Diesel engines have long been celebrated for their durability, efficiency, and ability to endure decades of demanding use. Among the countless diesel designs produced worldwide, a select few stand out for their exceptional longevity and minimal maintenance requirements.
These engines combine robust mechanical construction, conservative tuning, and straightforward engineering to achieve extraordinary mileage without major overhauls. From passenger cars to light-duty trucks, heavy-duty pickups, and commercial haulers, these powerplants have proven themselves in real-world applications, often surpassing 300,000, 500,000, and even one million miles when properly maintained.
This article highlights eight diesel engines that have earned legendary reputations for reliability. From the Mercedes-Benz OM617 and Cummins B-Series to the Caterpillar 3406E, each of these engines demonstrates how thoughtful engineering, heavy-duty materials, and mechanical simplicity can create a “bulletproof” diesel capable of outlasting the vehicles they power.
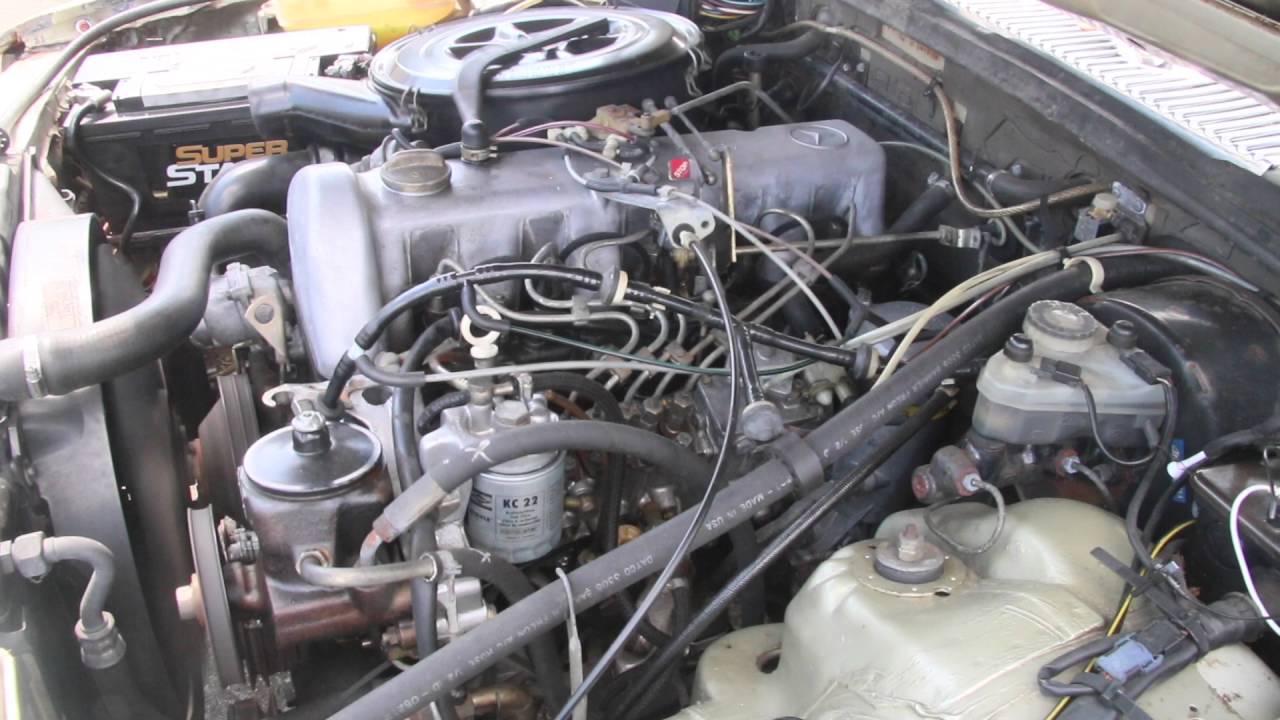
1. Mercedes-Benz OM617 3.0L Inline-5: The Legendary Bulletproof Diesel
The Mercedes-Benz OM617 3.0-liter inline-five diesel engine is widely regarded as one of the most reliable passenger vehicle engines ever built. Produced from 1974 to 1991, it powered iconic models such as the W123 300D and W116 300SD.
Its reputation for longevity stems from robust engineering, mechanical simplicity, and conservative performance tuning, allowing many examples to surpass 500,000 miles, with some taxis reportedly reaching over one million miles without major overhauls.
Built with a heavy-duty cast-iron block and cylinder head, the OM617 provides exceptional thermal stability and resistance to warping. Forged steel crankshafts and connecting rods, combined with a duplex timing chain, ensure long-lasting durability.
A high-capacity oil system and a gear-driven oil pump further improve lubrication reliability, while the entirely mechanical Bosch inline injection system eliminates failure-prone electronics, making the engine simple to maintain and service.
Even turbocharged variants, known as OM617A, were conservatively tuned to around 121–125 horsepower, emphasizing longevity over speed. Low RPM operation, indirect pre-chamber fuel injection, and minimal internal stress help the engine endure heavy use over decades.
Regular maintenance, including valve adjustments, coolant replacement, and monitoring glow plugs and vacuum lines, ensures the engine continues to perform reliably. Overheating is the main risk, particularly in turbo models, but proper care mitigates most issues.
Although the OM617 is slow by modern standards, it delivers steady torque at low speeds and impressive fuel efficiency, often reaching 25–30 miles per gallon. Its mechanical simplicity also allows it to run on alternative fuels such as biodiesel or waste vegetable oil.
