Experiencing a sudden loss of power while driving can be both frustrating and alarming. It not only affects your car’s performance but also poses potential safety risks, especially if it happens unexpectedly in the middle of traffic. There are various reasons why a car might lose power, ranging from minor issues like a clogged air filter to more serious problems like a failing fuel pump.
Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for addressing the issue promptly and preventing further damage to your vehicle. In this guide, we will explore seven common reasons why your car might be losing power while driving.
Each section will look into the symptoms, potential causes, and suggested solutions for these power loss issues. By understanding these factors, you can take proactive measures to maintain your car’s performance, ensure your safety on the road, and avoid costly repairs. Whether you’re a seasoned driver or new to car maintenance, this guide will provide valuable insights into diagnosing and resolving power loss problems in your vehicle.
1. Clogged Air Filter
A clogged air filter is one of the most common reasons for a loss of power in a car. The air filter is responsible for ensuring that clean air reaches the engine for combustion. Over time, the air filter can become clogged with dirt, dust, and debris, restricting the airflow to the engine. When the engine doesn’t receive enough air, it can’t burn fuel efficiently, leading to a reduction in power.
Symptoms of a clogged air filter include sluggish acceleration, poor fuel economy, and a rough idle. To check the air filter, locate it under the hood and remove it from its housing. Hold it up to a light source; if you can’t see light through the filter, it’s time to replace it. Replacing a clogged air filter is a simple and inexpensive maintenance task that can significantly improve your car’s performance.
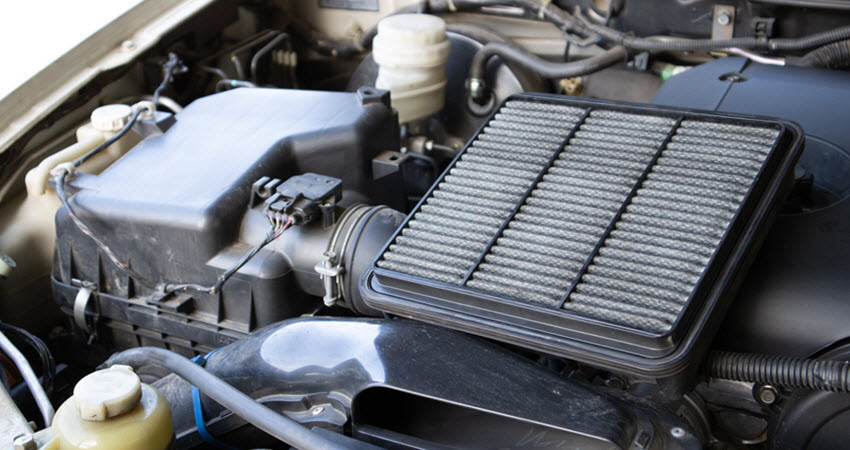

Regularly checking and replacing the air filter according to your vehicle’s maintenance schedule will help prevent power loss and ensure optimal engine performance. Additionally, a clean air filter helps reduce emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment.
Ensuring that your air filter is in good condition is a proactive step in maintaining your vehicle’s health and efficiency, keeping your car running smoothly and reliably.
2. Failing Fuel Pump
A failing fuel pump can cause a significant loss of power while driving. The fuel pump is responsible for delivering fuel from the gas tank to the engine. If the fuel pump is not working correctly, the engine may not receive an adequate supply of fuel, leading to power loss. Common symptoms of a failing fuel pump include sputtering at high speeds, difficulty starting the engine, and a noticeable loss of power, especially when driving uphill or under load.
In some cases, the car may stall or fail to start altogether. Diagnosing a failing fuel pump often requires a pressure test to measure the fuel pressure in the fuel line. If the pressure is below the manufacturer’s specifications, it indicates a problem with the fuel pump. Replacing a faulty fuel pump is a more complex and expensive repair, but it’s essential for maintaining your car’s performance and reliability.
