Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) have long been a polarizing technology in the U.S. market.
While they promise smoother acceleration and better fuel efficiency, many drivers associate them with rubber-band-like throttle response, short lifespans, and costly repairs.
Early CVTs especially those in Nissan and Jeep models earned a bad reputation due to overheating, belt slippage, and premature bearing failures.
But not all CVTs are created equal. Some automakers have refined their designs with better materials, stronger belt systems, and smarter software that mitigates stress on components.
For shoppers who want the efficiency of a CVT without the typical reliability trade-offs, here are 10 CVT units that have earned a reputation for lasting performance and dependability in U.S. conditions.
1. Toyota’s Direct Shift-CVT (Dynamic-Shift CVT)
Toyota’s Direct Shift-CVT, introduced on models like the Corolla and C-HR, corrected many of the classic CVT pain points.
It combines a traditional launch gear with a belt-and-pulley setup, allowing it to use mechanical gearing during takeoff when most CVT wear occurs. This hybrid design reduces heat buildup, cuts belt strain, and gives a more natural acceleration feel.
Toyota also uses high-quality fluid and conservative software mapping, making this transmission one of the most durable modern CVTs on the road.
Owners frequently see over 200,000 miles without major issues, as long as fluid changes are done at regular intervals.
When Toyota introduced its Direct Shift-CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) to the market, it wasn’t just presenting another incremental upgrade, it was setting out to redefine how drivers perceive CVT performance, smoothness, and responsiveness.
For years, CVTs have been criticized for their rubber-band sensation, slow response, and uninspiring driving feel. Toyota’s Direct Shift-CVT changes that perception entirely with its innovative launch gear and enhanced shift logic.
In this detailed analysis, we take the Direct Shift-CVT through both real-world and track testing to explore its strengths, limitations, and overall place in today’s automotive landscape.
Before diving into the Direct Shift-CVT, it’s worth understanding how a traditional CVT works. A conventional CVT uses a pair of pulleys connected by a metal belt, allowing for a continuous range of gear ratios.
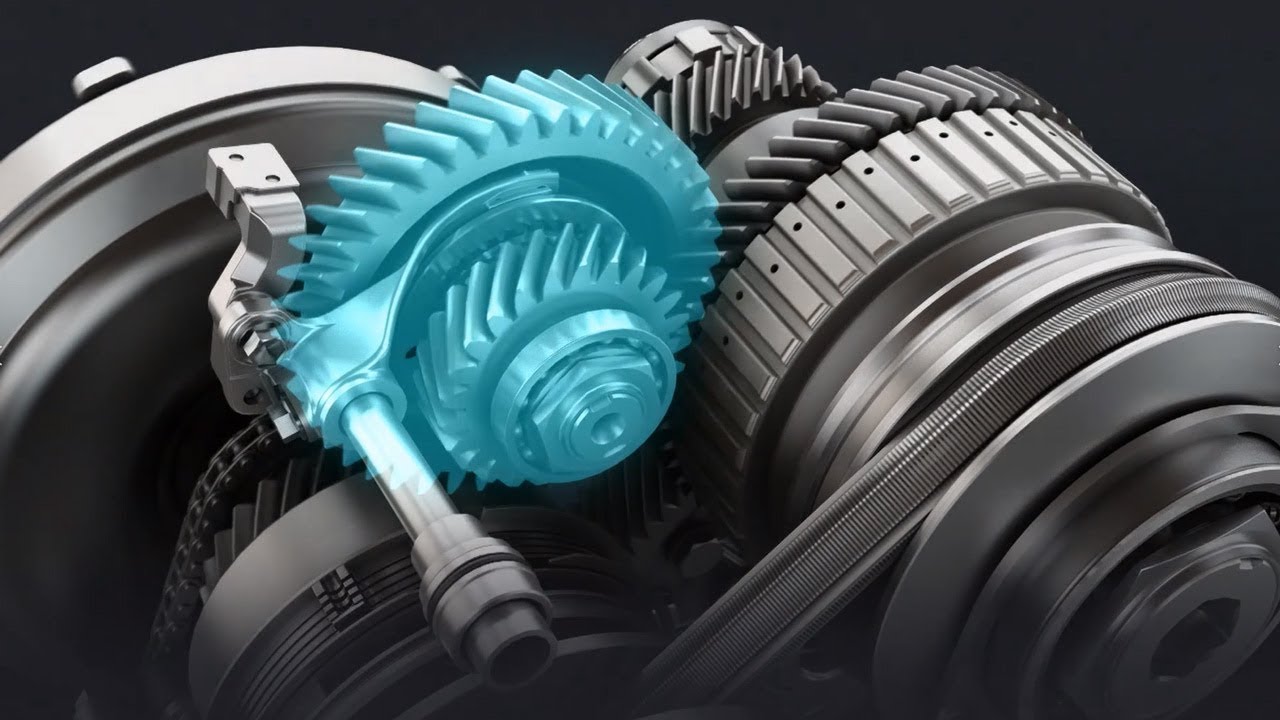
This setup helps the engine stay in its optimal power band, improving efficiency and smoothness. However, traditional CVTs have long struggled with a few common problems, laggy throttle response, sluggish acceleration, droning engine noise at high revs, and a lack of driver engagement. Toyota took these criticisms seriously and responded with a revolutionary idea: the Direct Shift-CVT.
