E
General Motors’ 4L80E stands as one of the most robust automatic transmissions ever produced, designed specifically for heavy-duty truck and performance applications where durability takes absolute priority over refinement or fuel economy.
Originally developed for military and commercial vehicle applications, the 4L80E later found its way into civilian trucks, SUVs, and high-performance vehicles where its bulletproof reputation preceded it.
The transmission’s foundation rests on a massive cast-iron case that provides exceptional strength and rigidity under extreme loads. This substantial construction, while adding weight compared to aluminum alternatives, ensures the transmission can withstand the tremendous forces generated by high-torque engines and heavy-duty applications such as towing, hauling, and off-road abuse.
The 4L80E’s internal architecture features oversized clutch drums, bands, and servo assemblies that distribute loads across larger surface areas, reducing wear and extending service life.

The planetary gear sets in the 4L80E utilize aerospace-grade materials and precision manufacturing techniques that result in components capable of handling substantially more torque than their ratings suggest.
Multiple clutch plates in each pack provide redundancy and improved heat dissipation, while the transmission’s generous fluid capacity ensures adequate lubrication and cooling even under sustained high-load conditions.
The unit’s torque converter features a robust lock-up mechanism that engages smoothly without the shuddering or premature wear common in lighter-duty applications.
Electronic controls in the 4L80E strike an optimal balance between sophistication and reliability. The transmission control module employs proven algorithms that prioritize smooth, predictable shifts over aggressive performance, resulting in reduced component stress and extended service life.
Adaptive learning capabilities allow the transmission to adjust its shift characteristics based on driving patterns and load conditions, optimizing performance while maintaining durability.
The 4L80E’s service record in heavy-duty applications demonstrates its exceptional reliability. Many commercial fleets report original transmissions operating smoothly beyond 500,000 miles with only routine maintenance.
The unit’s robust design makes it a popular choice for performance enthusiasts who subject their vehicles to track use, drag racing, and other high-stress applications where transmission failure could result in expensive engine damage or safety concerns.
3. ZF 5HP24/5HP30
ZF’s 5HP24 and 5HP30 transmissions represent German engineering at its finest, combining sophisticated technology with bulletproof reliability that has made them the transmission of choice for luxury European manufacturers including BMW, Audi, Jaguar, and Range Rover.
The ZF 5HP 24/30 is among the most reliable automatic transmissions that keep you away from transmission repair shops much longer than problematic transmissions.
These five-speed automatics demonstrate that advanced technology and long-term durability need not be mutually exclusive when proper engineering principles are applied.
The transmission’s foundation begins with a precision-cast aluminum case that provides optimal strength-to-weight ratio while incorporating sophisticated internal oil galleries for superior lubrication and cooling.
ZF’s meticulous attention to manufacturing tolerances ensures that every component fits precisely, reducing internal friction and wear while improving efficiency. The planetary gear sets feature premium materials and advanced surface treatments that resist wear even under sustained high-performance driving conditions.
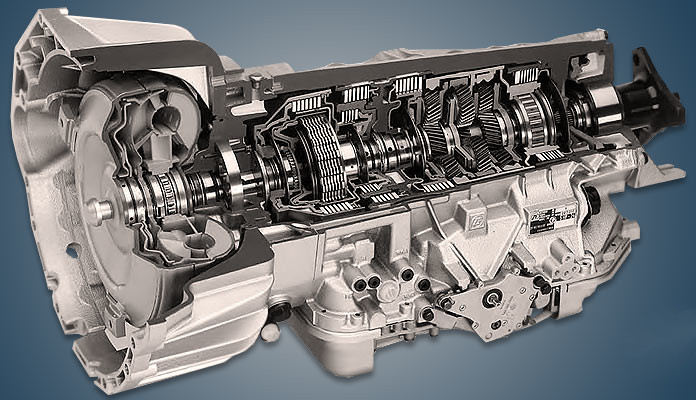
Internal clutch packs in the ZF units utilize advanced friction materials and sophisticated accumulator systems that provide smooth, consistent engagement throughout the transmission’s service life.
The torque converter incorporates ZF’s proprietary lock-up technology that engages progressively across multiple gears, reducing heat generation while improving fuel economy. Advanced damping systems within the converter eliminate the torque converter shudder that plagues many competitive units.
The transmission’s electronic control system represents a masterpiece of automotive software engineering, incorporating thousands of shift maps that adapt to driving conditions, load requirements, and individual driving styles.
Despite this sophistication, the system maintains exceptional reliability through robust hardware design and conservative programming that prioritizes component longevity. Advanced diagnostic capabilities allow technicians to identify potential issues before they result in component failure.
