In the last decade, hybrid technology has evolved from a novelty to a mainstream necessity.
With rising fuel costs, stricter emissions standards, and a national push toward cleaner transportation, hybrid vehicles have become a practical bridge between traditional combustion engines and full-electric powertrains.
But not all hybrid engines are created equal. Some have proven themselves as paragons of efficiency, reliability, and long-term ownership satisfaction, while others have left owners frustrated with costly repairs and unpredictable performance.
For US buyers especially those who depend on their vehicles daily understanding which hybrid systems stand the test of time can make or break the ownership experience.
Let’s dive into five hybrid engines that consistently impress owners, followed by five that have earned a reputation for being more trouble than they’re worth.
Hybrid Engines That Impress Owners
Hybrid engines have come a long way from being seen as just fuel-savers for eco-conscious drivers. Today’s hybrids combine efficiency with power, refinement, and advanced technology, earning praise from owners who appreciate their real-world benefits.
From trucks and SUVs to sedans, these engines deliver smooth acceleration, strong torque, and impressive fuel economy without compromising performance. In this article, we take a closer look at the hybrid powertrains that truly impress their owners and show how far hybrid engineering has evolved.
1. Toyota Hybrid Synergy Drive (2.5L)
Toyota’s Hybrid Synergy Drive remains the gold standard in the hybrid world. Found in millions of vehicles worldwide, the 2.5-liter version used in models like the RAV4 and Camry Hybrid has proven almost indestructible with proper maintenance.
The system’s ability to seamlessly blend electric and gasoline power means fewer mechanical stresses and smoother operation over time.
Owners consistently report excellent reliability, with many vehicles surpassing 200,000 miles without major issues.
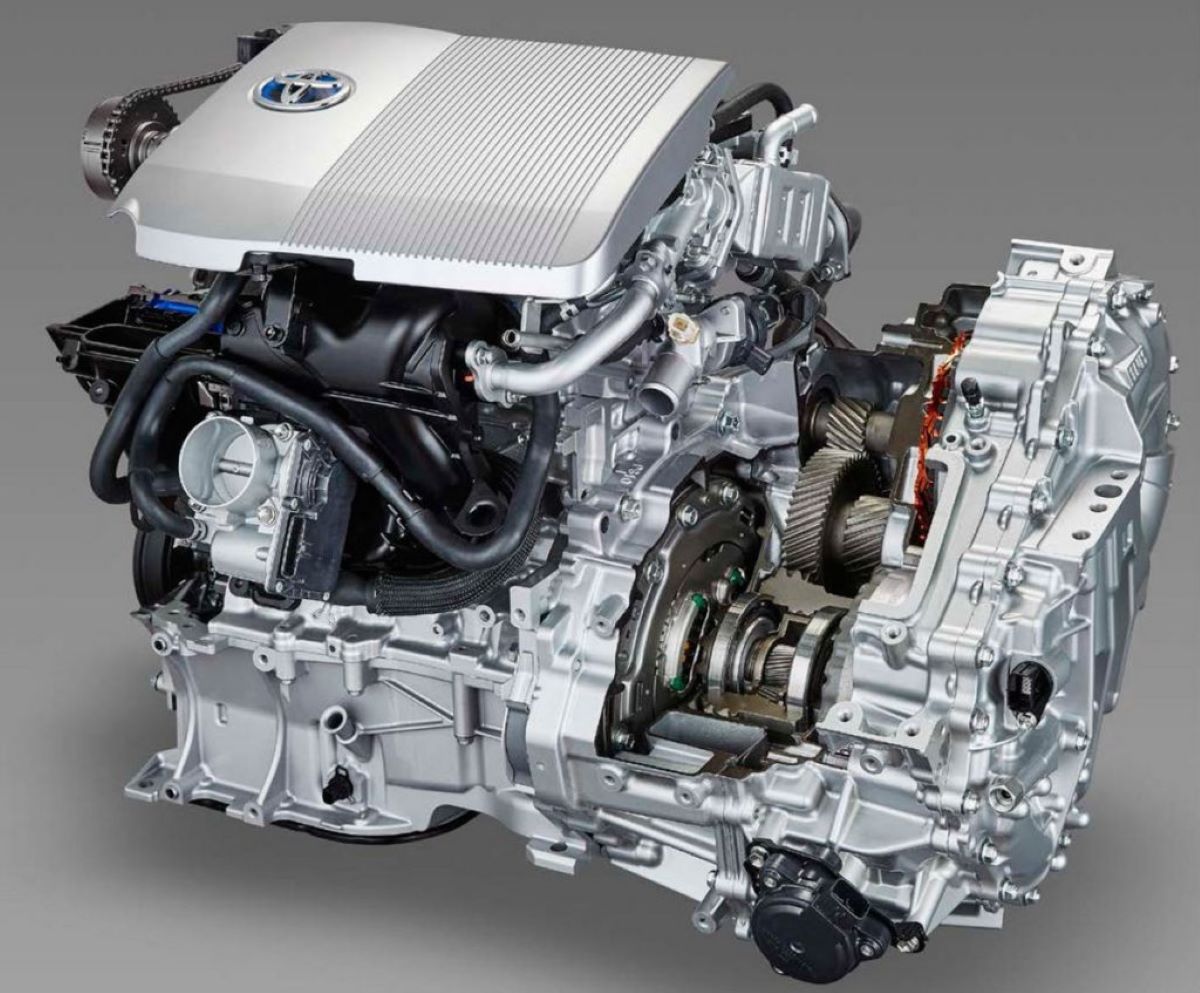

Its e-CVT transmission, often maligned in other vehicles, operates flawlessly here, contributing to fuel economy figures in the 40–45 mpg range.