Unlike a conventional CVT, Toyota’s Direct Shift-CVT blends the fuel efficiency of a variable transmission with the snappy response of a gear-driven automatic. The key innovation behind this design is its mechanical launch gear, which engages during initial acceleration from a stop.
This gear helps the car launch more like a traditional automatic transmission, eliminating the lazy takeoff that most CVTs suffer from. Once the vehicle reaches a certain speed, power is seamlessly transferred to the belt-and-pulley CVT system, optimizing fuel economy and maintaining smooth performance.
The result is a transmission that feels much more natural to drive. Compared to standard CVTs that rely solely on the belt system, the Direct Shift-CVT benefits from a fixed first gear that sharpens responsiveness and driver engagement. It also improves fuel efficiency and provides a more refined stepped-shift sensation under load.
To see how well this technology performs in practice, we tested it in two Toyota models—the 2025 Corolla LE and the 2025 C-HR. Both immediately felt more energetic off the line than their CVT-equipped predecessors.
Acceleration from a standstill was noticeably sharper, likely thanks to the mechanical launch gear at work. Under heavier throttle, the system mimics conventional gear changes, giving drivers a more familiar and engaging experience.
In city driving, the Direct Shift-CVT proved exceptionally smooth at low speeds, with no hint of the typical “rubber-band” effect. Acceleration felt linear and natural, while shifts were barely perceptible.
The engine also remained quiet and composed during regular driving, adding to the refined experience. On the highway, the transmission kept engine RPMs low, maximizing fuel economy without compromising performance.
Passing power was available without the need for aggressive downshifts, and there was none of the “gear hunting” feeling often associated with other automatic systems.
Overall, Toyota’s Direct Shift-CVT stands out as a clever evolution of a familiar concept. It addresses nearly every weakness that once defined CVTs, delivering a driving experience that feels responsive, efficient, and far more enjoyable than before.
Also Read: Top 10 Pickups That Rarely Need Engine Swaps
2. Honda’s Earth Dreams CVT (Mid-2010s and Newer)
Honda’s updated CVTs, found in the Civic, Accord, and CR-V, have overcome the teething issues of early generations. The Earth Dreams CVT uses a torque converter (unlike most CVTs) to smooth engagement and reduce the jerky feel that plagued older units.
Honda also engineered stronger steel belts and advanced lubrication systems that minimize internal friction.

The result is a CVT that not only improves fuel economy but also offers strong reliability, especially when used with the brand’s well-tuned 1.5L and 2.0L engines.
Regular maintenance and using Honda’s proprietary HCF-2 fluid are key to their longevity.
3. Subaru Lineartronic CVT
Subaru’s Lineartronic CVT is one of the most proven belt-driven units on the market. Unlike early CVTs that struggled with heat, Subaru integrated robust cooling systems and chain-driven mechanisms on its high-torque versions.
The Lineartronic’s step logic programming even mimics gear changes to avoid the “drone” effect, improving drivability and reducing wear on the pulleys.
It’s found across Subaru’s lineup from the Outback to the Crosstrek and routinely surpasses 150,000–200,000 miles with few complaints.
Subaru’s commitment to fluid maintenance intervals and design simplicity has made this one of the best long-term CVTs available.
The Subaru Lineartronic Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) is more than just another piece of technology, it’s a cornerstone of Subaru’s driving experience.
This unique automatic transmission system delivers a combination of efficiency, adaptability, and refinement that traditional gear-based systems simply can’t replicate.
At its core, the Subaru Lineartronic CVT is designed to deliver the smoothest and most efficient driving experience possible. Unlike conventional transmissions that rely on a series of fixed gears, the Lineartronic CVT uses a steel belt and variable pulleys to create a continuous range of gear ratios.
This design eliminates traditional gear shifting, providing uninterrupted acceleration and a seamless flow of power.
One of the transmission’s standout features is its adaptive control system, which automatically fine-tunes the transmission’s behavior to match driving style and road conditions, ensuring that the engine remains in its ideal power range.
