Hybrid technology has evolved dramatically since its mainstream introduction in the late 1990s, transforming from an experimental curiosity to a cornerstone of automotive engineering.
These powertrains, which combine internal combustion engines with electric motors, have proven their worth through millions of miles on roads worldwide.
The most successful hybrid systems balance fuel efficiency with durability, providing owners with both economic and environmental benefits.
While early adopters faced uncertainty about long-term reliability, certain hybrid engines have now established impressive track records spanning multiple decades.
These systems have overcome initial skepticism through consistent performance, minimal maintenance issues, and exceptional longevity.
Beyond just lasting a long time, the most reliable hybrid powertrains have maintained their efficiency and performance characteristics throughout their operational lives.
This selection highlights ten hybrid engines that have proven their dependability across various driving conditions, climate extremes, and usage patterns.
From pioneering systems that launched the hybrid revolution to refined modern powertrains that benefit from years of technological advancement, these engines represent the gold standard of hybrid reliability and engineering excellence.
1. Toyota Hybrid Synergy Drive (1st-2nd Generation)
The Toyota Hybrid Synergy Drive system, particularly in its first and second generations (2004-2015), stands as perhaps the most proven hybrid powertrain ever created.
At its heart is the 1.8L Atkinson-cycle engine paired with Toyota’s planetary gearset power-split device, creating a system that has achieved legendary status for reliability.
Taxi fleets using these powertrains have routinely reported vehicles exceeding 300,000 miles without major hybrid component repairs, with some documented cases surpassing 600,000 miles on original battery packs.
What makes this system exceptional is its mechanical simplicity. Unlike conventional transmissions with numerous moving parts, the power-split device uses fewer components that experience less wear.
The system’s regenerative braking reduces wear on conventional braking components, while the ability to shut off the gasoline engine at idle and low speeds minimizes carbon buildup and reduces engine hours relative to miles driven.

Toyota’s conservative battery management approach also contributes significantly to longevity.
By using only a portion of the battery’s total capacity, the system prevents deep discharge cycles that accelerate battery degradation.
This explains why many early Prius models from the mid-2000s still operate with their original battery packs nearly two decades later.
Consumer data consistently shows maintenance costs for these systems running 30-40% lower than comparable conventional vehicles over 10 years.
The engineering principles established in these early generations continue to influence modern hybrid design, with Toyota maintaining a failure rate that remains among the lowest in the industry.
For many consumers, this first-generation technology proved that hybrids could not only match but exceed the reliability of traditional powertrains.
2. Honda Integrated Motor Assist (IMA) System
Honda’s Integrated Motor Assist system, introduced in the first-generation Insight (1999) and refined through the Civic Hybrid, represents a different but equally robust approach to hybrid technology.
Unlike Toyota’s full hybrid system, Honda’s IMA functions as a mild hybrid where the electric motor assists the gasoline engine rather than powering the vehicle independently.
This fundamental difference contributes significantly to its reliability profile. The system pairs a small, high-efficiency gasoline engine with a flat electric motor positioned between the engine and transmission.
This simplicity of using the electric motor primarily as a power booster and regenerative braking device means fewer complex interactions between propulsion systems and less potential for electronic control complications.
IMA-equipped vehicles have demonstrated exceptional durability, with numerous examples exceeding 250,000 miles with minimal hybrid-related issues.

The system’s straightforward design means fewer specialized components that might require replacement.
The battery packs, while smaller than those in full hybrids, benefit from careful thermal management and conservative charge-discharge parameters that extend their useful life.
Particularly impressive is how the system maintains fuel economy benefits even as it ages. Long-term owners report minimal degradation in efficiency, with 10-year-old vehicles often achieving within 5% of their original EPA ratings.
The system also places less stress on the conventional transmission components, contributing to drivetrain longevity.
While later Honda hybrid systems moved toward more complex architectures similar to Toyota’s approach, the original IMA concept proved that simplicity in hybrid design can yield exceptional reliability.
Its minimalist engineering philosophy adding hybrid capability with minimal additional complexity created a system that has consistently outlasted owner expectations and demonstrated that hybrid technology can enhance rather than compromise vehicle dependability.