Toyota’s conservative approach to battery output and heat management also means fewer premature failures. It’s a perfect example of how refined engineering, rather than radical innovation, creates lasting success.
Toyota’s hybrid technology, known as Toyota Hybrid Synergy Drive (HSD), previously called the Toyota Hybrid System (THS), has evolved significantly since its introduction in 1997 with the Prius. Each generation has brought improvements in fuel efficiency, performance, and features, making Toyota one of the leading names in hybrid innovation.
The first generation (1997–2003) debuted with the original Prius, a compact sedan powered by a 1.5-liter engine. It achieved an impressive 41 mpg combined, which was far better than other Toyota sedans at the time. Standard features included air conditioning and electric power steering, though cargo space was limited due to the placement of the battery pack.
The second generation (2003–2009) brought a complete redesign, transforming the Prius into a 5-door liftback with increased luggage capacity and legroom.
It introduced the now-iconic “triangle silhouette,” designed for improved aerodynamics. Fuel efficiency climbed to 46 mpg combined, and Toyota replaced the original system with the more advanced Toyota Hybrid System II.
By the third generation (2009–2015), the Prius had grown in both size and technology. Equipped with a 1.8-liter engine, it delivered 50 mpg combined and introduced the first-ever Prius Plug-in Hybrid, which offered an 11-mile electric-only range.
The car adopted a more aerodynamic double-wave roof and expanded into new variants such as the Prius V (wagon) and Prius C (subcompact). Additional features like a touchscreen stereo, Bluetooth connectivity, and an optional solar panel also became available.
The fourth generation (2015–2022) made the Prius more efficient than ever, achieving 56 mpg combined without a plug-in setup. This version came standard with LED headlights and a refined double-wishbone rear suspension for a smoother ride.
It also introduced the first all-wheel-drive Prius model, while the plug-in version was renamed the Prius Prime, offering up to 25 miles of electric range. Larger touchscreens and Toyota Safety Sense features became standard, highlighting Toyota’s focus on technology and safety.
The fifth generation (2023–present) showcases an all-new design with even better fuel economy, reaching up to 57 mpg combined in front-wheel-drive versions. It offers an optional all-wheel-drive model powered by a permanent magnet rear electric motor.
Standard features include an 8-inch touchscreen with Apple CarPlay and Android Auto, with larger displays available on higher trims. The latest Prius Prime plug-in hybrid provides a longer 44-mile electric range and even offers an optional solar panel, demonstrating Toyota’s continued commitment to hybrid innovation and efficiency.
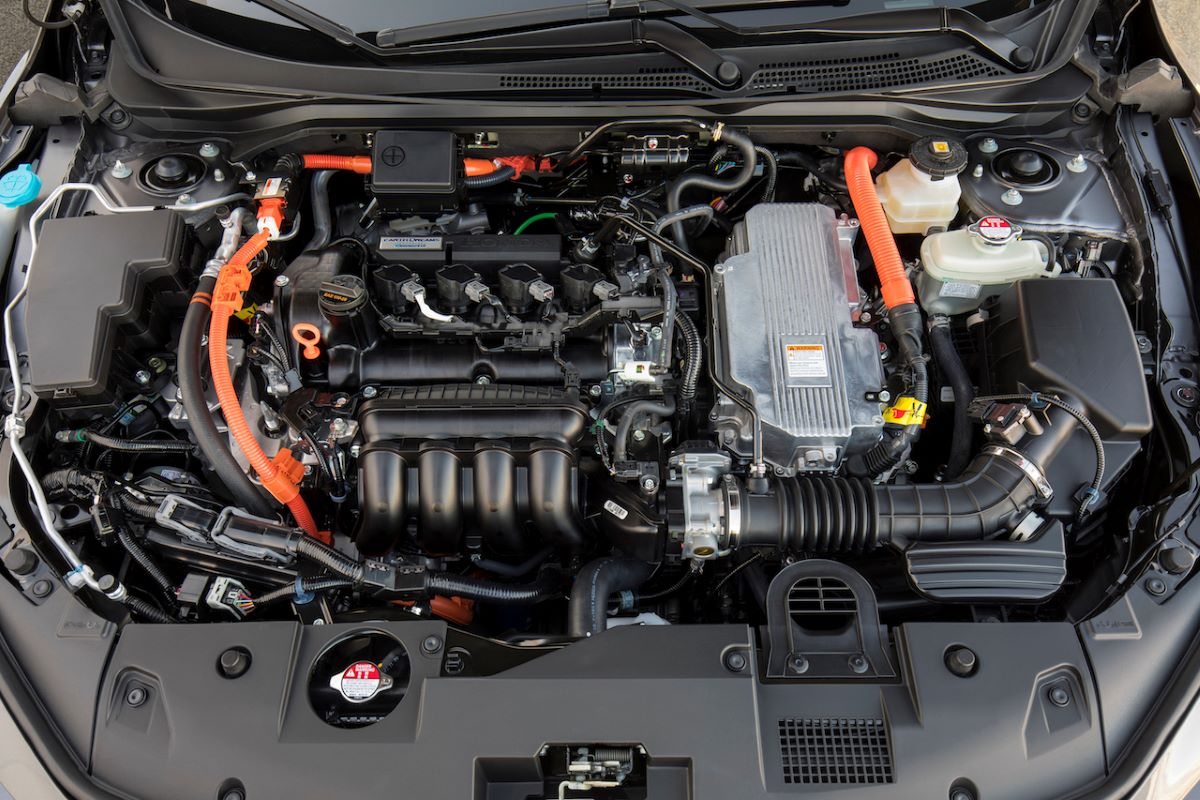
2. Honda i-MMD Hybrid (2.0L)
Honda’s Intelligent Multi-Mode Drive (i-MMD) system is one of the most refined and reliable hybrid setups on the market.