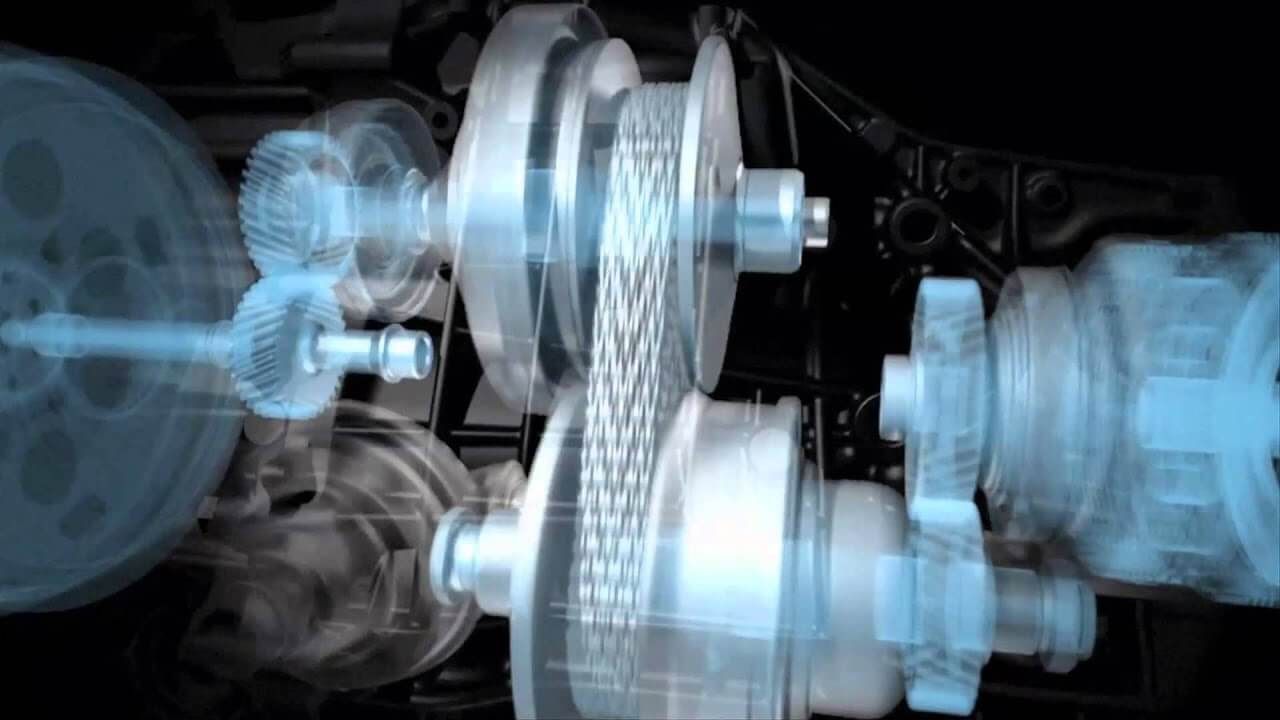
Combined with a reinforced transmission case and torque converter, it minimizes mechanical noise while delivering a quieter, more refined ride.
The result is a responsive and efficient system that works in perfect harmony with Subaru’s signature BOXER engine and Symmetrical All-Wheel Drive, offering a remarkably balanced and composed driving experience.
Subaru’s decision to adopt the Lineartronic CVT was driven by a goal to elevate both performance and fuel economy. Traditional automatic transmissions, while effective, are limited in their ability to balance smoothness with efficiency.
The Lineartronic CVT, by contrast, allows Subaru vehicles to maintain optimal engine speeds for any given situation, maximizing fuel efficiency without sacrificing performance.
Additionally, because the CVT has fewer moving parts, it’s lighter and more mechanically efficient, further contributing to better fuel economy and a smoother overall drive. In essence, Subaru embraced the CVT to deliver a seamless combination of comfort, responsiveness, and efficiency that enhances every journey.
To understand the difference between a Lineartronic CVT and a regular transmission, imagine a ten-speed bicycle. With a conventional transmission, you shift between fixed gears just as you would manually change gears on that bicycle to tackle different slopes or speeds.
Subaru’s Lineartronic CVT, however, changes this concept entirely. Instead of fixed gears, it employs two variable-width pulleys connected by a steel chain, allowing the transmission to adapt continuously to changing driving conditions.
Think of it as a bicycle gear that can automatically and infinitely adjust in real time to provide the perfect level of resistance. This means the engine is always operating at its most efficient point, delivering smooth, uninterrupted power and superior fuel economy compared to traditional systems.