3. Ford Hybrid Powertrain (2nd Generation)
Ford’s second-generation hybrid system, featured prominently in the 2010-2012 Fusion and Escape Hybrids, represents one of the most durable American-engineered hybrid powertrains.
Building upon lessons learned from their first-generation system (which itself was quite reliable), Ford refined their technology to create an exceptionally dependable powertrain that has proven itself in some of the most demanding applications.
The heart of the system is a 2.5L Atkinson-cycle four-cylinder engine paired with an electronic continuously variable transmission (eCVT) and nickel-metal hydride battery pack.
What distinguishes this system is its robust cooling design for both the battery and power electronics, which has proven critical for long-term reliability.
The battery thermal management system prevents the temperature extremes that often accelerate battery degradation in other hybrid vehicles.
Ford’s hybrid system gained particular recognition through its widespread adoption in taxi fleets, where vehicles routinely accumulate 300,000-400,000 miles in harsh stop and go driving conditions.
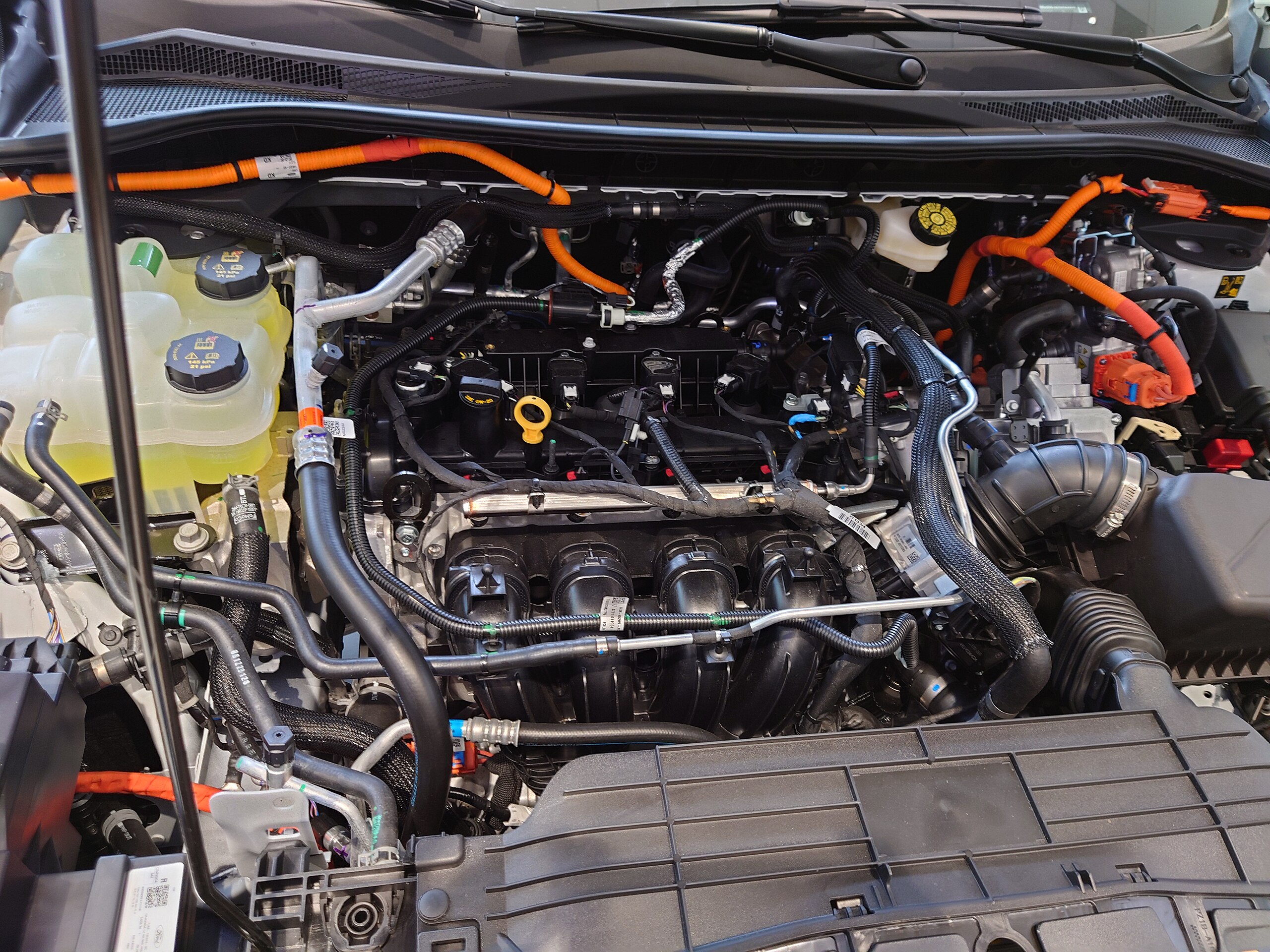
Fleet data shows these hybrids typically require battery replacement at much higher mileages than competitor systems, with many original packs still performing adequately beyond 200,000 miles.