Rather than relying heavily on gear-driven components, Honda uses electric motors for most low-speed propulsion, reducing wear and tear on the gasoline engine.
The 2.0-liter Atkinson-cycle engine, paired with dual electric motors, allows for whisper-quiet operation and a real-world fuel economy near 44 mpg in the Accord Hybrid.
What sets the i-MMD apart is its mechanical simplicity. Without a traditional transmission, there are fewer moving parts to fail. Owners appreciate its responsiveness and smooth transition between drive modes.
This hybrid setup has earned widespread praise from long-term owners and mechanics alike for its bulletproof reliability.
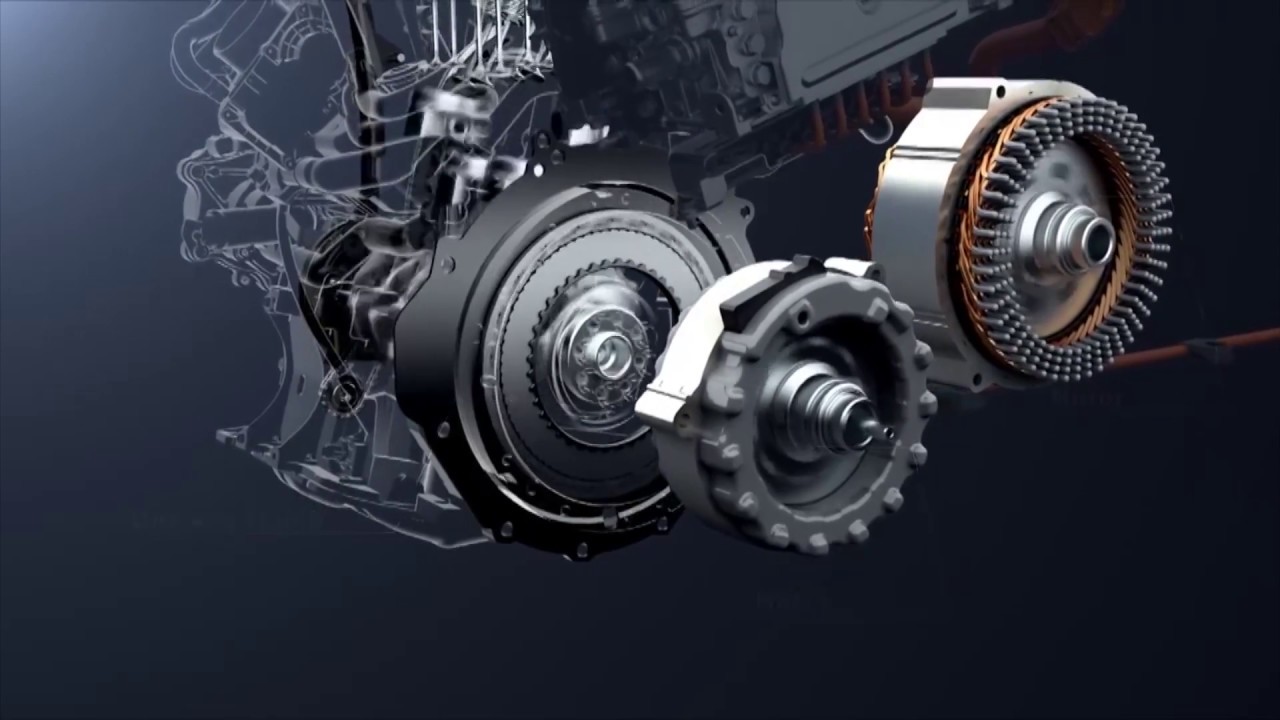
In 1997, Honda introduced the first-generation Integrated Motor Assist (IMA) hybrid system, marking the brand’s entry into hybrid technology. The first production car to feature this system was the 1999 Honda Insight.
Since then, the IMA system has undergone continuous refinement, evolving through six generations. As a typical parallel hybrid setup, it combines an internal combustion engine with an electric motor to improve fuel efficiency and performance.
The Honda IMA hybrid system primarily consists of an engine, an electric motor, a continuously variable transmission (CVT), and an Intelligent Power Unit (IPU). The electric motor takes the place of the conventional flywheel, maintaining the crankshaft’s rotational inertia.
This compact design ensures minimal space usage, with the IPU being the main component requiring additional room compared to traditional gasoline vehicles.