Behind the wheel, driving a Subaru equipped with the Lineartronic CVT feels noticeably different from a traditional automatic. The absence of gear shifts is immediately apparent, there’s no sensation of the car “climbing” through gears or any sudden dips in power.
Instead, acceleration feels linear and fluid, with the transmission seamlessly adapting to your speed and driving inputs.
By keeping the engine in its ideal power band at all times, the CVT ensures steady performance and smooth, quiet operation. The result is a more relaxed and enjoyable driving experience that feels natural and effortless.
Beyond comfort and smoothness, the Lineartronic CVT also has a profound effect on both performance and efficiency.
Because it continuously adjusts to keep the engine at its most effective power range, the transmission provides consistent acceleration without the interruptions that occur during traditional gear changes.
On top of that, its ability to hold the engine at the optimal RPM for fuel savings makes it highly efficient in a variety of driving conditions, whether you’re navigating stop-and-go city traffic or cruising on the highway.
Over time, this translates to lower fuel costs and reduced environmental impact, all while maintaining the engaging drive Subaru vehicles are known for.
4. Toyota Hybrid Synergy Drive CVT (eCVT)
Technically, Toyota’s hybrid CVT isn’t a traditional belt-driven setup but a planetary gear-based electronic CVT (eCVT).
This ingenious system uses electric motors and a power-split device instead of pulleys or chains, eliminating most wear-prone parts.

Found in the Prius, RAV4 Hybrid, and Camry Hybrid, these eCVTs have been known to last well beyond 300,000 miles.
Since they don’t rely on friction belts, they don’t suffer from the same overheating or fluid degradation issues as conventional CVTs. It’s easily one of the most reliable transmissions of any type ever built.
Also Read: 5 SUVs with Reliable Parking Sensors vs 5 with Phantom Beeps
5. Aisin CVTs in Toyota and Lexus Models
When Toyota doesn’t use its in-house CVTs, it often partners with Aisin a company renowned for bulletproof automatic gearboxes.
Aisin’s CVTs, such as the one found in the Lexus UX 200 and select Toyota models in overseas markets, use durable materials and conservative torque limits to extend lifespan.

They’re less stressed than the high-torque CVTs used by competitors and rarely fail prematurely.
The Japanese engineering philosophy behind Aisin prioritizes longevity over aggressive efficiency, which results in fewer heat-related breakdowns and belt slippages.
Aisin’s transmission technology has long been a cornerstone of the automotive industry, powering vehicles across a wide range of brands with precision, reliability, and innovation. The company produces a diverse lineup of transmission systems tailored to different driving needs and vehicle types.
When it comes to performance and reliability, Aisin transmissions have earned an industry-wide reputation for excellence. Their hallmark is smooth, consistent shifting that provides an enjoyable and refined driving experience.
Built with meticulous engineering and high-quality materials, Aisin transmissions are designed to withstand the test of time, offering impressive longevity and minimal maintenance requirements. Many units are known to perform flawlessly even after hundreds of thousands of miles, underscoring Aisin’s commitment to precision manufacturing and reliability.
A number of automakers trust Aisin’s expertise for their transmission systems, integrating them into some of the most popular and respected vehicle models on the road.
Toyota, for instance, equips many of its cars, including the Camry, Corolla, and RAV4, with Aisin transmissions to ensure dependable performance and efficiency. Lexus, Toyota’s luxury division, also relies on Aisin technology in models like the ES and IS for their trademark smoothness and quiet operation.
Mazda incorporates Aisin transmissions in models such as the Mazda3 and Mazda6, contributing to the brand’s sporty yet refined driving character. Even Subaru, recognized for its all-wheel-drive capability and durability, utilizes Aisin units in select vehicles to complement its performance-oriented design philosophy.
In conclusion, Aisin transmissions have set the benchmark for quality and dependability within the global automotive landscape.
Their blend of smooth shifting, long-lasting durability, and superior fuel efficiency makes them a preferred choice for both manufacturers and drivers alike. Whether your priority is comfort, performance, or longevity, an Aisin transmission delivers a balanced and rewarding driving experience that stands the test of time.
Also Read: 10 Manual Transmissions That Feel New Past 250,000 Miles
6. Jatco CVT8 (as Tuned for Mitsubishi and Nissan Sentra SR)
While Jatco’s reputation has been marred by some infamous early failures, the CVT8 generation marked a big leap forward especially in applications with lighter vehicles.
Mitsubishi’s Outlander and Nissan’s later Sentra SR trims benefit from software tuning that keeps torque loads within safe ranges, reducing stress on the belt and bearings.
The CVT8 also features an improved oil pump and cooling circuit. Owners who service them with NS-3 fluid and avoid excessive towing or high-heat conditions have reported solid reliability well past 150,000 miles.
