Manual transmissions represent the purest form of automotive engagement, offering drivers complete control over their vehicle’s power delivery and performance characteristics.
While automatic transmissions have become increasingly sophisticated and prevalent, the manual gearbox remains the choice of driving enthusiasts who value the mechanical connection between driver and machine.
However, not all manual transmissions are created equal, and the difference between a bulletproof gearbox and a problematic one can mean the difference between decades of reliable service and costly repairs that drain your wallet.
The engineering behind manual transmissions involves precise tolerances, high-quality materials, and robust synchronizer systems that enable smooth gear changes under various driving conditions.
The best manual transmissions combine durability with refinement, offering crisp shifts, long service life, and the ability to handle increased power without modification.
These transmissions typically feature stronger gear teeth, better bearing systems, improved lubrication pathways, and more sophisticated synchronizer rings that reduce wear and improve shift quality over time.
Conversely, problematic manual transmissions often suffer from design flaws, cost-cutting measures during manufacturing, or inadequate testing during development.
Common issues include weak synchronizers that cause grinding during shifts, inadequate bearing support leading to premature wear, poor gear geometry that creates excessive stress concentrations, and substandard materials that fail under normal operating conditions. Understanding these differences can help buyers make informed decisions and avoid costly ownership experiences.
5 Manual Transmissions That Never Quit
These exceptionally durable gearboxes feature robust synchronizer assemblies and precision-manufactured gear sets that deliver smooth shifting operation through years of enthusiastic driving across demanding performance applications and high-mileage usage scenarios.
Their thoughtful engineering includes hardened steel components, effective lubrication systems, and conservative gear ratios that resist the wear patterns typically created by aggressive clutch engagement or spirited driving during track events and daily commuting cycles.
From seamless gear changes that maintain crisp engagement feel to clutch-friendly operation that extends component life through proper synchronization timing, these remarkable transmissions continue providing reliable power transfer without developing grinding noises or shifting resistance issues.
Owners report decades of trouble-free operation with these bulletproof drivetrains a reliability-enhancing quality feature that proves its worth through maintained shifting precision and extended component longevity throughout high-performance driving applications and regular transportation duties.
1. Honda K-Series 6-Speed Manual Transmission
The Honda K-series 6-speed manual transmission stands as one of the most revered gearboxes in automotive history, earning its reputation through decades of reliable service across multiple Honda and Acura models.
Found in vehicles ranging from the Civic Si to the Acura RSX Type-S, this transmission represents Honda’s commitment to engineering excellence and long-term durability.
The K-series gearbox benefits from Honda’s extensive experience in manual transmission development, incorporating lessons learned from decades of motorsports participation and real-world testing.
What sets the K-series transmission apart is its exceptional build quality and attention to detail. The case is constructed from high-strength aluminum alloy with precisely machined bearing surfaces that maintain tight tolerances even after hundreds of thousands of miles.
The gear teeth feature advanced metallurgy with proper heat treatment that ensures longevity under both street driving and track conditions. Honda’s engineers paid particular attention to the synchronizer system, utilizing triple-cone synchronizers on the most frequently used gears to ensure smooth shifting throughout the transmission’s lifespan.
The internal components showcase Honda’s commitment to quality, with forged steel gear sets that can handle significantly more torque than the engines they’re paired with typically produce.
This over-engineering approach means that even modified vehicles with increased power output rarely experience transmission failures. The differential assembly features robust side gears and a strong ring and pinion setup that distributes loads evenly, preventing premature wear and ensuring consistent performance.