ZF’s commitment to quality extends throughout the manufacturing process, with extensive testing procedures that subject every transmission to simulated lifetime durability testing before approval for production.
The company’s global service network ensures that parts and expertise remain available worldwide, making these transmissions practical choices for international travelers and export vehicles. Real-world performance data from luxury vehicle fleets demonstrates the ZF units’ exceptional reliability.
Many high-mileage BMWs and Audis continue operating with original transmissions well beyond 300,000 miles, a testament to the engineering excellence that went into their development. Even when service becomes necessary, the transmissions’ modular design allows for cost-effective repairs using genuine ZF components.
4. Allison 1000/2000 Series
The Allison 1000 and 2000 series transmissions represent the gold standard for heavy-duty commercial and recreational vehicle applications, bringing commercial-grade durability to pickup trucks, motorhomes, and other demanding applications where transmission failure simply isn’t acceptable.
Originally developed for urban transit buses, fire trucks, and other commercial vehicles, these transmissions adapt their proven durability to civilian applications where their robust construction provides unmatched reliability.
The Allison’s foundation rests on a substantial aluminum case with integrated cooling circuits and mounting points designed to handle the extreme forces generated by high-torque diesel engines and heavy payload conditions.
Internal architecture features six forward speeds with multiple clutch packs for each gear, providing redundancy and improved load distribution that extends component life far beyond conventional automotive transmissions. The unit’s generous fluid capacity ensures adequate lubrication and cooling even during sustained high-load operation.
Clutch packs in Allison transmissions utilize commercial-grade friction materials and sophisticated hydraulic controls that provide smooth, consistent engagement under all operating conditions.
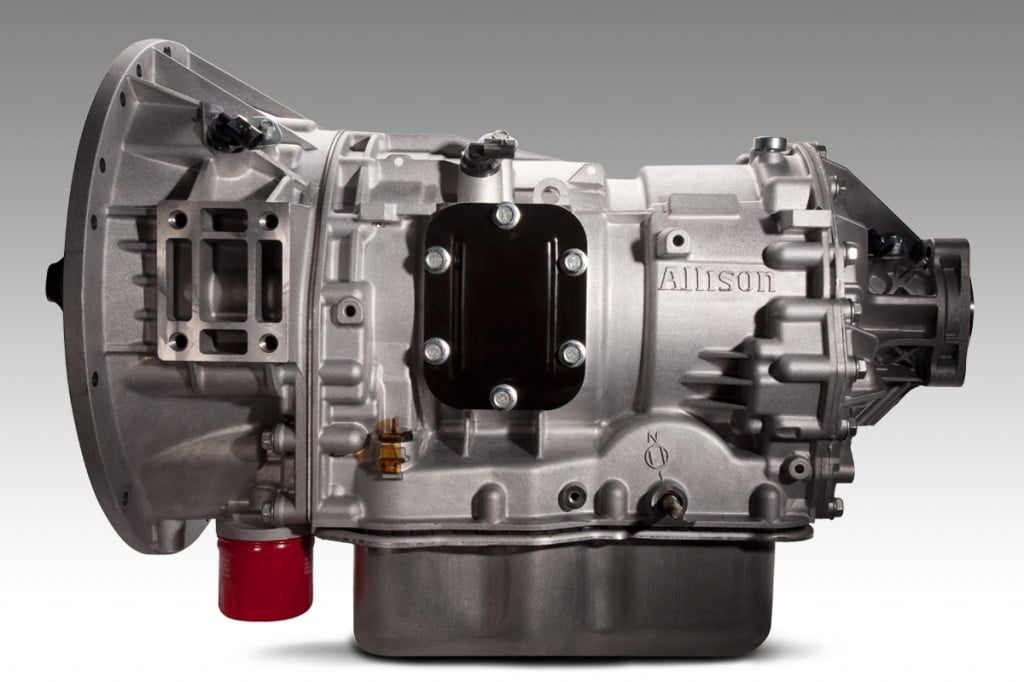

The transmission’s adaptive shift logic monitors operating conditions continuously, adjusting shift points and pressures to optimize performance while protecting internal components from excessive stress. Advanced prognostics systems can predict component wear and schedule maintenance before failures occur.
The Allison’s torque converter system differs significantly from conventional automotive designs, incorporating lock-up strategies optimized for heavy-duty applications.
The converter’s robust construction handles the extreme forces generated by high-torque engines while providing smooth power delivery across the entire operating range. Advanced damping systems eliminate the vibration and harshness that could compromise driver comfort or component longevity.
Electronic control systems in Allison transmissions represent decades of commercial vehicle experience, incorporating proven algorithms and robust hardware designed for continuous duty cycles that would destroy conventional automotive transmissions.