Today, the OM617 remains a favorite among enthusiasts, off-roaders, and anyone seeking a diesel engine that can outlast the chassis it powers. Its combination of over-engineered components, reliability, and timeless design has earned it the nickname “bulletproof” and a legendary place in automotive history.
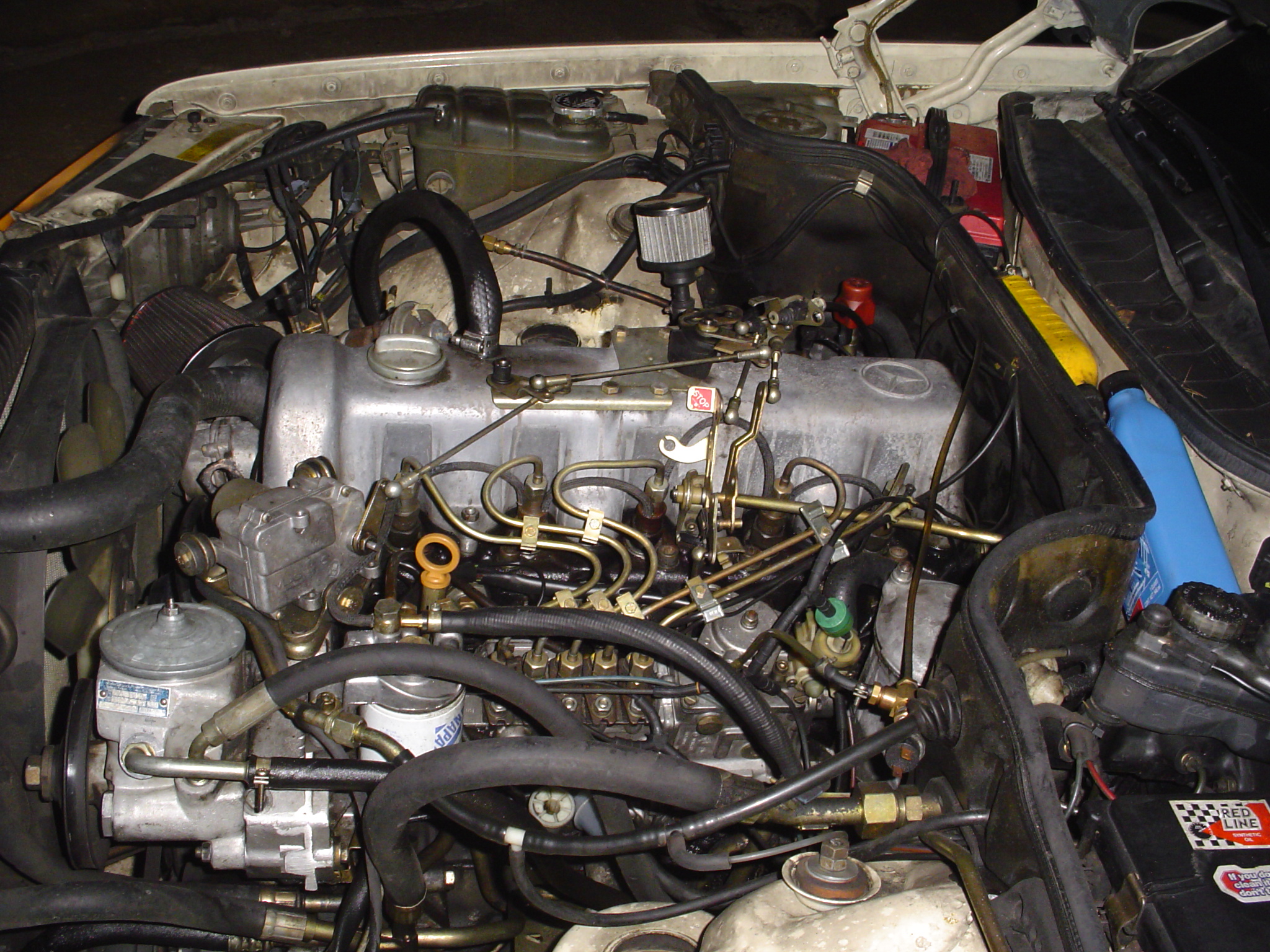

2. Cummins 5.9L B-Series: The Legendary Diesel for Longevity
The Cummins 5.9L B-Series diesel engine, produced from 1989 to 2007, is renowned for its exceptional durability and “bulletproof” reputation. Powering Dodge Ram trucks, it earned legendary status among enthusiasts for its ability to exceed 400,000 miles, with many examples surpassing one million miles when properly maintained.
Its longevity is rooted in overbuilt components, mechanical simplicity, and conservative factory tuning, reflecting the engine’s industrial origins.
Early 12-valve models (1989–1998) are particularly revered due to their mechanical P7100 injection pump, which requires no electronics, minimizing potential failure points.
These engines feature a cast-iron block and head, forged steel crankshaft and connecting rods, and a gear-driven system, providing extreme resistance to thermal stress, high cylinder pressures, and catastrophic failure. Inline-six design contributes to fewer moving parts, excellent oil circulation, and balanced stress distribution.
The later 24-valve engines (1998.5–2007) introduced four valves per cylinder and electronic controls for improved airflow and efficiency.
While they incorporated the VP44 or common-rail injection systems, which added potential electronic vulnerabilities, their internal architecture remained robust, and proper maintenance ensured comparable longevity. Both 12- and 24-valve variants deliver high torque at low RPM, reducing wear on bearings, pistons, and rings. Direct injection enhances combustion efficiency while maintaining low stress on components.