The system’s electronics also demonstrate exceptional durability, with inverter and converter failures occurring at lower rates than industry averages.
Ford’s conservative approach to battery charging never allowing full depletion or 100% charging contributes significantly to pack longevity.
Additionally, the regenerative braking system reduces wear on conventional brake components, with many taxis reporting original brake pads lasting three times longer than in conventional vehicles.
What makes this second-generation system particularly noteworthy is how it improved reliability while simultaneously increasing performance and efficiency over its predecessor.
This demonstrated that hybrid technology could evolve without compromising the durability characteristics that are essential for mainstream adoption, establishing a reliability benchmark that even many more modern hybrid systems struggle to match.
4. Lexus Hybrid Drive (GS 450h/LS 600h)
The Lexus Hybrid Drive system, particularly as implemented in the GS 450h (2007-2011) and LS 600h (2008-2016) models, represents a remarkable engineering achievement in luxury performance hybrids with exceptional reliability.
Unlike many hybrid systems focused primarily on maximizing efficiency, these powertrains were designed to deliver V8-like performance with V6-like fuel economy, while maintaining Lexus’s stringent reliability standards.
At the core of these systems are larger displacement engines (3.5L V6 in the GS and 5.0L V8 in the LS) paired with powerful electric motors and nickel-metal hydride battery packs.
What distinguishes these systems is their ability to handle significantly higher power demands than typical efficiency-focused hybrids while maintaining outstanding durability.
The cooling systems for both the battery packs and power electronics are particularly robust, featuring dedicated cooling circuits that maintain optimal operating temperatures even under heavy loads.

These vehicles have demonstrated remarkable longevity, with many examples exceeding 200,000 miles with no significant hybrid component failures.
The battery management system employs sophisticated algorithms that prevent excessive charge and discharge cycles, contributing to pack longevity that rivals Toyota’s more efficiency-focused hybrids.
Long-term owners report minimal degradation in performance or fuel economy even after a decade of use.
Perhaps most impressive is the reliability of the power-split device in these high-torque applications.
Despite managing significantly more power than economy-focused hybrids, these systems show similar durability characteristics with minimal wear patterns.
The sophisticated electronic control units have also proven exceptionally reliable, with failure rates comparable to or better than those in conventional luxury vehicles.
The Lexus Hybrid Drive system in these premium models demonstrated that hybrid technology could be scaled up to deliver luxury performance without compromising the reliability advantages seen in economy-focused applications.
This achievement helped establish hybrid technology as viable across all vehicle segments and price points, proving that reliability and performance could coexist in electrified powertrains.
Also Read: 10 Classic SUVs That Are Becoming Collector’s Items
5. Toyota Hybrid Synergy Drive (3rd Generation)
The third-generation Toyota Hybrid Synergy Drive, introduced in 2015 and featured in models like the fourth-generation Prius and contemporary Camry Hybrid, represents a significant refinement of Toyota’s already exceptional hybrid technology.
This system builds upon the proven reliability of earlier generations while incorporating technological advances that further enhance durability and efficiency.