The system’s engine is optimized for efficiency through Honda’s i-VTEC (Variable Valve Timing and Lift Electronic Control), i-DSI (Intelligent Dual-Spark Ignition), and VCM (Variable Cylinder Management) technologies.
In the Honda CR-Z, for example, the 1.5-liter i-VTEC engine produces 83 kW of peak power and 145 N·m of torque, achieving real-world fuel consumption of around 5.4 liters per 100 kilometers.
The electric motor, located between the engine and transmission, is a compact and thin “sheet motor” that provides additional torque when needed. In the CR-Z, this motor delivers up to 10 kW of power and 78 N·m of torque.
While it mainly plays an assistive role, the IMA system allows limited electric-only driving during certain conditions, such as low-speed cruising, classifying it as a medium-sized hybrid. The system operates with a standard 7-speed CVT transmission for smooth power delivery.
The IMA’s Intelligent Power Unit (IPU) integrates a Power Control Unit (PCU) and a nickel-metal hydride battery pack.
The PCU houses three main components: the Battery Control Module (BCM), Motor Control Module (MCM), and Motor Drive Module (MDM). Together, these elements manage the energy flow between the motor, engine, and battery for optimal efficiency.
The Honda IMA hybrid system functions through several distinct operating modes: startup and acceleration, rapid acceleration, low-speed cruising, light acceleration and high-speed cruising, deceleration or braking, and parking.
During startup and acceleration, the engine operates at low-speed valve timing while the motor assists with extra power for smoother takeoff and reduced fuel use.
In rapid acceleration, the motor and engine work together, with the motor powered by the battery to enhance performance. At low speeds, the system can shut off the engine entirely, running solely on electric power for zero emissions.
During light acceleration and high-speed cruising, the engine alone powers the vehicle at an efficient valve timing, while the motor remains inactive. When decelerating or braking, the motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy into electricity stored in the battery.
The braking system uses signals from the brake pedal sensor to coordinate regenerative and mechanical braking, maximizing energy recovery. In parking mode, both the engine and motor shut down to conserve fuel and reduce emissions, automatically restarting when the brake pedal is released.
Overall, Honda’s IMA hybrid system demonstrates a balance between efficiency, compact design, and performance, marking a key step in the brand’s journey toward advanced hybrid mobility.
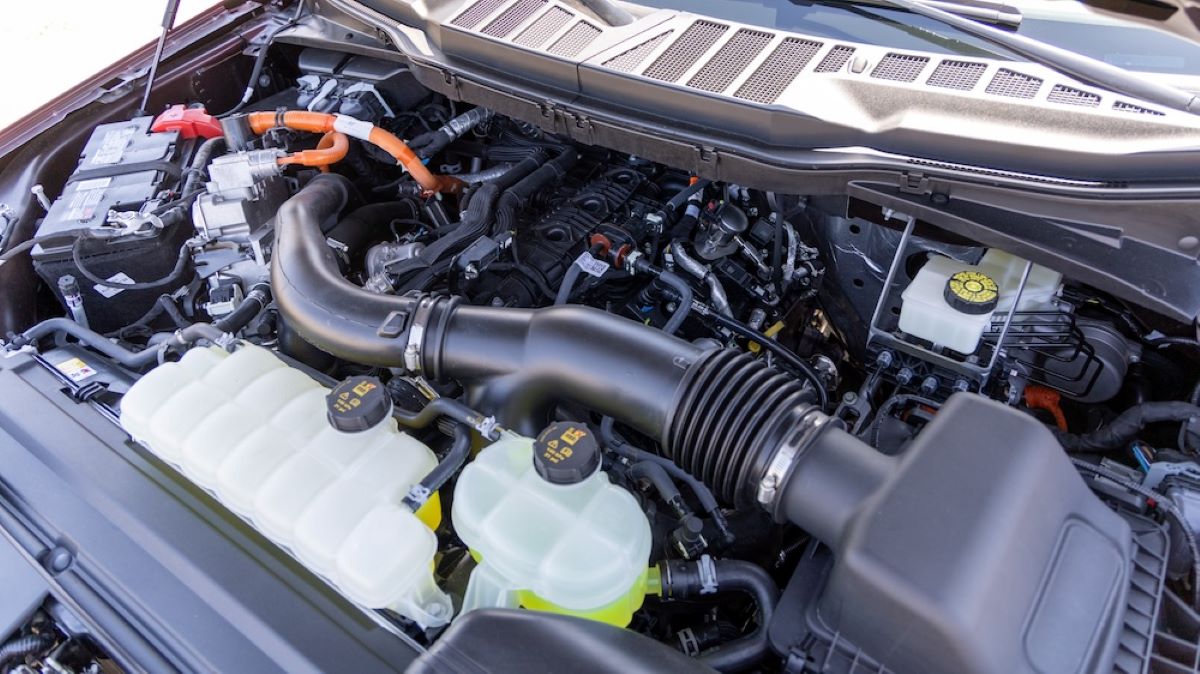
3. Ford PowerSplit Hybrid (2.5L)
Ford’s latest generation of PowerSplit hybrid technology has matured significantly, and the 2.5-liter engine found in the Escape and Maverick Hybrid is a strong performer.
Early versions in the Fusion Hybrid had issues, but the new design delivers robust reliability, fuel efficiency, and performance that appeals to American drivers.