Performance-wise, the 12-valve engines produced 160–215 horsepower and 400–440 lb-ft of torque, while 24-valve versions ranged from 215–325 horsepower and 420–610 lb-ft of torque depending on configuration.
Conservative tuning and low-stress operation ensure that these engines remain durable under decades of service. Pre-emission designs also avoided complex systems like EGR and DPF, reducing maintenance headaches.
The Cummins 5.9L B-Series is simple to service, highly tunable, and built to outlast the trucks it powers. Early 12-valve engines are celebrated as “million-mile” engines due to mechanical reliability, while later 24-valve common-rail engines offer a modern balance of power and durability.
For enthusiasts and heavy-duty users alike, the 5.9L remains a benchmark for long-lasting diesel engineering, demonstrating that thoughtful design and over-engineering can produce a drivetrain capable of decades of dependable performance.
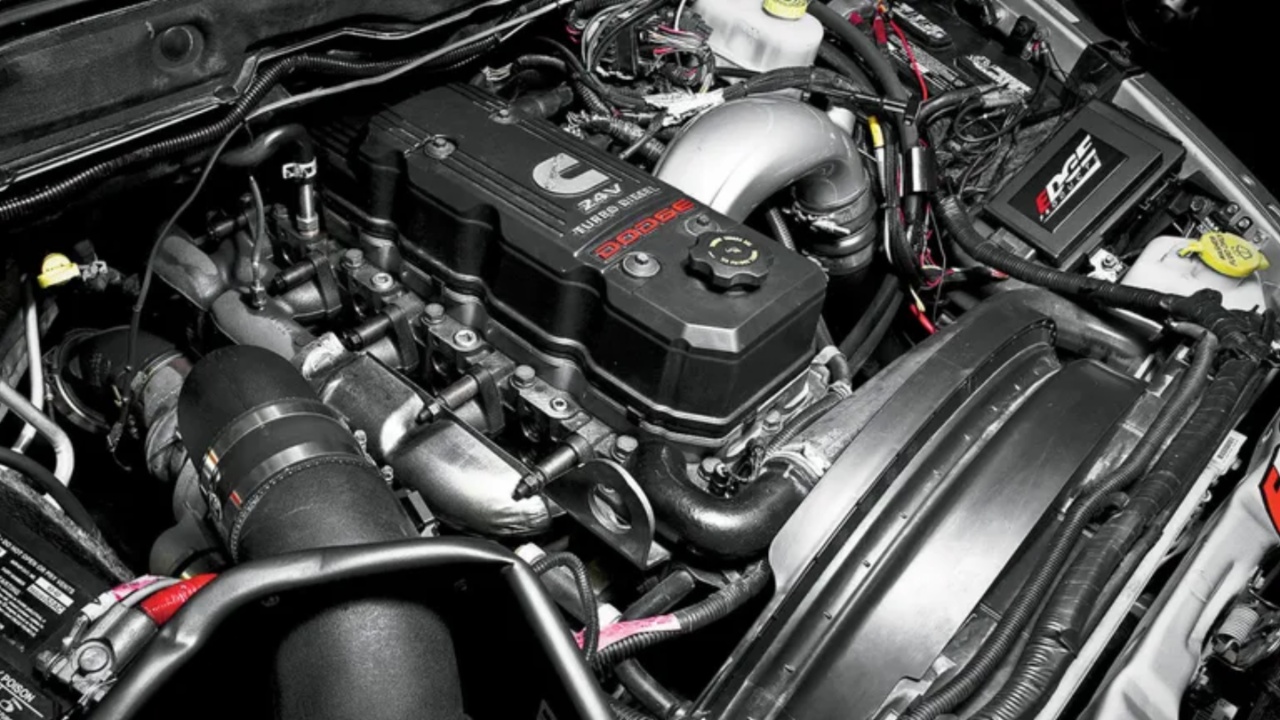

3. Ford 7.3L Power Stroke V8: The Benchmark for Diesel Reliability
Produced by Navistar International for Ford from 1994.5 to 2003, the 7.3L Power Stroke V8 is widely regarded as one of the most reliable and durable diesel engines ever built for light-duty trucks.
Its longevity, often exceeding 300,000 to 500,000 miles and sometimes reaching 1 million miles with proper care, stems from heavy-duty engineering, conservative factory tuning, and a lack of complex emissions systems. Early models avoided modern EPA-driven components like Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) or Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF), which often reduce engine lifespan.
The engine’s robust construction plays a major role in its durability. It features a cast-iron block and cylinder heads for exceptional heat and pressure resistance, along with forged-steel connecting rods on early models (pre-2001). Six head bolts per cylinder, similar to medium-duty commercial engines, prevent head gasket failures under heavy loads.
The 7.3L also uses a fixed-geometry Garrett turbocharger known for longevity, and a large, externally-mounted oil cooler to maintain stable oil temperatures even during prolonged towing or high-stress operation.
Power delivery is conservative by modern standards, ranging from 210 hp and 425 lb-ft to 275 hp and 525 lb-ft, allowing internal components to operate well below their maximum stress levels.
The Hydraulic Electronic Unit Injector (HEUI) system, which uses engine oil to pressurize fuel injectors up to 21,000 psi, is highly reliable when oil is maintained properly. Simple design, limited electronics, and straightforward mechanical systems make the 7.3L easy to service, even for DIY mechanics, and reduce potential points of failure.
While considered “bulletproof,” proper maintenance is critical for longevity. Common minor issues include camshaft position sensor failures, injector O-ring leaks, and turbocharger up-pipe oil leaks, all of which are generally easy to repair.