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) have long been a divisive topic among driving enthusiasts. They’re often criticized for their lack of engagement, as their main contribution to driver feedback tends to be the steady drone of the engine under hard acceleration.
Still, despite the lukewarm reception from enthusiasts, CVTs continue to gain ground against manual and traditional automatic transmissions. Toyota, for instance, made a bold move by equipping three-quarters of its 2014 Corolla lineup with a belt-and-pulley CVT as standard.
Even when overtaking, the CVT delivers added thrust without the telltale jolt of a gear change, maintaining a calm, consistent flow of power.
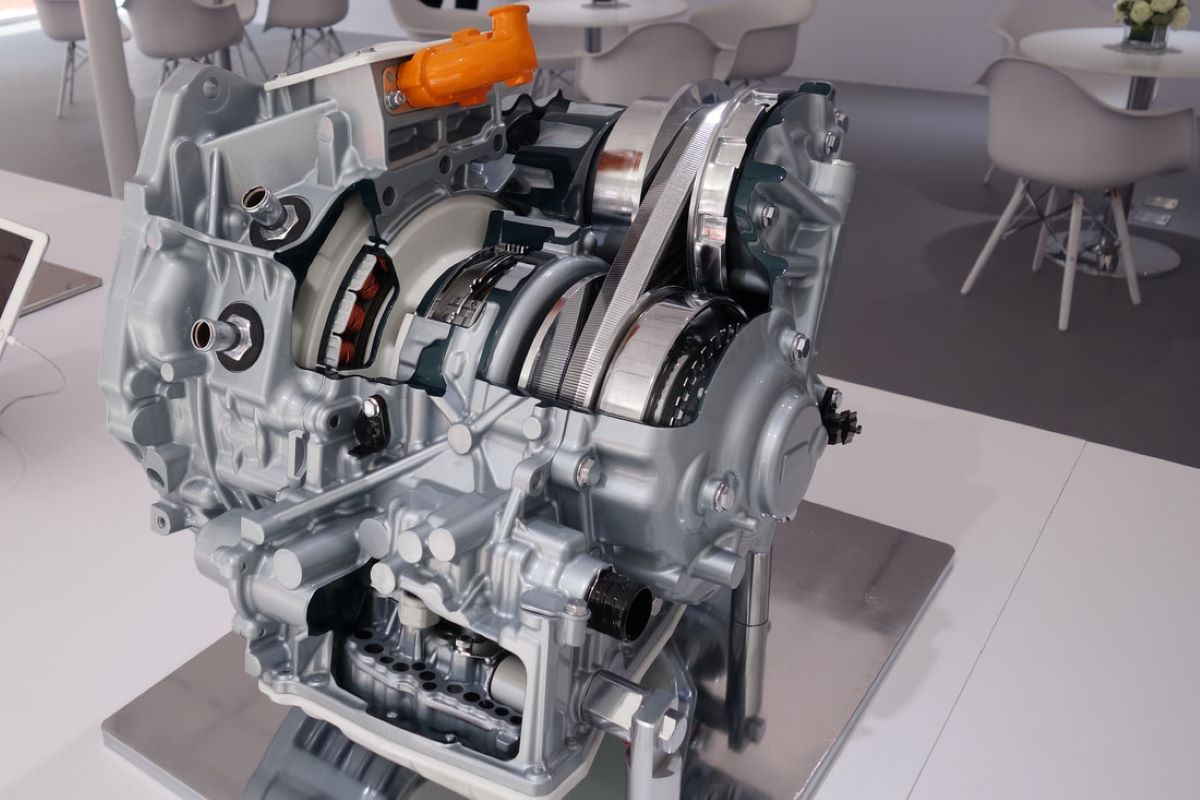
Several automakers have developed their own CVT technology, including Audi, Honda, Hyundai, Subaru, and Toyota. Meanwhile, Nissan, through its majority ownership of transmission manufacturer JATCO,has become a global leader in CVT production.
JATCO supplies nearly half of the world’s gearless transmissions, serving automakers such as Chrysler, GM, Mitsubishi, and Suzuki. In fact, nearly half of Nissan’s U.S. lineup now uses JATCO-built CVTs, demonstrating the company’s deep commitment to the technology.
Manufacturers’ growing interest in CVTs stems largely from their advances in efficiency. Nissan reported a 40 percent reduction in internal friction with its two eighth-generation JATCO transmissions featured in the 2013 Altima.
These improvements contributed to a 10-to-15 percent boost in overall fuel economy—no small feat in today’s efficiency-driven market.