The system’s diagnostic capabilities provide detailed information about transmission operation, allowing fleet managers to optimize maintenance schedules and identify potential issues before they result in costly failures.
Service records from commercial fleets demonstrate Allison’s exceptional durability. Many transit buses and delivery trucks accumulate over one million miles with original transmissions still operating smoothly, a testament to the engineering excellence that characterizes these units.
When applied to pickup trucks and motorhomes, this durability translates to virtually bulletproof reliability for recreational and light commercial applications.
Also Read: 5 Paint Finishes That Stay Vibrant For Years Vs. 5 Prone To Peeling
5. Mercedes-Benz 722.6
Mercedes-Benz’s 722.6 five-speed automatic transmission represents the perfect synthesis of German engineering precision and long-term durability, serving as the foundation for countless luxury vehicles while maintaining exceptional reliability throughout extended service lives.
The 722.4 is among the most reliable automatic transmissions, and its successor, 722.6, continues this tradition of excellence through sophisticated design and meticulous manufacturing standards.
The transmission’s construction begins with a precision-cast aluminum case featuring integrated cooling circuits and mounting points engineered to handle the diverse powertrains found in Mercedes-Benz vehicles, from efficient four-cylinder engines to powerful V12 units.
Internal components utilize premium materials and advanced manufacturing techniques that ensure precise tolerances and superior surface finishes, reducing friction and wear while improving efficiency throughout the transmission’s service life.
Planetary gear sets in the 722.6 feature hardened steel components with specialized surface treatments that resist wear even under high-performance driving conditions.
Multiple clutch packs provide smooth, consistent engagement while distributing loads across larger surface areas, reducing component stress and extending service life. The transmission’s sophisticated hydraulic control system ensures precise shift timing and pressure regulation under all operating conditions.
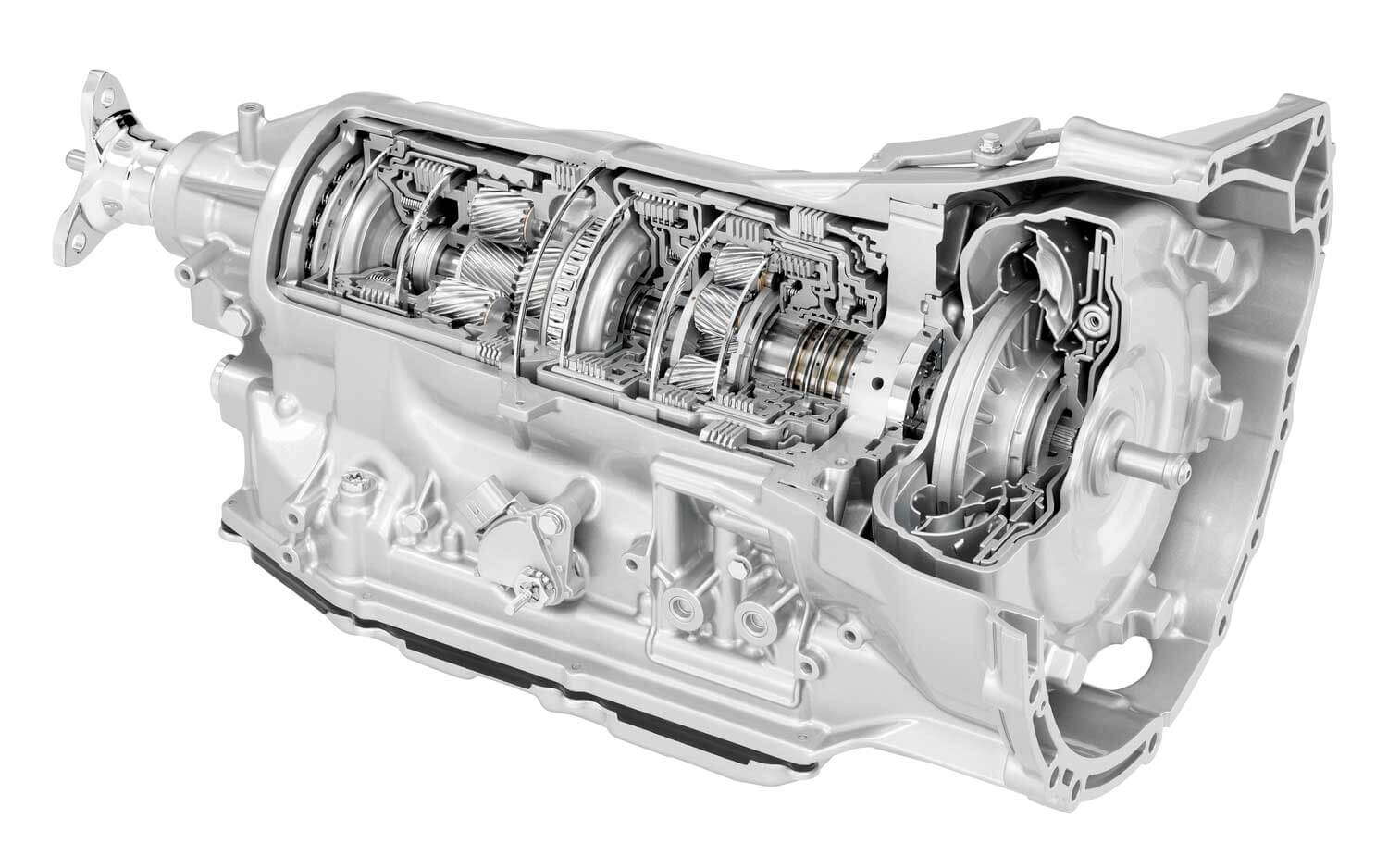
The 722.6’s torque converter incorporates Mercedes-Benz’s advanced lock-up technology that engages progressively across multiple gears, reducing heat generation while improving fuel economy.