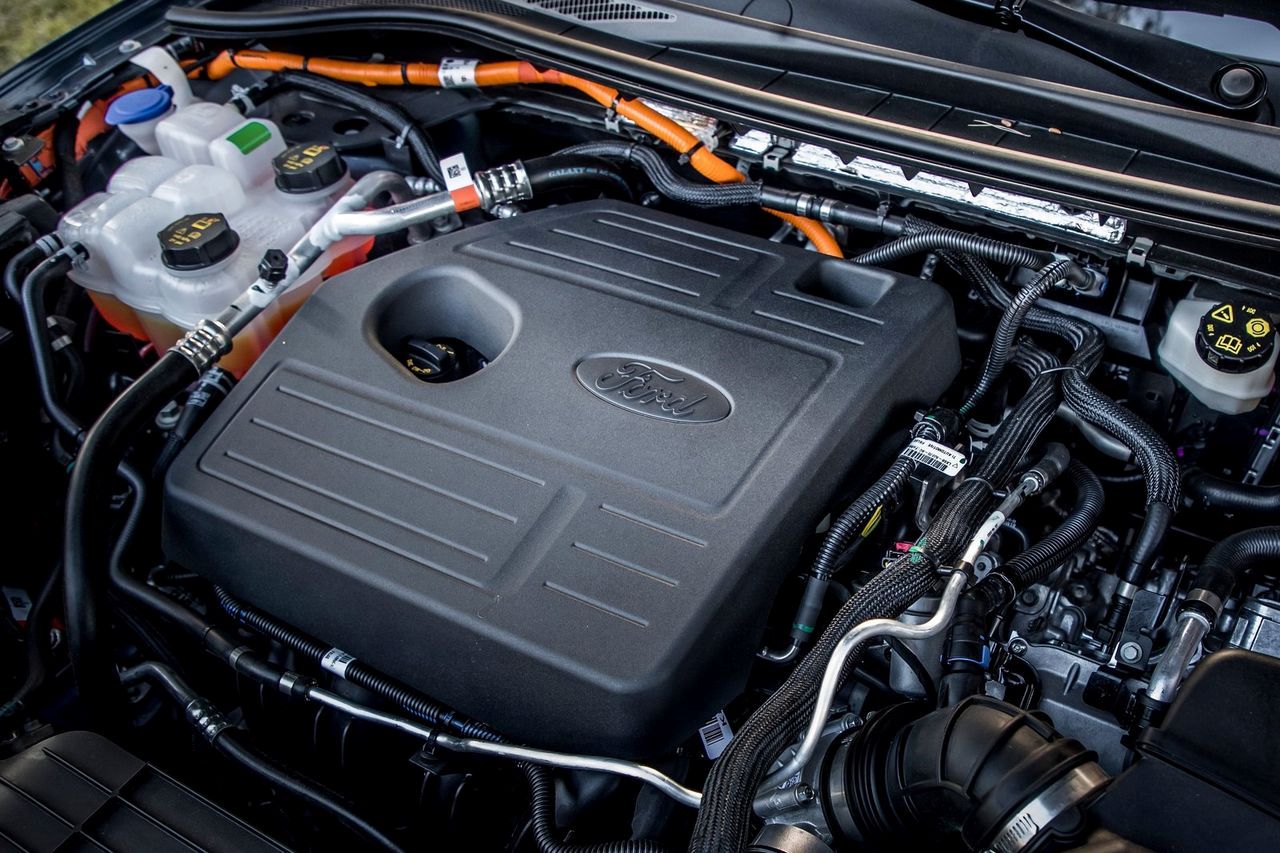

Owners love that it feels more “normal” to drive than some rivals, thanks to Ford’s tuning and regenerative braking feel. The system is particularly efficient in city driving, where it frequently switches to electric power.
With thousands of Maverick Hybrids now crossing the 100,000-mile mark without major mechanical failures, Ford has proved that American engineering can deliver a dependable hybrid powertrain.
4. Lexus 3.5L V6 Hybrid
When luxury meets reliability, Lexus often leads the pack. The brand’s 3.5-liter V6 hybrid engine combines effortless power with Toyota’s proven hybrid know-how.
Found in several Lexus models, this setup blends a silky-smooth gasoline engine with electric assistance that enhances both performance and efficiency.

What truly impresses owners is the longevity. It’s not uncommon for these engines to last well over 250,000 miles with minimal degradation in performance or battery health.
Lexus’ hybrid batteries are known for exceptional cooling and longevity, while the power delivery remains seamless even as the vehicle ages. For drivers wanting quiet luxury with hybrid reliability, this is the dream setup.
5. Hyundai/Kia 1.6L Hybrid
Hyundai and Kia have come a long way in hybrid development. Their 1.6-liter turbocharged hybrid system, paired with a six-speed automatic, has surprised many critics by proving both efficient and reliable.
It offers solid power, delivering over 40 mpg combined in most applications, while still feeling responsive something early hybrids often lacked.
Owners report that this system strikes a great balance between traditional driving dynamics and hybrid efficiency. The inclusion of a real gearbox, rather than a CVT, appeals to drivers who want a natural feel.
Over the last few years, Hyundai’s hybrid reliability scores have risen sharply, putting it in the same league as long-standing Japanese competitors.