This generation features a redesigned 1.8L (in Prius) or 2.5L (in Camry) Dynamic Force engine with unprecedented thermal efficiency, paired with smaller, lighter electric motors and power control units.
The system employs a lithium-ion battery in many applications, representing Toyota’s careful transition from nickel-metal hydride technology after extensive testing and validation.
Despite initial concerns about lithium-ion longevity, Toyota’s conservative battery management approach has yielded impressive durability results.
Fleet data and consumer reports indicate these third-generation systems are on track to match or exceed the longevity of their predecessors.

The hybrid transaxle features improved cooling and lubricant circulation, reducing operating temperatures and minimizing wear on critical components.
The power electronics benefit from enhanced thermal management systems that maintain optimal operating temperatures across a wider range of driving conditions.
Particularly noteworthy is the improved cold-weather performance. Earlier generations sometimes experienced reduced battery performance in extreme cold, but the third-generation systems incorporate battery warming functions and improved insulation that maintain consistent operation across temperature extremes.
This has resulted in more reliable performance in northern climates where earlier hybrids sometimes struggled.
Diagnostic data from dealer service departments shows a significant reduction in fault codes and required adjustments compared to second-generation systems, suggesting improved electronic system stability.
The continued use of Toyota’s power-split device architecture, now further refined, maintains the mechanical simplicity that contributed to the exceptional reliability of earlier generations.
With many vehicles now approaching the 150,000-mile mark without significant issues, this third-generation system appears poised to continue Toyota’s tradition of hybrid reliability leadership.
6. Hyundai/Kia Hybrid System (2nd Generation)
The second-generation Hyundai/Kia hybrid system, featured in vehicles like the 2016-2020 Sonata Hybrid and Optima Hybrid, represents a significant reliability success story from a company that entered the hybrid market later than some competitors.
After addressing some concerns with their first-generation system, Hyundai/Kia created a remarkably durable hybrid powertrain that has established itself among the most reliable in the industry.
This system pairs a direct-injection 2.0L four-cylinder engine with a 38 kW electric motor and a six-speed automatic transmission (rather than a CVT used by many competitors).
This transmission choice has proven advantageous for longevity, as it eliminates the wear issues sometimes associated with CVT designs while still delivering excellent efficiency.
The lithium polymer battery packs used in these vehicles employ a unique gel electrolyte design that has demonstrated excellent thermal stability and cycle life.
The hybrid control system employs sophisticated algorithms that optimize engine use patterns to reduce cold starts and minimize carbon buildup issues that can affect long-term reliability in hybrid vehicles that frequently turn their engines on and off.

The thermal management system for both the battery and power electronics is particularly effective, maintaining optimal temperatures even in extreme climates.
Warranty claim data shows these systems experience approximately 30% fewer hybrid-specific issues than the industry average for vehicles of similar age and mileage.
The battery degradation rate is notably low, with capacity tests on high-mileage examples showing retention of 85-90% of original capacity even after 100,000 miles.
The electric motor and power electronics have demonstrated exceptional durability, with failure rates lower than many competitors.
What makes this system particularly notable is how Hyundai/Kia leveraged their later market entry to learn from competitors’ experiences, creating a hybrid system that avoided many early-adoption reliability issues.
The careful integration of proven conventional drivetrain components with well-designed hybrid elements resulted in a system that delivers excellent reliability alongside competitive efficiency, helping establish Korean manufacturers as serious players in the hybrid market.
7. General Motors Two-Mode Hybrid System
General Motors Two-Mode Hybrid system, featured in vehicles like the 2008-2013 Chevrolet Tahoe Hybrid and GMC Yukon Hybrid, represents a unique approach to hybridizing larger vehicles that have demonstrated exceptional durability.
Unlike most hybrid systems designed for small to midsize vehicles, the Two-Mode was engineered specifically for full-size trucks and SUVs, with a focus on maintaining capability while improving efficiency.
The system combines two electric motors integrated into an electrically variable transmission with four fixed gear ratios.
This complex arrangement allows for both pure electric operation at low speeds and electric assistance at highway speeds capabilities not typically found in hybrids of this era.