Sophisticated damping systems within the converter eliminate vibration and harshness that could compromise refinement or component longevity. The converter’s robust construction handles the diverse torque characteristics of Mercedes-Benz engines while providing smooth power delivery.
Electronic control systems represent Mercedes-Benz’s decades of transmission development experience, incorporating thousands of shift maps that adapt to driving conditions, engine characteristics, and individual driving styles.
Despite this sophistication, the system maintains exceptional reliability through conservative programming and robust hardware design that prioritizes longevity over aggressive performance. Advanced self-diagnostic capabilities monitor transmission operation continuously, alerting drivers to potential issues before component damage occurs.
Real-world durability data from taxi fleets and high-mileage enthusiast vehicles demonstrates the 722.6’s exceptional reliability. Many vehicles accumulate over 400,000 miles with original transmissions operating smoothly, requiring only routine maintenance throughout their service lives.
The transmission’s modular design facilitates cost-effective repairs when necessary, while Mercedes-Benz’s global parts network ensures component availability worldwide.
5 Transmissions That Drop Torque Converters Early
These unfortunately designed automatic transmissions suffer from undersized torque converters with inadequate lockup clutch capacity, thin converter shells, and insufficient internal bracing that allow catastrophic failure under normal driving conditions, including moderate acceleration and routine highway cruising.
Their compromised construction features lightweight stator assemblies that crack under load, inadequate fluid circulation systems that cause overheating, and poorly designed lockup mechanisms that create destructive vibrations throughout the drivetrain.
Owners frequently report catastrophic converter failures requiring complete transmission replacement, often experiencing sudden loss of power, metallic debris contamination throughout fluid systems, and cascade failures that destroy pumps, valve bodies, and planetary assemblies, creating dangerous driving situations and repair costs that exceed vehicle value while leaving drivers stranded without warning.
1. Nissan CVT (Jatco CVT7/CVT8)
Nissan’s continuously variable transmissions, primarily manufactured by Jatco, have become synonymous with premature failure and costly repairs, particularly the CVT7 and CVT8 variants found in popular models like the Altima, Sentra, Rogue, and Pathfinder.
A bigger problem is high transmission temperatures, sending the vehicle into limp mode. The cooling system on the CVT cannot handle the amount of heat generated by the belts and pulleys. As a solution, Nissan offered an external transmission cooler upgrade, but even that did not always help.
The fundamental design flaw in Nissan’s CVT implementation stems from inadequate cooling systems that cannot handle the heat generated by the steel belt and pulley system under normal driving conditions.
Unlike traditional automatic transmissions with multiple gear ratios, CVTs rely on a continuous steel belt running between variable-diameter pulleys to provide infinite gear ratios.
This system generates substantially more heat than conventional transmissions, requiring sophisticated cooling systems that Nissan failed to adequately implement.
The belt and pulley system represents the CVT’s primary failure point, with the steel belt stretching or breaking under normal operating conditions, particularly when the transmission overheats.
By the nature of design, CVT transmissions are not as robust or reliable as more traditional planetary or counter shaft transmissions. The main failure mode is the steel belt and the mating tapered sheeves.