The 1.6-liter engine, a key member of Hyundai and KIA’s G4CR family, is widely recognized for its compact design, dependable performance, and impressive fuel efficiency. It has become a cornerstone powerplant across both brands’ lineups, striking an ideal balance between practicality and driving enjoyment.
Designed primarily for urban commuters and everyday drivers, the 1.6L engine combines ease of use with a touch of spirited performance, making it suitable for a broad range of vehicles and lifestyles.
A major highlight of this engine is its ability to deliver responsive power while maintaining excellent fuel economy. Incorporating modern engineering features such as a multi-point fuel injection system, it precisely manages the air-fuel mixture to ensure optimal combustion efficiency.

The result is a smooth, quiet ride with reduced emissions, an essential quality in today’s eco-conscious automotive market. This combination of performance and efficiency has made the 1.6L engine a favorite among drivers seeking a balance between sustainability and driving enjoyment.
Across Hyundai and KIA’s diverse lineup, the 1.6L engine has proven its versatility and reliability. In the Hyundai Elantra, it enhances agility and fuel efficiency, ideal for city driving.
The KIA Forte uses this engine to provide an affordable yet engaging ride for those who value both economy and performance. The Hyundai Kona, a subcompact SUV, benefits from the engine’s lively nature, delivering an enjoyable urban driving experience.
Meanwhile, the KIA Seltos leverages the same powertrain to stand out in the competitive compact SUV segment, blending strength with efficiency. Lastly, the Hyundai i30 hatchback pairs the 1.6L engine’s responsiveness with its sporty design, offering a fun and practical drive.
Each of these applications underscores the engine’s adaptability, proving it can power everything from sleek sedans to versatile crossovers with equal competence.
Beyond its technical achievements, the 1.6L engine has been instrumental in helping Hyundai and KIA expand their global footprint, winning over consumers with its balance of reliability, efficiency, and performance.
As both automakers continue to innovate, this engine remains a prime example of their dedication to crafting powertrains that meet the evolving demands of modern drivers.
Hybrid Engines That Constantly Break
While hybrid vehicles are celebrated for their fuel efficiency and environmental benefits, not every hybrid powertrain lives up to the promise. Some models have developed reputations for frequent breakdowns, costly repairs, or complex mechanical issues that frustrate their owners.
From battery failures to transmission troubles, these hybrids prove that advanced technology doesn’t always guarantee reliability. In this article, we take a look at the hybrid engines that constantly break, highlighting the models that have left drivers disappointed rather than impressed.
1. Ford Fusion Hybrid (First Generation, 2010–2012)
While Ford has improved dramatically, its early hybrid systems were plagued with issues. The first-generation Fusion Hybrid often suffered from battery cooling problems and software glitches that caused sudden shutdowns or “limp mode.”
Owners also reported transmission shuddering and complete hybrid drive failures after 100,000 miles.

Repair costs for early Fusion Hybrids could be eye-watering, especially since replacement batteries and modules weren’t easily available.
These reliability struggles nearly derailed Ford’s hybrid reputation before the brand bounced back with newer models.
2. Nissan Hybrid System (2014–2017)
Nissan’s brief experiment with hybrid technology was nothing short of a disaster. The system, which combined a supercharged 2.5-liter engine with a single electric motor, was overly complex and poorly integrated.
Owners reported erratic performance, transmission issues, and hybrid battery failures far earlier than expected.
By 2018, Nissan abandoned the setup entirely, and parts availability became a nightmare for owners.
Many vehicles required expensive repairs that exceeded their resale value, effectively making this one of the worst hybrid attempts in modern automotive history.
The standard Nissan Rogue comes equipped with a 2.5-liter four-cylinder engine that produces 170 horsepower and is paired with a continuously variable automatic transmission (CVT).
Unfortunately, the CVT’s sluggish response and syrupy power delivery make the engine sound strained under heavy throttle, as if it’s dragging the Rogue rather than propelling it forward.
There’s also a hybrid version that combines a 2.0-liter four-cylinder engine with an electric motor, producing a total of 176 horsepower and utilizing the same CVT. Both versions are available with either front-wheel or all-wheel drive.
You don’t need to take the Rogue to a test track to notice its lack of speed, a short drive around a parking lot makes it evident. Acceleration trails significantly behind most competitors in its class, leaving the Rogue feeling underpowered.
While its soft suspension does deliver a smooth and relaxed ride, that’s about the only redeeming quality of its driving experience.
The overly plush setup sacrifices handling precision, causing noticeable body movement through corners, even at moderate speeds. Furthermore, the Rogue lacks the solid, stable feel that inspires confidence on straight stretches of highway, making it one of the less engaging options in the compact SUV segment.
3. Chrysler Pacifica Hybrid (2017–2020)
The idea of a plug-in hybrid minivan thrilled American families—until the real-world reliability issues started surfacing. Early Pacifica Hybrids were hit with repeated recalls for battery fires, charging malfunctions, and stalling while driving.