Regular maintenance and using high-quality fuel can help prolong the life of the fuel pump and prevent power loss issues. Ensuring your fuel system is in good condition is vital for your vehicle’s performance, preventing unexpected breakdowns, and maintaining smooth engine operation.
3. Dirty Fuel Injectors
Dirty or clogged fuel injectors can lead to a loss of power in your car. Fuel injectors are responsible for delivering precise amounts of fuel into the engine’s combustion chambers. Over time, deposits can build up in the injectors, restricting the flow of fuel and causing an uneven fuel-air mixture. This can result in poor engine performance, reduced power, and decreased fuel efficiency.
Symptoms of dirty fuel injectors include rough idling, misfires, and sluggish acceleration. To clean the fuel injectors, you can use a fuel injector cleaner additive in your fuel tank, which helps dissolve the deposits and improve fuel flow. For more severe clogs, a professional cleaning service may be required.
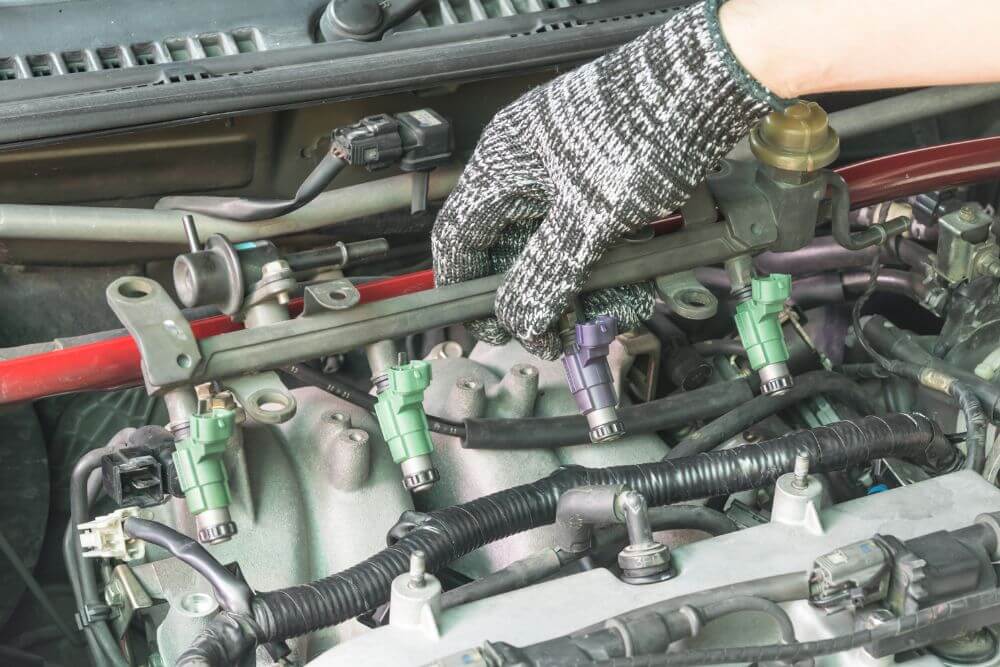

Regular use of high-quality fuel and fuel additives can help prevent the buildup of deposits in the injectors. Keeping your fuel injectors clean ensures that your engine receives the right amount of fuel, maintaining optimal performance and preventing power loss.
Addressing fuel injector issues promptly can enhance your vehicle’s efficiency, reduce emissions, and provide a smoother driving experience, ensuring your engine runs at its best.
4. Faulty Spark Plugs
Faulty spark plugs are another common cause of power loss in a car. Spark plugs are responsible for igniting the air-fuel mixture in the engine’s cylinders, creating the combustion needed for power. If the spark plugs are worn out, dirty, or damaged, they may not produce a strong enough spark, leading to incomplete combustion. This can result in misfires, reduced power, and poor fuel economy.