Pre-2003 models, especially 1999–2003, are often regarded as the best years for reliability, offering refinements while maintaining simplicity. Older 1994.5–1997 models, particularly in Old Body Style trucks, are also highly reliable and popular among enthusiasts due to their mechanical simplicity.
Limitations of the 7.3L include lower horsepower and torque compared to modern Power Stroke diesels, increased noise and vibration, and aging components due to the engine’s age. Nevertheless, its exceptional durability, ease of maintenance, and dependable low-end torque make it ideal for towing, work, and long-term ownership.
For buyers seeking a diesel engine that prioritizes longevity and low maintenance over modern performance and complexity, the Ford 7.3L Power Stroke V8 remains a benchmark for reliability in light-duty trucks.
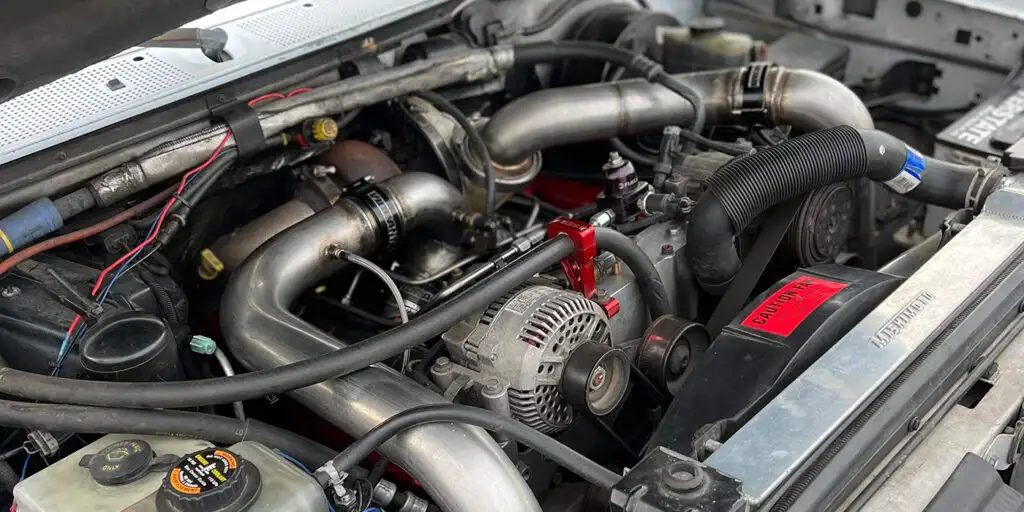

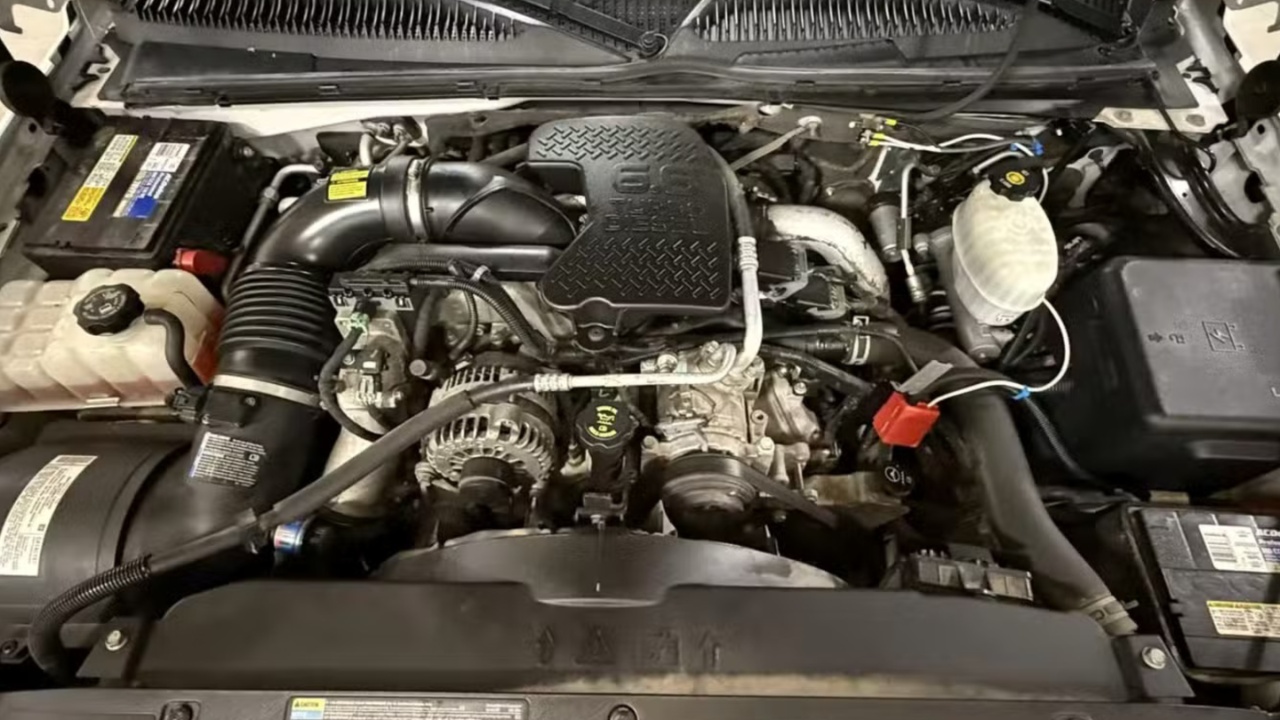
4. Isuzu/GM 6.6L Duramax V8: Pre-Emissions Diesel Power with Proven Durability
The 6.6L Duramax V8, a collaboration between Isuzu and General Motors, launched in 2001 and quickly became a benchmark for reliable diesel performance in light- and heavy-duty trucks. The LB7 generation, produced from 2001 to 2004, introduced high-pressure common-rail fuel injection for GM trucks, offering 300 horsepower and 520 lb-ft of torque.