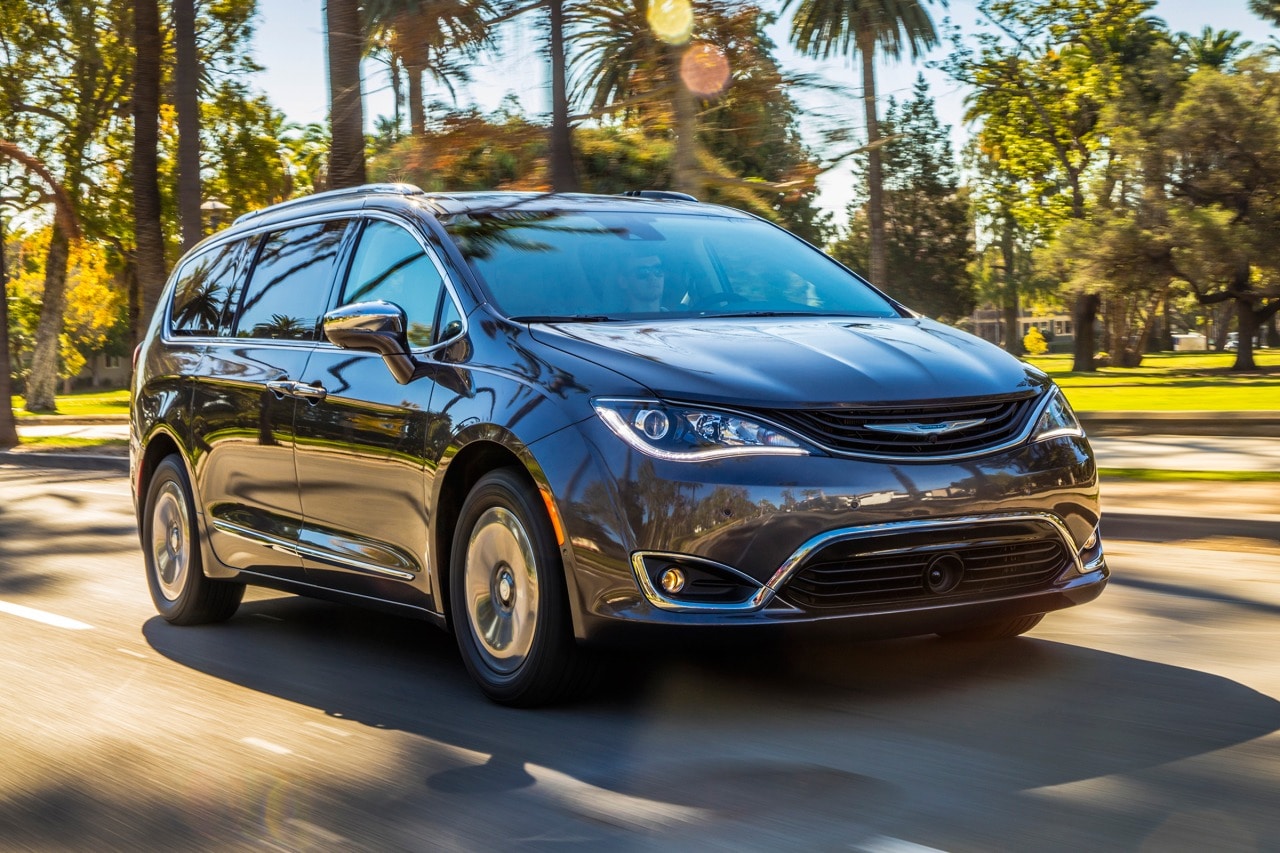

Owners reported powertrain faults, sudden shutdowns, and poor dealer support. Even when repairs were made under warranty, many problems resurfaced.
While later models have seen improvements, the early Pacifica Hybrid remains a cautionary tale of rushing complex hybrid technology to market before it’s truly ready.
4. GM eAssist Mild Hybrid (2012–2016)
GM’s eAssist system wasn’t a “full hybrid” in the traditional sense it was more of a glorified start-stop system with minimal electric assist. Unfortunately, it combined the worst of both worlds: added complexity without major efficiency gains.

Owners complained about failing battery packs, control module issues, and starter motor wear due to the constant stop-start cycles. The system’s benefits didn’t justify the headaches, leading to widespread dissatisfaction.
GM quietly phased it out in favor of focusing on EV development, leaving many owners stuck with high repair costs and questionable long-term reliability.
5. BMW ActiveHybrid System
BMW’s early hybrids were high on ambition but low on durability. Their complex twin-turbocharged engines paired with electric assist systems introduced excessive heat and electrical load leading to reliability nightmares.
The ActiveHybrid 5 and 7 were notorious for inverter failures, software malfunctions, and astronomical repair costs once warranties expired.
These models were heavy, inefficient compared to rivals, and frequently left owners with multi-thousand-dollar repair bills.
BMW’s experiment with hybrids during this era was short-lived, and the brand has since focused more effectively on plug-in hybrid and EV systems under the iPerformance banner.
Hybrid technology has revolutionized the way Americans think about fuel economy and sustainability. But like any engineering frontier, not every design gets it right the first time.
Brands like Toyota, Honda, and Lexus have refined their hybrid systems to near perfection earning the trust of millions of drivers.
The BMW ActiveHybrid 5 represents a sophisticated fusion of luxury, performance, and hybrid innovation, appealing to modern drivers who seek efficiency without sacrificing the thrill of driving.