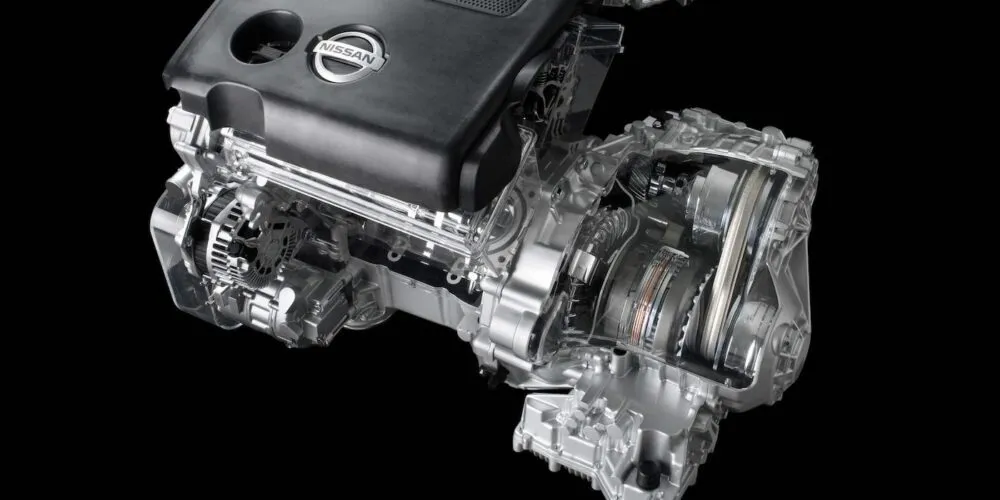

When overheating occurs, the belt’s tension changes, causing slipping, jerking, and eventual complete failure that often requires entire transmission replacement.
Nissan’s CVT programming exacerbates the cooling problems by allowing the transmission to operate at temperatures that damage internal components.
The electronic control module lacks adequate temperature monitoring and protection algorithms, permitting continued operation even when component damage is occurring. Many owners report sudden transmission failure without warning, often stranding them in dangerous situations.
The economic impact of Nissan CVT failures has been devastating for owners, with replacement costs often exceeding the vehicle’s value, particularly in older models.
Honda cars released during 1999-2004 usually face transmission issues. Car models such as Accord, Civic, and Odyssey are the worst example of Honda CVT transmission problems.
While this quote refers to Honda, similar patterns emerge with Nissan vehicles, where CVT failures cluster around specific model years and mileage ranges. Multiple class-action lawsuits have targeted Nissan for CVT reliability issues, with settlements requiring extended warranties and repair coverage.
However, many owners still face substantial out-of-pocket expenses when failures occur outside warranty periods. The widespread nature of these problems has significantly impacted Nissan’s reputation and resale values for affected models.
2. Ford Focus DPS6 Dual-Clutch
Ford’s PowerShift DPS6 dual-clutch automatic transmission, found in the Focus and Fiesta from 2012-2016, represents one of the most problematic transmission designs in modern automotive history, plaguing owners with constant shuddering, premature clutch failure, and unpredictable performance that created safety concerns and massive repair bills.
The DPS6’s fundamental flaw stems from Ford’s attempt to adapt a dual-clutch design optimized for performance applications to everyday commuter vehicles without adequate development time or real-world testing.
Unlike traditional automatics with torque converters, dual-clutch transmissions use computer-controlled clutches that must engage and disengage precisely to provide smooth operation.
Ford’s implementation suffered from inadequate clutch control algorithms that caused constant slipping, overheating, and premature wear. The transmission’s clutch actuator system proved particularly problematic, with seals failing prematurely and allowing fluid contamination that degraded performance.
Owners reported constant shuddering during acceleration, particularly from low speeds, creating an unpleasant driving experience and raising safety concerns about the vehicle’s ability to accelerate smoothly in traffic situations.