Toyota has also made notable strides with its “intelligent shifting” CVT design. To reduce parasitic losses, the automaker engineered an innovative engine-driven oil pump featuring two discharge ports.
The low-pressure outlet manages lubrication, while the variable high-pressure port provides the hydraulic force required to grip the steel belt tightly between the pulleys. This clever configuration prevents slippage and reduces power loss, improving both reliability and efficiency.
To make the driving experience more engaging, Toyota equipped the Corolla S’s CVT with a sport mode, paddle shifters, and seven simulated “gears.”
These artificial steps help mitigate two of the CVT’s most common complaints: the “rubber-band” sensation, where the engine revs climb before the car’s speed catches up, and the perceived lack of driver involvement.
The result is a transmission that strikes a more satisfying balance between efficiency and enjoyment, signaling how far CVT technology has evolved.
7. Subaru High-Torque Lineartronic (Used in the Ascent and Outback XT)
Subaru developed a heavier-duty version of its CVT to handle turbocharged engines like the 2.4L found in the Ascent and Outback XT.
Instead of a steel belt, it uses a robust chain mechanism capable of managing over 350 lb-ft of torque.
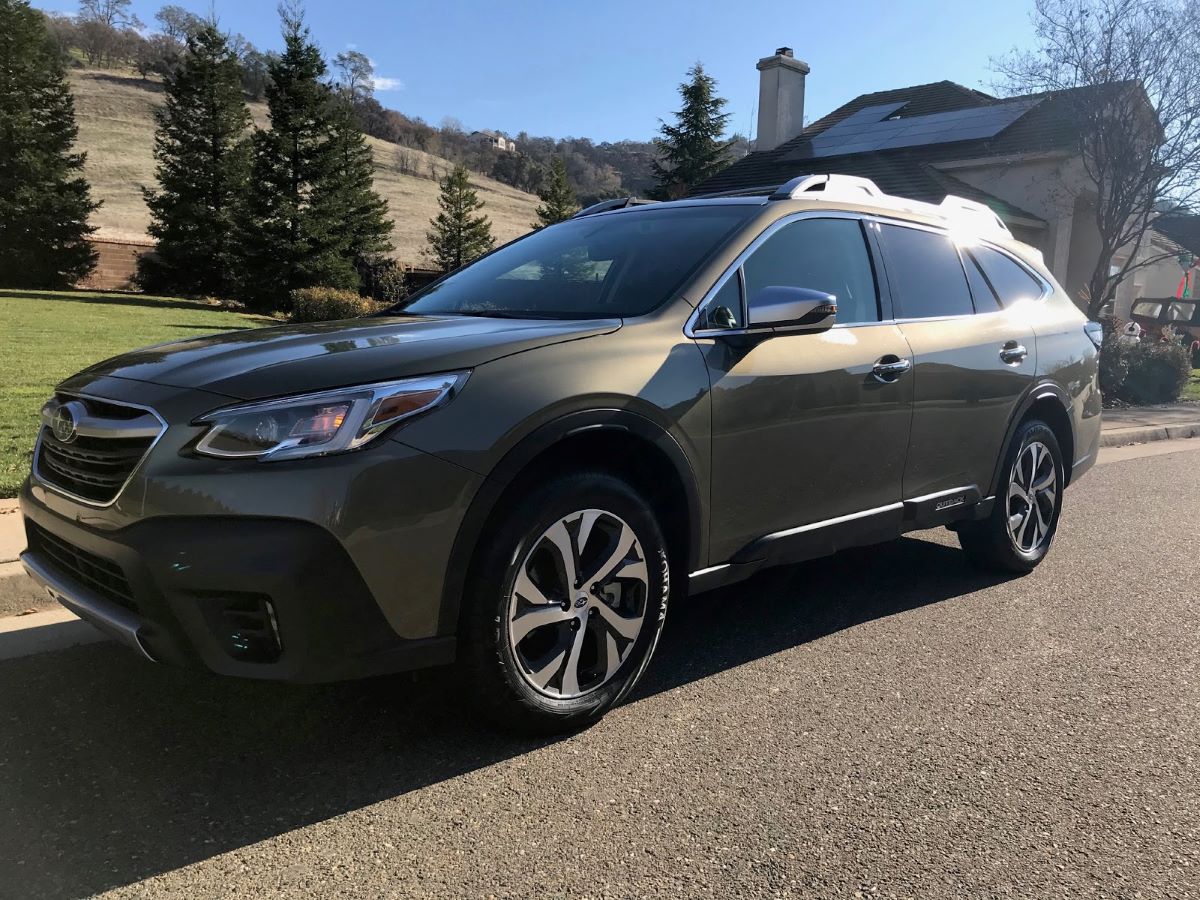

Combined with enhanced transmission cooling and smart shift mapping, the high-torque Lineartronic has proven remarkably resilient even under demanding towing conditions.