Introduced as part of BMW’s initiative toward sustainable mobility, this model merges a robust gasoline engine with an electric motor, delivering an engaging driving experience while keeping fuel consumption and emissions in check. Yet, as with any advanced machine, the ActiveHybrid 5 has its share of complexities and potential issues.
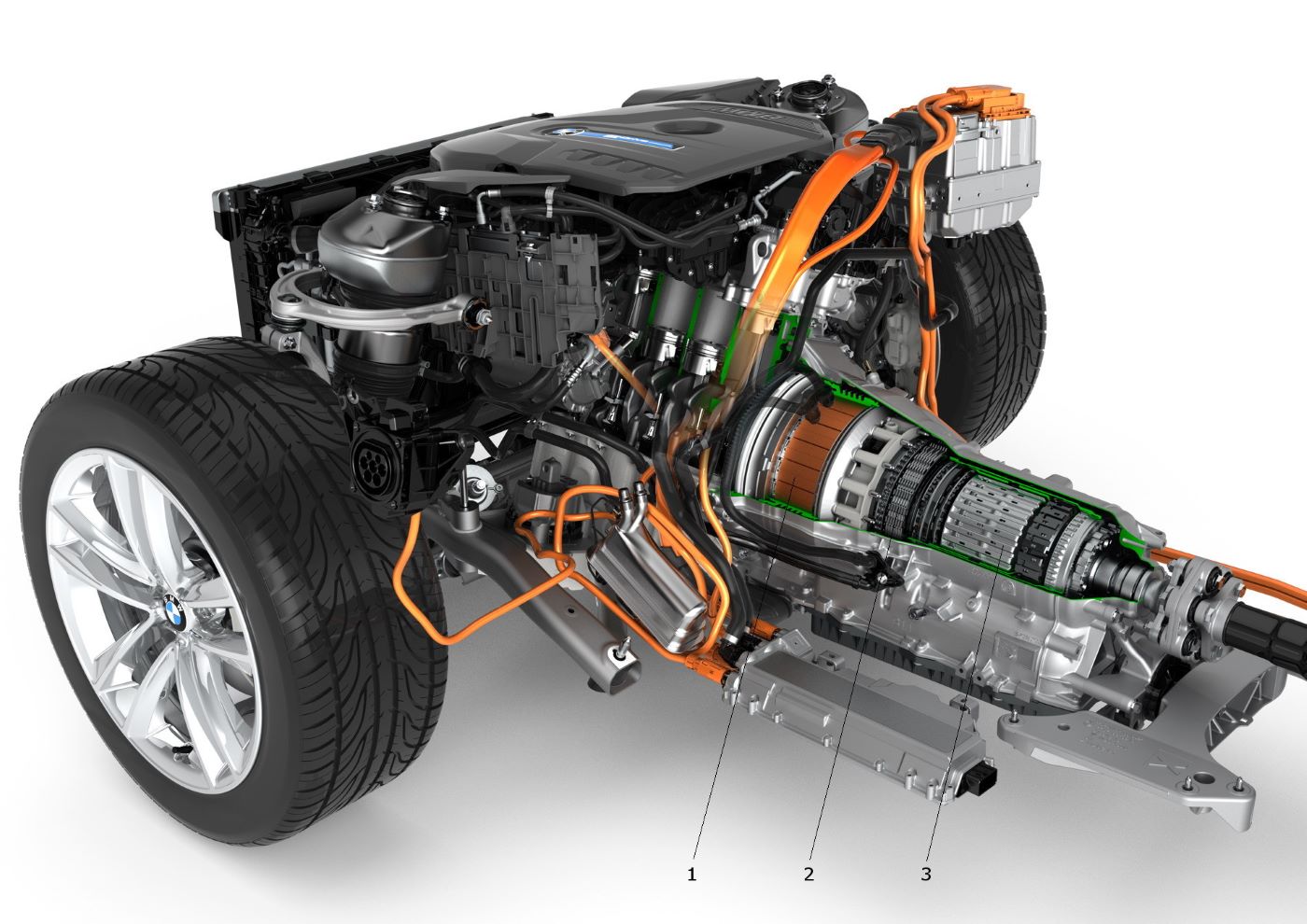

In terms of reliability, the ActiveHybrid 5 receives mixed feedback from owners and experts alike. While BMW’s engineering excellence ensures strong performance, the integration of hybrid technology adds an extra layer of complexity that may give rise to maintenance challenges.
Routine care is critical, and BMW emphasizes following its recommended service schedule to maintain peak performance. This includes regular inspections of the hybrid battery, electric motor, and gasoline engine.
Owners are also encouraged to rely exclusively on genuine BMW components and authorized service centers to preserve reliability and efficiency.
Despite its many strengths, the intricacy of the hybrid system introduces certain challenges that prospective buyers should understand. Being aware of the potential issues associated with the ActiveHybrid 5 is key to making an informed purchasing decision and ensuring long-term satisfaction.
The following sections will explore the most commonly reported problems from owners and industry experts, offering a thorough look at what to expect from this refined yet complex hybrid luxury sedan.
Meanwhile, others like early Ford, Nissan, and BMW hybrids serve as reminders that complexity doesn’t always equal reliability.
For US buyers considering a hybrid in 2025 and beyond, it pays to research the powertrain, not just the model. Stick with proven systems, and you’ll enjoy the quiet efficiency hybrids are known for without the frustration of endless repairs.