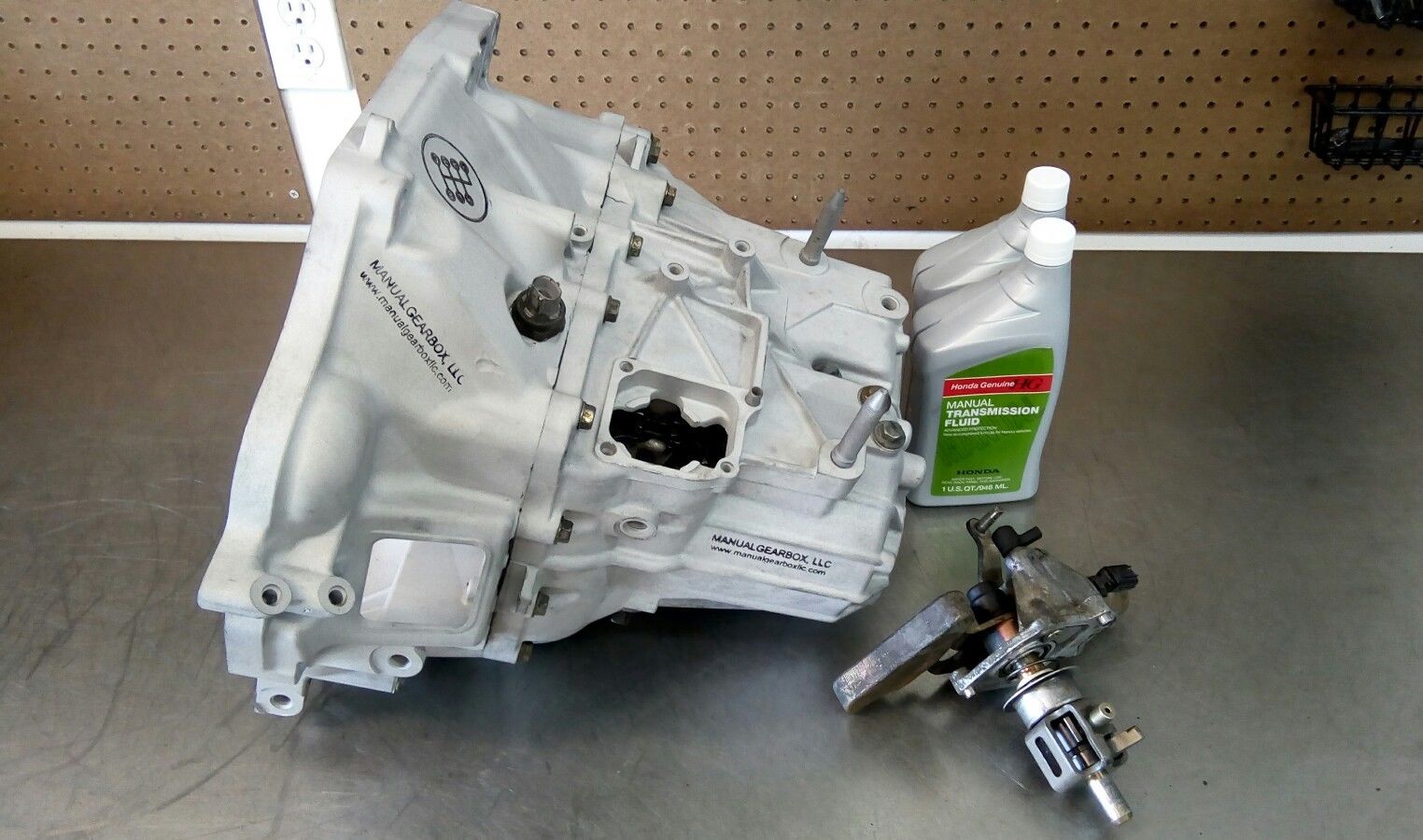

Maintenance requirements for the K-series transmission are minimal, typically requiring only periodic fluid changes with Honda’s specified manual transmission fluid.
The transmission’s design allows for easy servicing, with accessible drain and fill plugs that make fluid changes straightforward for both professional mechanics and dedicated enthusiasts. Many owners report trouble-free operation well beyond 200,000 miles with nothing more than regular fluid changes and proper driving techniques.
The shift feel of the K-series transmission is consistently praised by automotive journalists and owners alike. The short-throw shifter provides precise engagement with clear gate definition, making it easy to find the desired gear even during spirited driving.
The cable-operated shifter mechanism reduces play and maintains consistent feel throughout the transmission’s service life, unlike some linkage-based systems that develop slop over time.
Performance enthusiasts particularly appreciate the K-series transmission’s ability to handle increased power levels. Many turbocharged and supercharged Honda engines producing double the original power output continue to use stock transmissions without issue.
The robust internals and conservative factory ratings mean that the transmission rarely becomes the limiting factor in performance modifications, allowing enthusiasts to focus on engine upgrades without transmission concerns.
Racing applications have further proven the K-series transmission’s durability, with many examples serving in amateur and professional motorsports without modification.
The transmission’s ability to withstand repeated high-RPM shifts, aggressive launches, and sustained high-speed operation demonstrates its exceptional engineering and construction quality. Even in failure-prone racing environments, properly maintained K-series transmissions often outlast other drivetrain components.
2. Toyota/Lexus R154 5-Speed Manual Transmission
The Toyota R154 5-speed manual transmission represents the pinnacle of Japanese engineering excellence, designed specifically to handle the substantial torque output of Toyota’s high-performance engines while maintaining the reliability standards that define the Toyota brand.