The LBZ, produced from 2006 to 2007, strengthened the engine block, improved connecting rods, resolved the LB7 injector issues, and increased output to 360 horsepower and 650 lb-ft of torque. With proper maintenance, both engines are known to exceed 300,000 to 500,000 miles.
Durability is built into the core design. Both the LB7 and LBZ feature cast-iron blocks, forged steel crankshafts, and robust connecting rods. The LB7 includes induction-hardened cylinder bores for wear resistance, while the LBZ adds thicker block webbing and reinforced rods, making it the most desirable pre-emissions Duramax.
Aluminum cylinder heads reduce weight, and advanced cooling systems maintain optimal temperatures. These engines were designed before Diesel Particulate Filters and Diesel Exhaust Fluid systems were implemented, which helps reduce heat stress and avoids excessive backpressure that can damage head gaskets and seals.
Fuel is delivered through Bosch high-pressure common-rail injection. The LB7 is known for injector failures that can contaminate engine oil, while the LBZ uses upgraded injectors to solve this problem.
Early models benefit from proper fuel filtration to maintain consistent fuel pressure. Both engines are paired with Allison 1000 automatic transmissions. The LB7 uses a 5-speed version, while the LBZ uses a 6-speed unit. These transmissions reduce engine stress at highway speeds and provide smooth, reliable power delivery.
Maintenance is essential for long life. Regular oil changes, cooling system flushes, and attention to water pumps with plastic impellers help prevent failures. Minor issues such as fuel filter housing leaks or weak tie rods can occur, but are relatively easy to repair. With proper care, these engines deliver strong low-RPM torque, excellent towing capability, and consistent highway performance.
The LB7 is valued for its pioneering durability but requires diligence with injectors and head gaskets. The LBZ is widely regarded as the best pre-emissions Duramax, combining stronger internals, no emissions systems that increase stress, and reliable performance.
These engines represent a balance of mechanical strength, simplicity, and longevity. For those seeking a powerful, dependable diesel engine without the complications of modern emissions technology, the LB7 and LBZ Duramax V8 remain excellent choices.

Also read: 5 Engines With Cheap Coil Packs vs 5 With Pricey Ignition Parts
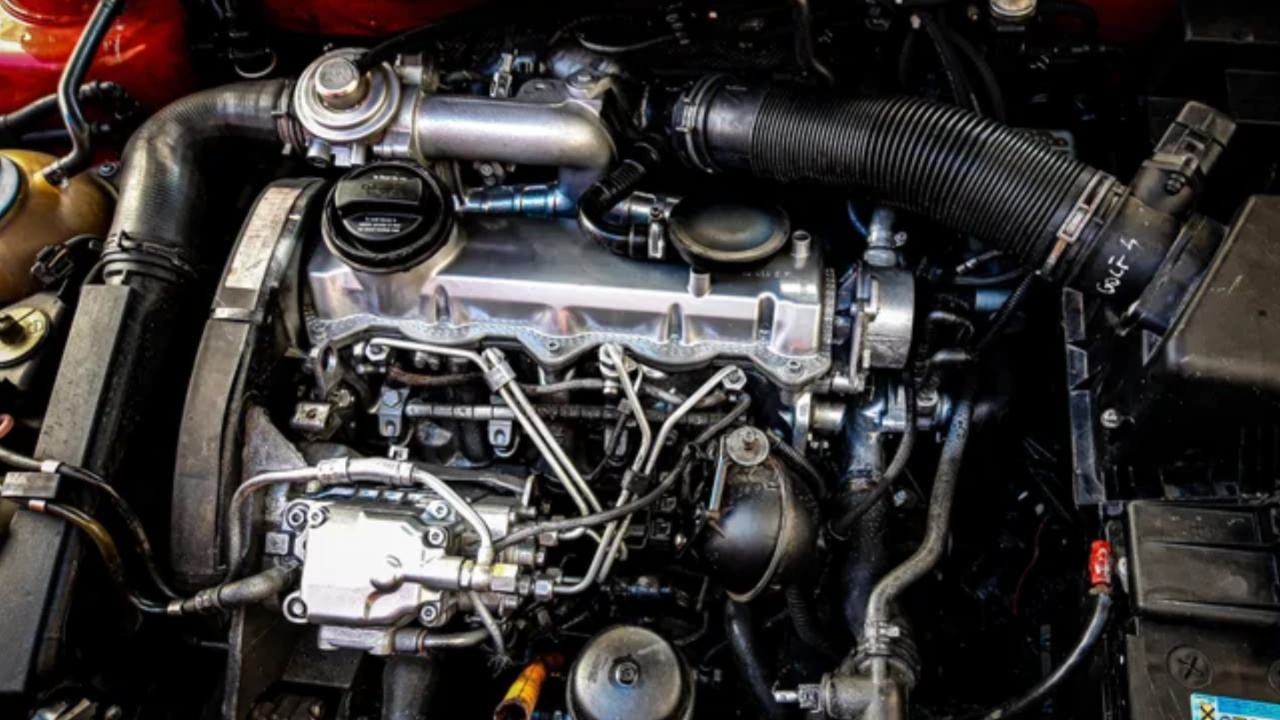
5. Volkswagen 1.9L TDI ALH: High-Mileage Efficiency and Reliability
The Volkswagen 1.9L TDI ALH, produced from 1998 to 2003, is widely regarded as one of the most reliable small-displacement diesel engines ever made. Found in models such as the Golf, Jetta, and Beetle, it combines mechanical simplicity, exceptional fuel efficiency, and robust construction, allowing many examples to reach 300,000 to 500,000 miles with basic maintenance.