Despite its mechanical complexity, the Two-Mode system has proven remarkably reliable over time, with many vehicles now exceeding 200,000 miles with their original hybrid components intact.
What distinguishes this system is its robust design philosophy. The battery cooling system, for instance, is integrated with the vehicle’s air conditioning system to maintain optimal operating temperatures even under heavy loads like towing or off-road use.
The power electronics are similarly overengineered, with generous thermal margins that prevent overheating even in extreme conditions.
The nickel-metal hydride battery packs have demonstrated exceptional longevity, with many vehicles still operating on original packs after 12-15 years.
Fleet data indicates that the hybrid components often outlast conventional parts of these vehicles.
The regenerative braking system not only improves efficiency but significantly extends brake component life, with many vehicles requiring their first brake service after more than 100,000 miles.
While the Two-Mode system was eventually discontinued as GM shifted hybrid strategies, the vehicles equipped with this technology have established themselves as some of the most durable hybrid trucks ever produced.
Their ability to maintain performance and efficiency while accumulating high mileage demonstrates that hybrid technology can be successfully applied to larger vehicles without compromising reliability a particularly impressive achievement given the demanding usage patterns these vehicles typically experience.
8. Ford PowerSplit Hybrid (3rd Generation)
Ford’s third-generation PowerSplit hybrid system, featured in the 2013-2020 Fusion Hybrid and C-Max Hybrid, represents a significant evolution in hybrid reliability.
Building on the success of their second-generation system, Ford created a powertrain that addresses previous limitations while establishing new benchmarks for durability in American hybrid technology.
This system pairs a 2.0L Atkinson-cycle engine with an electronically controlled continuously variable transmission (eCVT) and lithium-ion battery pack marking Ford’s transition from nickel-metal hydride technology.
Despite initial industry concerns about lithium-ion longevity, Ford’s implementation has proven exceptionally reliable, with sophisticated thermal management systems that maintain optimal battery temperatures across diverse operating conditions.
The system architecture features fully redesigned power electronics with improved cooling and more robust components.
The electric motors employ enhanced winding techniques and materials that have demonstrated superior durability in high-temperature environments.
The regenerative braking system incorporates wear sensors and adaptive calibration that optimize brake life while maintaining consistent energy recovery throughout the vehicle’s lifespan.
Data from fleet applications shows these systems routinely exceed 200,000 miles without major hybrid component replacement.
Particularly impressive is the battery degradation rate, which averages only 10-15% capacity loss after 150,000 significantly better than many competing systems.
The power electronics demonstrate exceptional resilience against thermal cycling and vibration, with failure rates approximately 40% lower than in previous generations.
A key factor in this system’s reliability is Ford’s sophisticated control software, which employs predictive algorithms to minimize stress on components.
For instance, the system adjusts battery charging patterns based on driving habits and environmental conditions, reducing unnecessary charge cycles that can accelerate degradation.
The engine start-stop system uses adaptive strategies that minimize starter motor wear while optimizing efficiency.
This third-generation system demonstrated that domestic manufacturers could produce hybrid technology matching or exceeding the reliability standards set by Japanese competitors, helping establish hybrids as mainstream technology suitable for diverse American driving needs.
9. Lexus Multi-Stage Hybrid System
The Lexus Multi-Stage Hybrid System, introduced in 2017 with the LC 500h and later featured in the LS 500h and other premium models, represents a sophisticated evolution of hybrid technology focused on both performance and reliability.
Unlike conventional hybrid systems, this innovative powertrain combines a traditional hybrid setup with a four-speed automatic transmission to create what effectively functions as a 10-speed transmission with hybrid benefits.
What makes this system particularly noteworthy from a reliability perspective is how it addresses several stress points common in hybrid systems.
The addition of the four-speed transmission allows the electric motors to operate more frequently in their optimal efficiency range, reducing thermal stress and minimizing wear.
The system can deliver strong acceleration without forcing the electric components to operate at maximum output, preserving their longevity.