This setup offers an excellent balance of efficiency, smoothness, and strength that’s unusual for a CVT-equipped SUV.
8. Honda HR-V and Insight CVTs (with Low-Torque Engines)
In applications where torque demands are modest, Honda’s CVTs shine brightest. The Insight and HR-V, both powered by smaller engines, put minimal strain on the transmission and Honda’s software keeps revs in efficient, low-wear ranges.

Because of these mild demands, these CVTs rarely suffer from belt stretch or pulley wear. Many owners have documented over 180,000 miles with nothing more than routine fluid changes.
It’s a case where pairing the right engine with the right CVT tuning makes all the difference in long-term reliability.
9. Nissan Kicks and Versa CVTs (Improved Jatco CVT7)
While Nissan’s larger vehicles suffered from notorious CVT breakdowns, its smaller cars benefited from lighter-duty designs that didn’t push the limits of the hardware.
The Jatco CVT7 used in the Nissan Kicks and Versa has proven far more reliable than its predecessors thanks to improved belt design, better oil flow, and reduced internal friction.
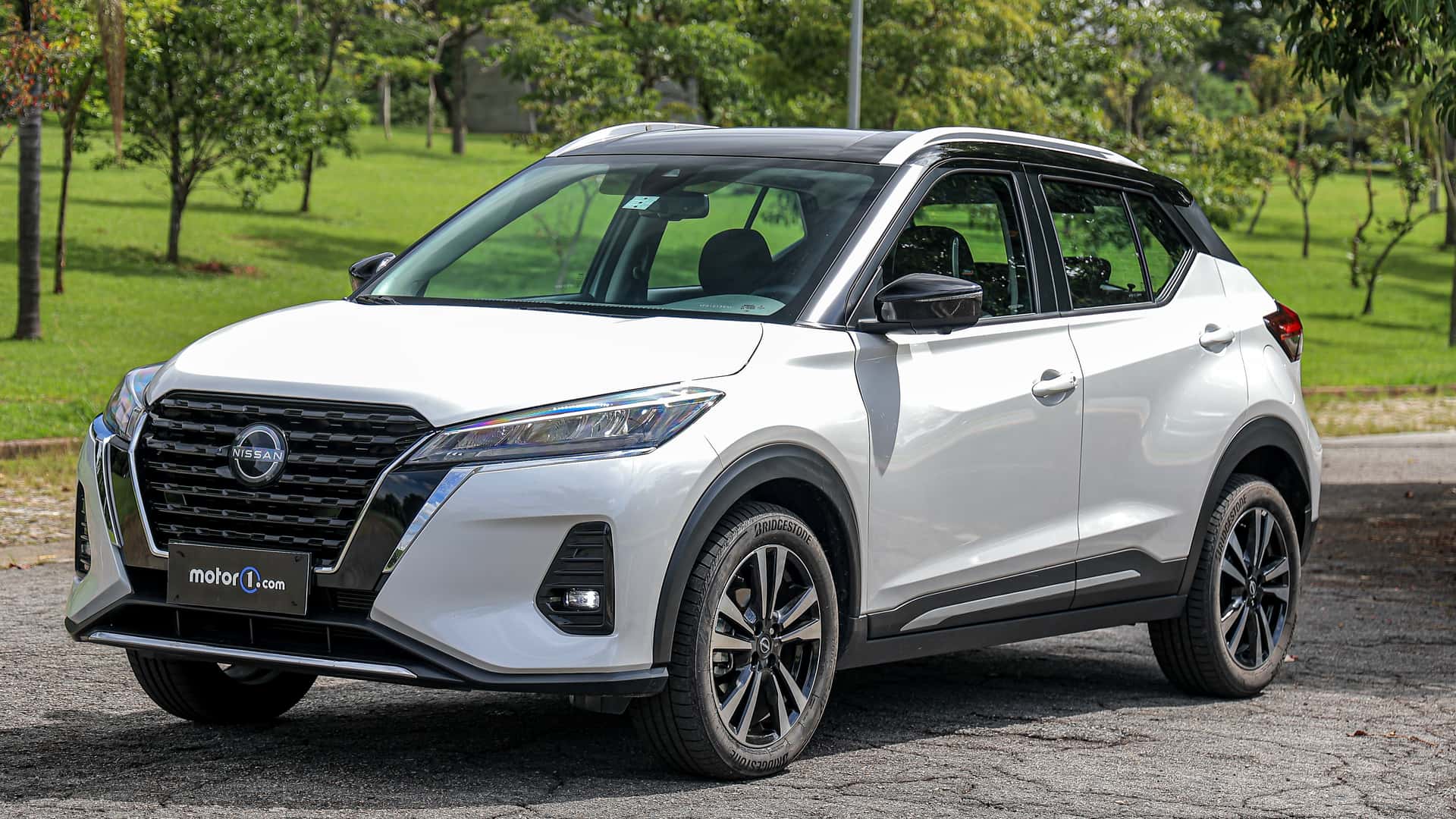

Because the Kicks and Versa don’t produce excessive torque, the CVT rarely overheats or slips. These newer compact Nissans show that when the technology is right-sized, even Jatco’s CVTs can earn solid reliability marks.