Its popularity among enthusiasts stems from a balance of durability, ease of repair, and the ability to achieve 40–50 MPG under normal driving conditions.
Longevity begins with its engineered strength. The ALH features a cast-iron block, forged crankshaft, and connecting rods built to withstand high compression and thermal stress. Its simple eight-valve SOHC layout reduces the number of moving parts, limiting potential failure points.
The VE rotary fuel injection pump is mechanically reliable and less sensitive to fuel quality than later “pumpe-düse” or common-rail systems, ensuring consistent operation over hundreds of thousands of miles.
The engine operates efficiently at low RPMs, further reducing wear on internal components. A straightforward Garrett VNT-15 turbocharger delivers sufficient boost without the complexity of variable-geometry modern units.
Regular maintenance, particularly high-quality oil changes and timing belt replacements every 70,000 to 100,000 miles, is crucial for preventing catastrophic engine damage in this interference engine. Cleaning the intake manifold to remove carbon buildup and monitoring the turbo actuator are common but manageable tasks.
Performance is modest but practical. With 90 horsepower and 155 lb-ft of torque, the ALH is not a high-speed engine but provides strong low-end torque suitable for commuting, light towing, and daily driving. Manual transmissions pair best with this engine, as automatic units from the era are less durable. The engine is also compatible with minor biodiesel blends, adding versatility for eco-conscious owners.
For enthusiasts, tuning options include upgraded fuel nozzles, Stage 2 software remaps, and stronger clutches for improved drivability. Its accessibility and simplicity make it ideal for DIY maintenance, allowing the engine to remain reliable for decades.
The Volkswagen 1.9L TDI ALH represents a perfect combination of efficiency, simplicity, and mechanical durability. Its proven track record for reaching high mileage, low operating costs, and strong fuel economy makes it a favorite among daily drivers, commuters, and tuners seeking a dependable, long-lasting diesel engine.

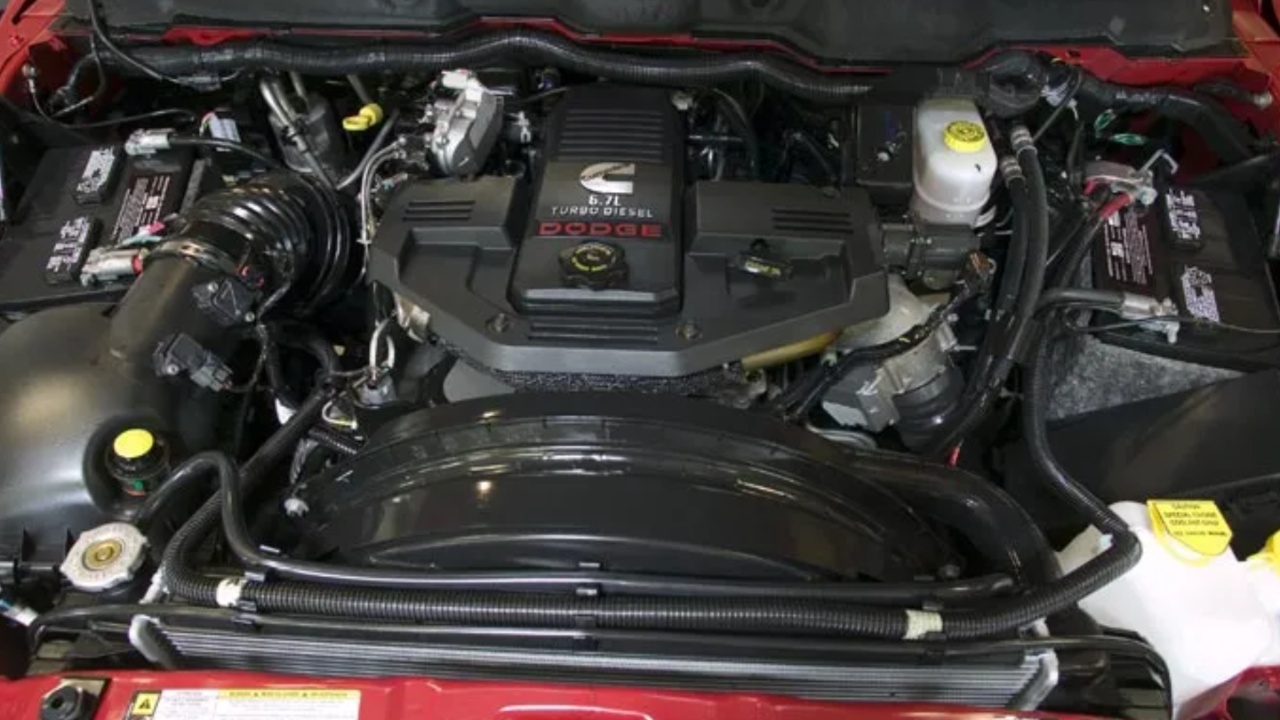
6. Cummins 6.7L Turbo Diesel: Commercial-Grade Durability in Heavy-Duty Trucks
The Cummins 6.7L Turbo Diesel, introduced in 2007 as the successor to the legendary 5.9L, is widely regarded for its commercial-grade durability and long-haul reliability.