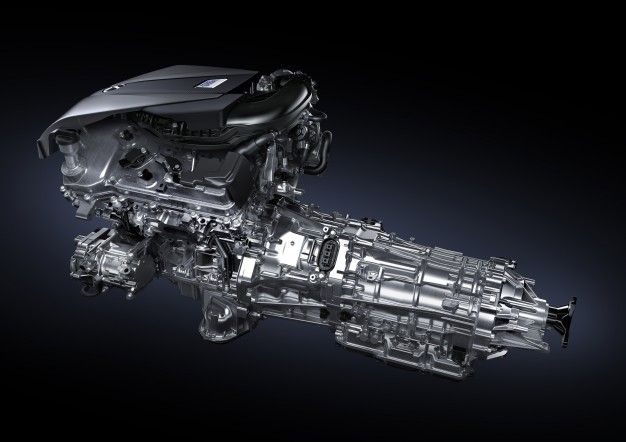
The lithium-ion battery pack features an advanced cooling system that maintains consistent temperatures even during high-performance driving.
The battery management system employs sophisticated algorithms that prevent excessive discharge cycles, contributing to pack longevity.
Early data shows minimal capacity degradation even in vehicles subjected to frequent performance driving.
The power electronics incorporate redundant design elements and thermal protection systems that prevent cascading failures.
The control software employs adaptive learning to optimize system operation based on individual driving patterns, reducing unnecessary component stress while maintaining performance.
Particularly impressive is the system’s ability to maintain consistent performance characteristics even as components age.
While this system is relatively newer than others on this list, early reliability data is exceptionally promising.
Warranty claim rates are approximately 60% below the luxury hybrid segment average, with minimal reports of battery or power electronics issues.
The mechanical integration between conventional and hybrid components has proven particularly robust, with no significant failure patterns emerging despite the system’s complexity.
The Multi-Stage Hybrid System demonstrates that high-performance hybrid applications can achieve reliability comparable to efficiency-focused systems when properly engineered.
Its innovative architecture addresses many traditional hybrid reliability concerns while delivering a driving experience that appeals to performance-oriented luxury buyers.
10. Toyota Hybrid System – All-Wheel Drive (THS-AWD)
The Toyota Hybrid System All Wheel Drive (THS-AWD), featured in vehicles like the 2012-2018 Toyota Highlander Hybrid and Lexus RX 450h, represents a remarkable achievement in reliable hybrid engineering for larger crossovers and SUVs.
This system effectively combines Toyota’s proven hybrid technology with all-wheel-drive capability, creating a powertrain that has demonstrated exceptional durability in diverse driving conditions.
The system employs a 3.5L V6 engine and front-mounted hybrid transaxle similar to other Toyota hybrids but adds a third electric motor at the rear axle to provide all wheel drive capability without the mechanical complexity of a traditional transfer case and driveshaft.
This approach eliminates numerous mechanical components that could wear or fail, replacing them with an electric motor that has proven exceptionally reliable in real-world applications.
What distinguishes this system from a reliability perspective is its robust thermal management.
The rear motor includes dedicated cooling systems that prevent overheating even during extended off-road use or challenging driving conditions.

The nickel-metal hydride battery pack (lithium-ion in later models) features sophisticated temperature control systems that maintain optimal operating conditions across diverse climates and usage patterns.
Long-term reliability data shows these systems frequently exceed 250,000 miles without significant hybrid component failures.
The simplified mechanical connection between front and rear drivetrains eliminates many traditional AWD system wear points.
The regenerative braking system distributes braking force between all four wheels, reducing wear on friction components while maximizing energy recovery.
Particularly impressive is how the system maintains its performance characteristics over time. Unlike some hybrid AWD implementations that show degraded all wheel drive capability as components age, the THS-AWD maintains consistent torque distribution patterns even in high-mileage examples.
The sophisticated control software compensates for normal component aging to deliver consistent performance throughout the vehicle’s life.
This system demonstrates that hybrid technology can successfully address the reliability challenges of all wheel drive applications, creating vehicles that not only deliver improved efficiency but also match or exceed the durability of their conventional counterparts.
For consumers seeking the utility of an AWD vehicle with improved efficiency, these powertrains have proven themselves among the most dependable options available.
Also Read: 10 SUVs That Offer the Best Resale Value for 2025