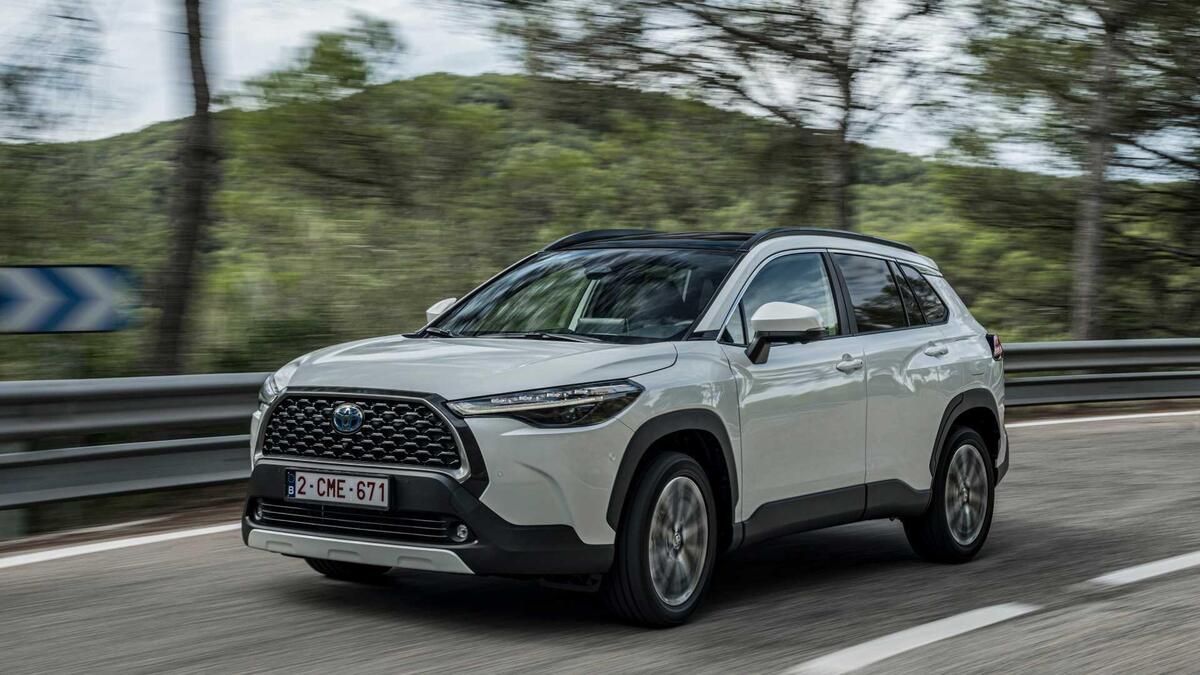
10. Toyota Corolla Cross CVT (2022-Present)
The Corolla Cross uses Toyota’s latest generation Direct Shift-CVT with refined cooling channels, an updated launch gear, and improved pulley metallurgy.
It’s specifically calibrated for North American driving habits, prioritizing smoothness under urban stop-and-go conditions and durability in highway cruising.
The transmission is also paired with Toyota’s rigorous testing standards, including extreme-heat endurance runs in Arizona and Nevada.
It’s not uncommon for early owners to rack up high mileage without any transmission issues an increasingly rare achievement among compact SUVs with CVTs.

Not all CVTs deserve the bad rap they get. Over the past decade, the technology has evolved dramatically, with better materials, smarter programming, and hybridized designs that sidestep earlier weaknesses.
Toyota and Subaru lead the reliability pack, with Honda close behind. Nissan and Mitsubishi have improved substantially with newer Jatco designs, though long-term results still depend on maintenance and driving habits.
For U.S. drivers who rack up mileage in all climates from humid Southeast summers to the freezing Midwest these 10 CVTs represent the systems most likely to endure.
The key takeaway? A well-engineered CVT with good fluid and smart programming can last as long as any traditional automatic, provided it’s treated with the same care.