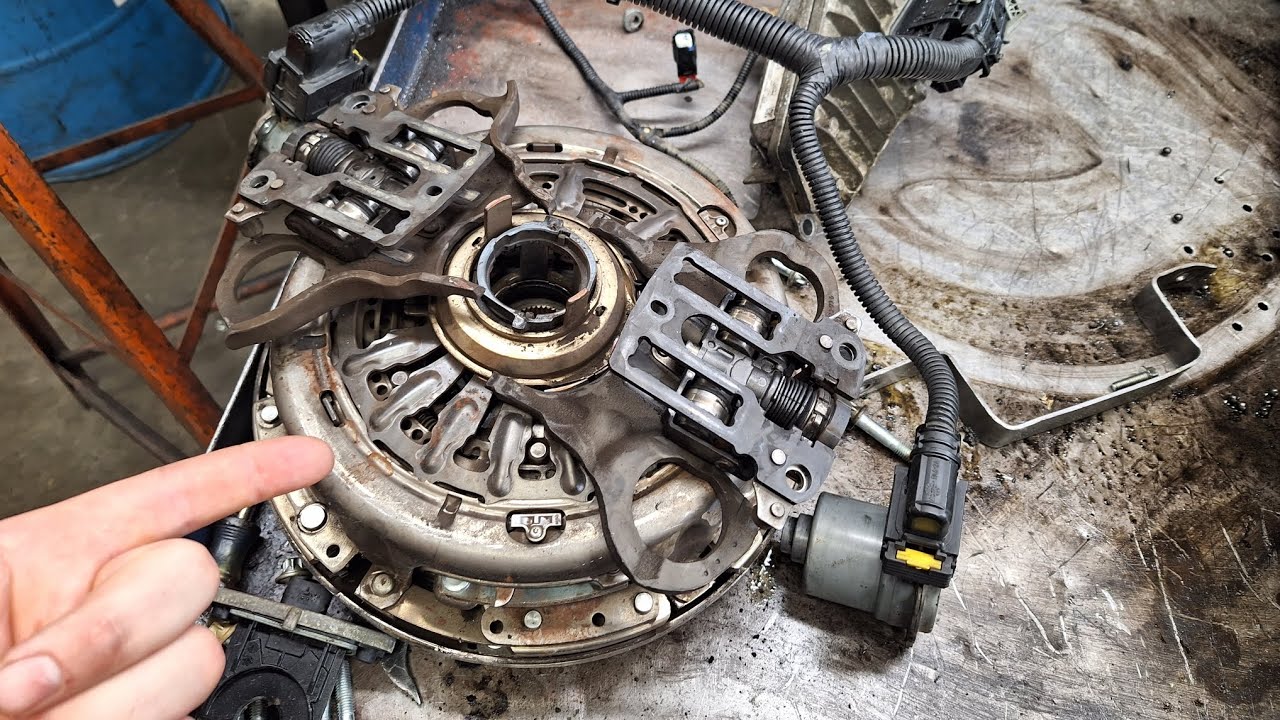
The transmission’s electronic control module lacked adequate adaptive learning capabilities, failing to compensate for clutch wear and changing operating conditions.
Ford’s attempts to address DPS6 problems through software updates and component revisions proved largely unsuccessful, with many vehicles requiring multiple transmission replacements under warranty.
The company issued numerous technical service bulletins and extended warranty coverage, but problems persisted throughout the transmission’s production run. Many owners reported that even after multiple repairs, the fundamental shuddering and performance issues returned within months.
Unlike conventional automatic transmissions that typically fail gradually with warning signs, the DPS6 often experienced sudden, complete failures that left owners stranded.
The transmission’s complex design made repairs expensive and time-consuming, often requiring specialized tools and training that many service facilities lacked.
3. Chrysler 41TE/42LE
Chrysler’s 41TE and 42LE four-speed automatic transmissions, found in minivans and sedans throughout the 1990s and early 2000s, earned notoriety for premature electronic failures, particularly involving the torque converter clutch solenoid and related control systems that caused shuddering, overheating, and complete transmission failure often before 100,000 miles.
The transmission’s electronic control system represented an early attempt at sophisticated shift management, but suffered from inadequate component quality and poor integration between mechanical and electronic systems.
The torque converter clutch solenoid, responsible for engaging and disengaging the converter’s lock-up mechanism, frequently failed due to contamination, overheating, or electrical problems that caused the converter to operate incorrectly.
When the torque converter clutch system malfunctioned, it created a cascade of problems, including overheating, fluid degradation, and eventual failure of other transmission components.
The solenoid’s location within the transmission made replacement expensive and time-consuming, often requiring complete transmission removal. Many owners discovered that the relatively inexpensive solenoid failure had caused extensive damage to other components, necessitating complete transmission rebuilds.