Symptoms of faulty spark plugs include rough idling, difficulty starting the engine, and decreased acceleration. To check the spark plugs, remove them from the engine and inspect their condition. If they appear worn, fouled, or covered in deposits, it’s time to replace them.
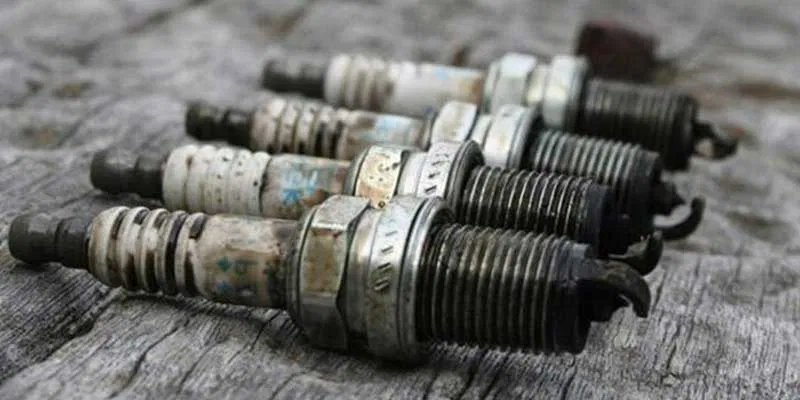

Regularly replacing spark plugs according to your vehicle’s maintenance schedule is essential for maintaining engine performance. Using high-quality spark plugs and ensuring they are properly gapped can help prevent power loss and keep your engine running smoothly. Regular spark plug maintenance ensures efficient combustion, enhances fuel efficiency, and improves engine performance, contributing to a reliable and powerful driving experience.
5. Malfunctioning Mass Airflow Sensor
The mass airflow (MAF) sensor is a crucial component of your car’s engine management system. It measures the amount of air entering the engine and sends this information to the engine control unit (ECU), which adjusts the fuel injection accordingly. A malfunctioning MAF sensor can send incorrect data to the ECU, leading to an improper fuel-air mixture and causing power loss. Symptoms of a malfunctioning MAF sensor include rough idling, poor acceleration, and a decrease in fuel efficiency.
In some cases, the check engine light may also illuminate. To diagnose a faulty MAF sensor, a mechanic may use a diagnostic scanner to check for error codes related to the sensor.
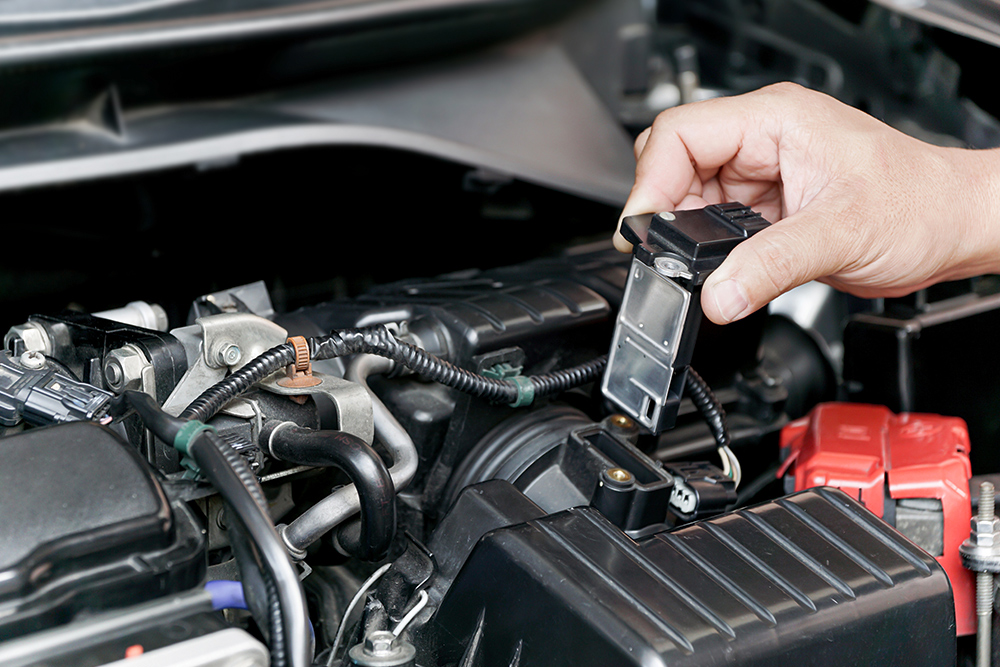

Cleaning the MAF sensor with a specialized cleaner can sometimes resolve the issue, but if the sensor is damaged, it may need to be replaced. Regularly checking and cleaning the MAF sensor can help maintain optimal engine performance and prevent power loss.