Designed to meet stricter emissions standards while retaining the robust foundation of its predecessor, the 6.7L combines a deep-skirted cast-iron block, forged steel crankshaft, and high-strength internals to handle extreme torque and heavy-duty use. Many engines exceed 300,000 to 500,000 miles, and in commercial hauling, reaching over 500,000 miles is common with proper maintenance.
Its longevity begins with a solid mechanical design. The inline-six configuration provides inherent balance, reducing vibration and long-term fatigue on the crankshaft and engine block. Maximum torque is achieved at low RPMs, minimizing stress and wear on pistons, bearings, and rings.
The engine’s gear-driven systems, high-capacity oil pumps, and robust cooling setup are engineered for severe-duty cycles such as towing, hauling, and long-distance operation. Over-engineered components and high-strength materials ensure the engine can endure repeated heavy loads without premature failure.
Advanced fuel and turbo systems are integrated for efficiency without sacrificing reliability. The Bosch high-pressure common-rail fuel system and variable geometry turbocharger provide precise fuel delivery and consistent boost while reducing thermal and mechanical stress under load.
Despite these upgrades, the 6.7L remains easier to service than many V8 competitors due to its inline-six layout and relatively straightforward architecture.
While mechanically strong, the 6.7L relies on strict maintenance for long-term durability. Oil changes, fuel filter replacements, and proper care of emissions components, such as EGR valves and DPF systems, are critical. Common issues to monitor include EGR valve clogging, VGT turbo actuator failures, and, in 2019+ models, hydraulic lifter problems often linked to incorrect oil viscosity.
Power and performance vary by output level, with high-output variants producing up to 1,075 lb-ft of torque, making the 6.7L a favorite for towing and commercial applications. Compared to competitors like Ford Power Stroke and GM Duramax, the 6.7L stands out for its slower-revving, low-stress nature and rebuildable design.
The Cummins 6.7L Turbo Diesel delivers commercial-grade reliability in a heavy-duty pickup truck. With proper maintenance and attention to emissions-related components, it remains one of the most durable diesel engines available for modern trucks.

7. Toyota 1HZ 4.2L Inline-6: The Bulletproof Diesel Workhorse
The Toyota 1HZ 4.2L Inline-6 is a naturally aspirated diesel engine renowned for its legendary reliability and ability to operate in extreme conditions. Introduced in 1990, it is widely used in Toyota Land Cruiser 70 and 100 series models, as well as Coaster buses, particularly in regions like Africa and Australia.
The 1HZ prioritizes durability over speed, featuring a mechanical fuel injection system, a single overhead cam design, and no turbocharger or complex electronics. Its simplicity allows it to withstand harsh environments, poor-quality diesel, and minimal maintenance, often surpassing 500,000 to 700,000 kilometers (over 300,000–400,000 miles) without major service.
One of the key strengths of the 1HZ is its robust mechanical construction. The engine block and cylinder head are made of thick cast iron, providing excellent heat dissipation and resistance to cracking. Internally, it uses a forged steel crankshaft supported by seven main bearings, ensuring rigidity and long-term durability.
The engine produces a modest 129 horsepower and 285 Nm of torque, resulting in low stress on internal components and contributing to its exceptional lifespan.
The 1HZ employs indirect injection with a swirl-chamber design, allowing it to run reliably on low-cetane, low-quality diesel fuel. Its high compression ratio of 22.4:1 ensures strong ignition and reliable cold starts.
Timing is controlled by a gear-driven system, avoiding potential failures associated with chains or belts, although early belt replacements at around 100,000 kilometers are recommended. Large oil capacity (around 7.4 liters) enables extended oil-change intervals, further enhancing endurance in demanding operations.
Mechanical simplicity makes the 1HZ highly serviceable in remote locations. Without electronic sensors or an ECU, it can be maintained with basic hand tools, making it ideal for overlanding, mining, military, and rural applications. While it is nearly indestructible, neglecting cooling system maintenance or timing belt replacement can lead to overheating and head damage.
Despite its legendary reliability, the 1HZ is not fast. Acceleration is slow, fuel economy ranges from 11 to 13 L/100km under load, and it produces a tractor-like noise. It lacks a turbocharger, limiting overtaking and high-speed performance compared to turbocharged variants like the 1HD-T or 1HD-FTE.
The Toyota 1HZ remains a benchmark for longevity, simplicity, and durability. Its ability to operate on low-grade fuel, tolerate harsh conditions, and be field-repaired makes it the preferred choice for users prioritizing reliability and ease of maintenance over speed and modern performance features.