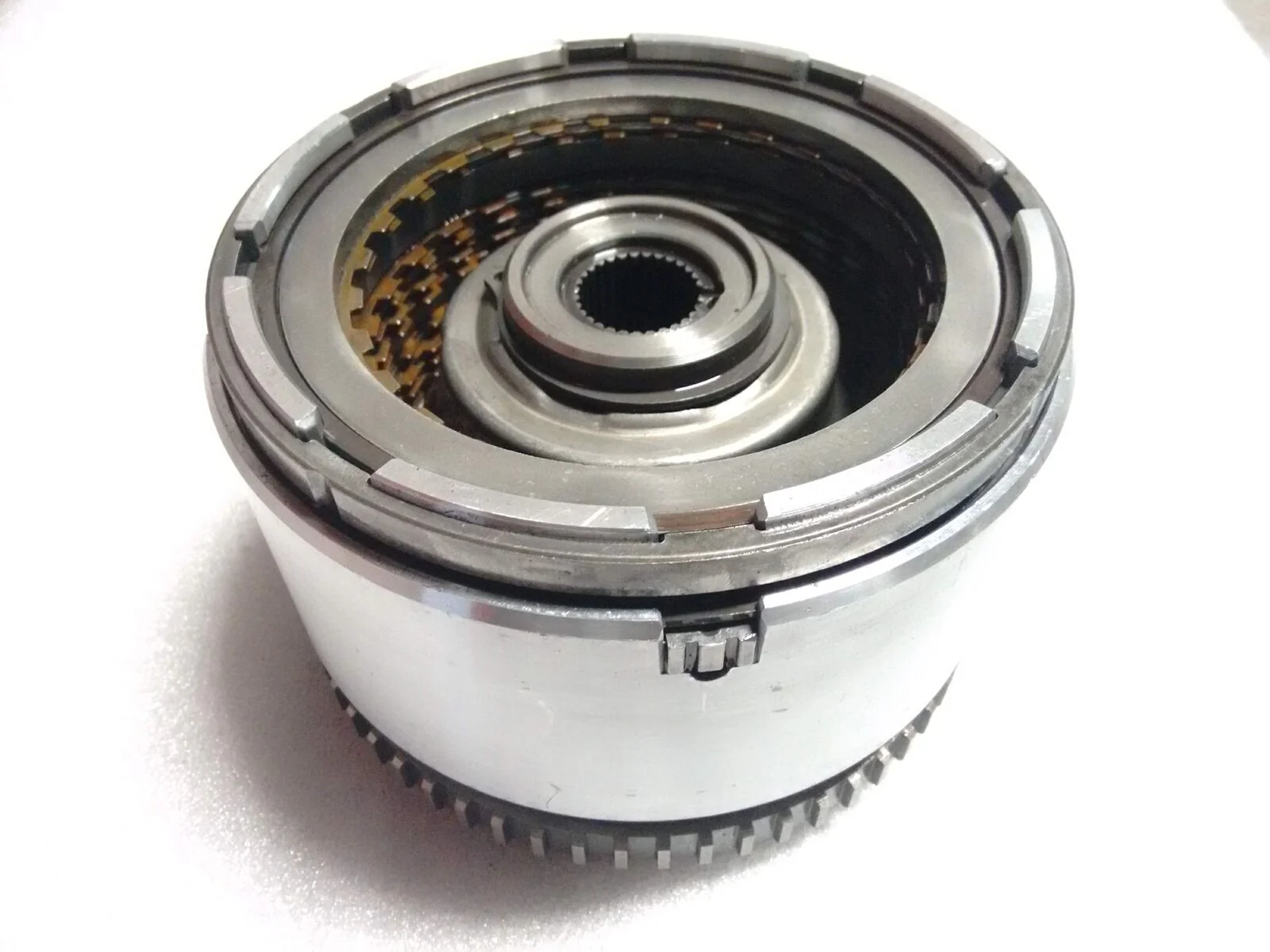

The 41TE/42LE’s valve body design compounded the electronic problems, with narrow passages that became clogged easily when fluid degraded due to overheating.
The transmission’s cooling system proved inadequate for sustained operation with a malfunctioning torque converter clutch, creating a vicious cycle where electronic failures led to overheating, which caused further electronic and mechanical damage. Chrysler’s response to these problems was inconsistent, with some owners receiving warranty coverage while others faced substantial repair bills.
The company issued technical service bulletins addressing specific failure modes, but the fundamental design flaws persisted throughout the transmission’s production run. Many independent repair shops developed specialized expertise in 41TE/42LE repairs due to the high volume of failures.
The transmission’s problems significantly impacted Chrysler’s reputation during a critical period when the company was competing against increasingly reliable Japanese alternatives.
Many loyal Chrysler customers switched brands after experiencing 41TE/42LE failures, particularly given the high cost of repairs relative to vehicle values. The transmission’s poor reliability contributed to declining minivan sales and damaged Chrysler’s position in the family vehicle market.
4. Honda Judder-Prone Units (1999-2004)
Honda’s automatic transmissions from 1999-2004, particularly those found in the Accord, Civic, Odyssey, and Acura TL, developed a reputation for premature clutch pack failure and torque converter problems that often manifested as transmission judder, slipping, and complete failure well before expected service intervals.
Honda cars released during 1999-2004, usually face transmission issues. Car models such as Accord, Civic, and Odyssey are the worst example of Honda CVT transmission problems.
The root cause of these failures stemmed from Honda’s decision to reduce transmission fluid capacity and modify clutch pack materials to improve fuel economy and reduce manufacturing costs.
The economic impact on Honda owners was substantial, with many facing repair bills exceeding $3,000-4,000 for transmission replacement or rebuilds.
Unlike typical Honda reliability, these transmissions often failed catastrophically without warning, leaving owners stranded and facing emergency repair situations. The problems significantly damaged Honda’s reputation for reliability and contributed to increased scrutiny of the company’s quality control processes.