Ensuring the MAF sensor is functioning correctly supports accurate fuel management, improves engine efficiency, and provides a more consistent and powerful driving experience.
6. Worn Timing Belt
The timing belt plays a critical role in synchronizing the engine’s camshaft and crankshaft, ensuring that the engine’s valves open and close at the correct times. A worn or damaged timing belt can slip or break, causing the engine’s timing to go out of sync. This can result in a loss of power, misfires, and even severe engine damage if left unaddressed.
Symptoms of a worn timing belt include ticking noises from the engine, rough idling, and difficulty starting the engine. Checking the timing belt for signs of wear, such as cracks, fraying, or missing teeth, is essential for preventing power loss and potential engine damage.
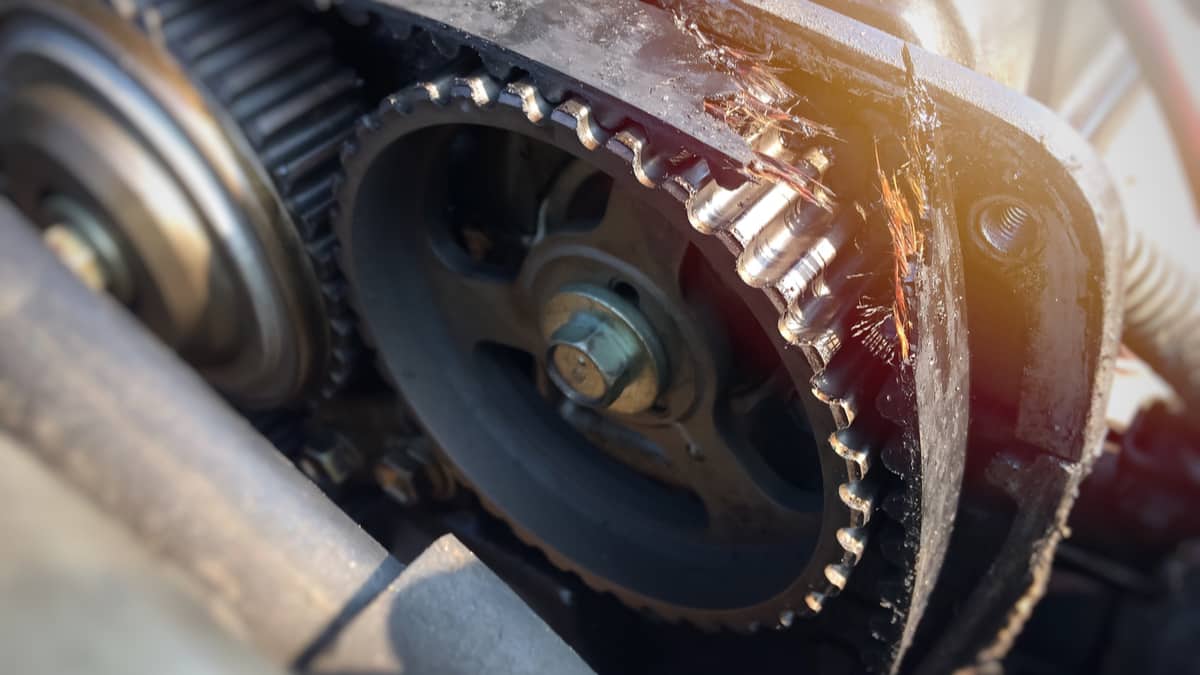

Most manufacturers recommend replacing the timing belt every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, but it’s essential to follow your vehicle’s maintenance schedule. Replacing a worn timing belt can be a complex and expensive repair, but it is crucial for maintaining engine performance and avoiding costly damage. Keeping your timing belt in good condition ensures proper engine synchronization, enhances performance, and extends the lifespan of your vehicle’s engine.