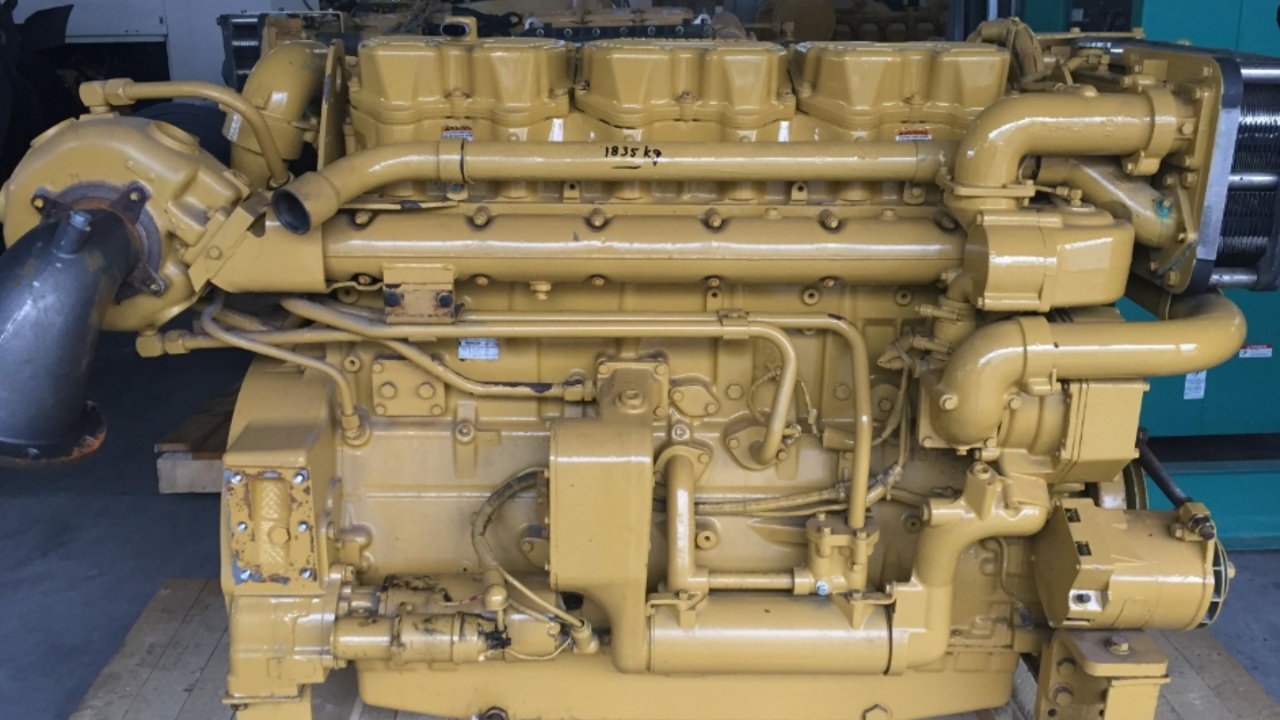
8. Caterpillar 3406E: Legendary Heavy-Duty Diesel Durability
The Caterpillar 3406E diesel engine is considered one of the most durable and long-lasting commercial engines ever produced. Manufactured in the 1990s, it bridged the gap between fully mechanical diesels and electronically controlled models while maintaining Caterpillar’s reputation for heavy-duty construction.
With a massive 14.6-liter displacement and wet-sleeve cylinder design that allows liners to be replaced without removing the engine, the 3406E has become a benchmark for long-haul trucking reliability. Many units routinely exceed 1,000,000 miles before requiring an in-frame overhaul.
The engine’s longevity comes from its robust mechanical components. It has a thick-walled iron block with a deep-skirt design, providing rigidity to withstand extreme torque and combustion pressures. The crankshaft is forged steel, and cross-bolted main bearings keep it securely in place under heavy loads. Wet-sleeve cylinder liners improve cooling efficiency and simplify major repairs compared to cast-in-block designs.
Produced from 1993 to 2004, the 3406E was released after the mechanical issues of earlier models were addressed, but before complex emissions systems such as EGR and DPF became standard. This makes the engine less prone to failures caused by complicated emissions hardware. Its electronic controls are simple, with fewer sensors than modern engines, combining precise fuel delivery with proven mechanical strength.
Fuel is delivered through the Electronic Unit Injection system, which provides optimized timing and precise metering. The engine produces peak torque at low RPM, around 1,200, which allows trucks to haul heavy loads without high engine speeds. This low-RPM design reduces wear on pistons, bearings, and other internal components.
Regular maintenance is essential for achieving high mileage. Using high-quality 15W-40 oil, performing scheduled valve and injector adjustments, and addressing oil leaks, particularly near the rear cover and flywheel housing, are critical. Certain serial prefixes, such as 2WS, 1LW, and 6NZ, are highly valued for stronger blocks and reliability. Early 5EK-prefix engines were prone to crankshaft issues, while later 2WS models are praised for torque delivery and durability.
The 3406E produces between 400 and 600 horsepower in stock form and can be tuned to higher output using ECM adjustments. It is widely used in heavy-haul, vocational, and long-distance trucking applications where pulling power and durability are more important than fuel economy. Common issues include oil leaks, cylinder head gasket failures, and minor electronic diagnostic requirements.
Compared to competitors such as the Cummins C-15, the 3406E provides superior low-RPM torque and raw pulling power, while Cummins engines have a slight advantage in fuel efficiency. The combination of heavy-duty construction, simple electronic integration, and rebuildable design makes the Caterpillar 3406E a legendary diesel engine that has earned its place in trucking history.

The eight diesel engines featured in this guide illustrate that longevity does not require cutting-edge technology or maximum horsepower. Instead, over-engineered components, low-stress tuning, and mechanical simplicity are the hallmarks of long-lasting diesel design.
Whether it is the Mercedes-Benz OM617 powering a classic sedan, the Cummins 5.9L and 6.7L dominating light- and heavy-duty trucks, or the Caterpillar 3406E pulling loads across highways for decades, these engines prove that durability can coexist with practical performance.
Enthusiasts, commuters, and commercial operators alike can benefit from understanding the strengths and limitations of these power plants. By prioritizing regular maintenance, proper lubrication, and monitoring common weak points, owners can achieve extraordinary mileage and reliable operation.
These engines set the benchmark for what a diesel can endure, demonstrating that with robust engineering, simple design, and careful care, high mileage without major overhauls is not just possible, it is expected.
Also Read: 10 Cars With Steering So Good Outperforming Everything Else