5. GM 4T65E
General Motors’ 4T65E four-speed automatic transmission, found in numerous front-wheel-drive vehicles including the Buick Century, Oldsmobile Intrigue, Pontiac Grand Prix, and Chevrolet Impala, became notorious for premature failures, particularly involving the torque converter clutch, pressure control solenoid, and related electronic systems that caused shuddering, slipping, and complete transmission failure often before 100,000 miles.
The 4T65E’s problems stemmed from cost-cutting measures that reduced the robustness of critical internal components while increasing the transmission’s complexity through additional electronic controls.
The pressure control solenoid, responsible for regulating hydraulic pressure throughout the transmission, frequently failed due to contamination or wear, causing erratic shift patterns and eventual transmission damage. This solenoid’s failure often went undetected until extensive damage had occurred.
The transmission’s torque converter clutch system proved particularly problematic, with the apply valve sticking due to contamination or wear particles in the transmission fluid.
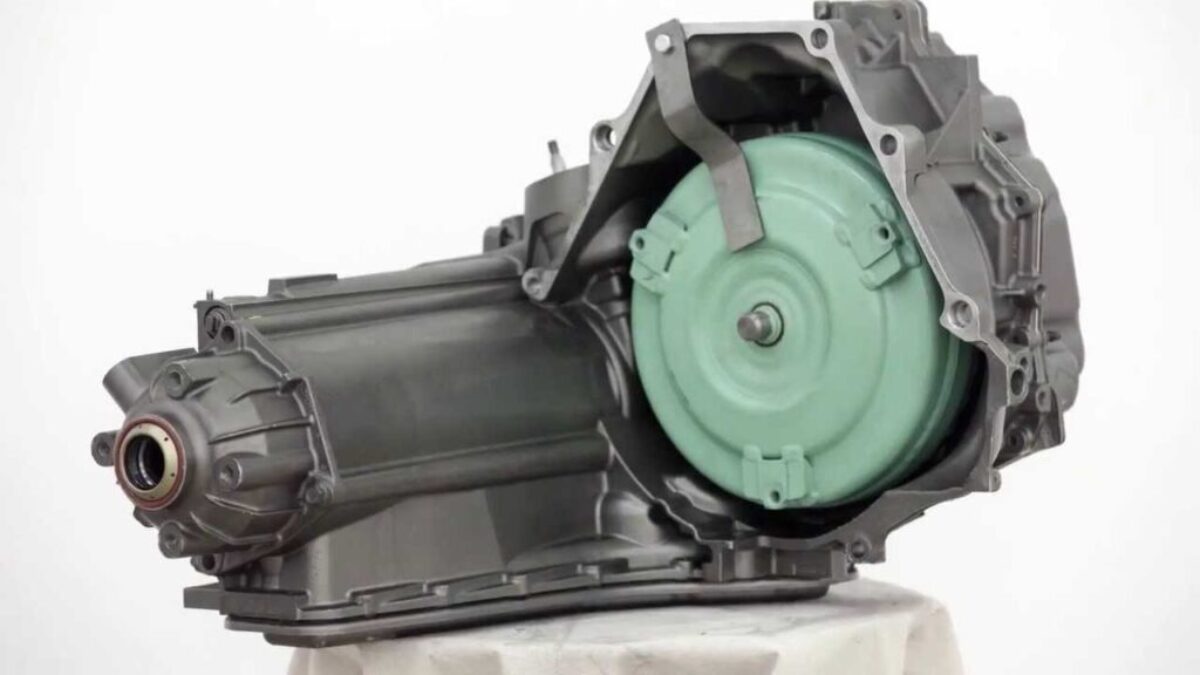

When this occurred, the converter clutch would engage inappropriately or fail to disengage, causing severe shuddering, overheating, and rapid wear of internal components. The problem was exacerbated by the transmission’s inadequate filtration system, which allowed contaminants to circulate freely.
GM’s electronic control strategy for the 4T65E proved overly aggressive in pursuit of fuel economy improvements, with shift patterns and pressures that stressed internal components beyond their design limits.
The transmission control module’s adaptive learning capabilities often masked developing problems until catastrophic failures occurred, leaving owners with no warning before complete transmission failure. The 4T65E’s case design contributed to its problems, with inadequate ribbing and mounting points that allowed excessive flexing under load.
Many owners faced multiple transmission failures under warranty, with some vehicles requiring three or more transmission replacements before achieving acceptable reliability. The transmission’s problems contributed to declining sales of affected vehicles and damaged GM’s reputation during a critical competitive period.
Also Read: 5 Convertibles That Leave You Smiling for Years vs. 5 That Leak and Creak