7. Exhaust System Issues
Problems with the exhaust system can also lead to a loss of power in your car. The exhaust system is responsible for expelling exhaust gases from the engine and reducing harmful emissions. Issues such as a clogged catalytic converter, a damaged muffler, or a broken exhaust pipe can restrict the flow of exhaust gases, causing the engine to lose power.
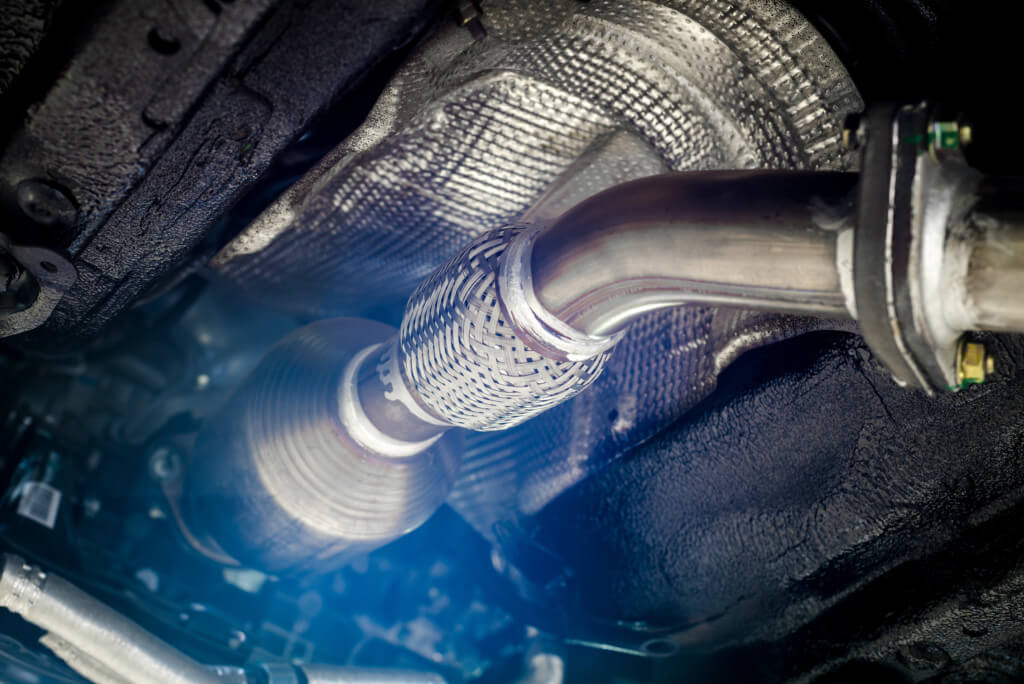

Symptoms of exhaust system issues include decreased acceleration, poor fuel economy, and unusual noises from the exhaust. In some cases, the check engine light may also illuminate. To diagnose exhaust system issues, a mechanic may inspect the exhaust components for damage or blockages. Repairing or replacing damaged exhaust components can restore proper exhaust flow and improve engine performance.
Regular maintenance and addressing exhaust issues promptly can help prevent power loss and ensure your vehicle operates efficiently. Keeping your exhaust system in good condition reduces emissions, enhances engine performance, and provides a quieter and more comfortable driving experience.