Originally developed for the Mark IV Supra and other high-performance Toyota applications, the R154 has earned legendary status among enthusiasts for its ability to handle extreme power levels while maintaining smooth, precise operation throughout its service life.
Toyota’s engineers designed the R154 with motorsports applications in mind, resulting in a transmission that far exceeds the requirements of street driving.
The case construction utilizes high-grade aluminum alloy with thick walls and extensive ribbing that provides exceptional rigidity while maintaining reasonable weight.
This robust foundation ensures that the transmission maintains proper gear alignment and bearing preload even under extreme operating conditions, preventing the flexing that can cause premature wear in lesser transmissions.
The gear sets within the R154 feature exceptionally high-quality materials and manufacturing processes. Each gear is precision-forged from high-strength steel alloys and undergoes extensive heat treatment to achieve optimal hardness characteristics.
The gear teeth profiles are precisely machined to ensure smooth power transfer while minimizing stress concentrations that could lead to premature failure. Toyota’s attention to detail extends to the smallest components, with even the detent balls and springs manufactured to exacting specifications.
One of the R154’s most impressive characteristics is its synchronizer system, which utilizes large-diameter bronze synchronizer rings with aggressive cone angles that provide positive engagement even during rapid shifting.
The synchronizers are generously sized and feature advanced surface treatments that reduce wear and maintain effectiveness throughout the transmission’s service life.
This robust synchronizer design enables the R154 to provide smooth shifts even when cold, a characteristic that sets it apart from many performance transmissions that require warm-up periods.
The differential assembly represents another area where Toyota’s engineering excellence shines through. The R154 features a robust limited-slip differential option that provides superior traction while maintaining durability under extreme conditions.
The differential case and side gears are manufactured from high-strength materials with precise tolerances that ensure long service life and consistent operation. Even in open differential configurations, the R154’s differential assembly demonstrates exceptional durability and smooth operation.
Maintenance procedures for the R154 are straightforward, requiring only periodic fluid changes with Toyota’s specified gear oil. The transmission’s robust design means that properly maintained examples regularly exceed 300,000 miles without major issues.
Many high-mileage examples continue to shift smoothly and operate quietly, a testament to the quality of materials and manufacturing processes employed in their construction.
The R154’s reputation extends far beyond Toyota’s original applications, with the transmission becoming a popular swap option for enthusiasts seeking bulletproof reliability in high-performance applications.
The transmission’s compact dimensions and robust construction make it suitable for a wide range of vehicles, while its ability to handle extreme power levels ensures that it remains relevant even in modern high-performance builds.
Performance testing has demonstrated the R154’s exceptional capabilities, with properly built examples handling over 1000 horsepower in drag racing applications.
The transmission’s robust internals and conservative factory ratings provide substantial safety margins that allow for extreme performance modifications without transmission concerns. This over-engineering approach ensures that the R154 remains reliable even when pushed far beyond its original design parameters.
3. Getrag 420G 6-Speed Manual Transmission
The Getrag 420G 6-speed manual transmission represents German engineering precision at its finest, combining robust construction with refined operation to create one of the most durable and pleasant-to-use transmissions ever produced.
Developed through collaboration between BMW and Getrag, this transmission served in numerous high-performance BMW applications and has earned recognition for its exceptional longevity and smooth operation under various driving conditions.
German engineering philosophy emphasizes over-engineering and attention to detail, characteristics that define every aspect of the 420G’s design and construction.
The transmission case features thick aluminum walls with extensive internal ribbing that provides exceptional rigidity while maintaining optimal weight distribution.
The bearing supports are generously sized and precisely machined to maintain proper preload throughout the transmission’s service life, ensuring consistent operation and preventing premature wear.
The gear sets within the 420G showcase Getrag’s expertise in transmission design, featuring helical-cut gears with optimized tooth profiles that minimize noise while maximizing strength.
Each gear undergoes extensive heat treatment processes that create a hard surface layer while maintaining a tough core, providing optimal wear resistance without brittleness. The gear ratios are carefully selected to provide smooth progression while maintaining optimal engine operation across various driving scenarios.
Synchronizer design represents one of the 420G’s strongest features, utilizing advanced multi-cone synchronizers on all forward gears that provide smooth engagement regardless of temperature or driving conditions.
The synchronizer rings feature advanced friction materials that maintain effectiveness throughout the transmission’s service life, while the generous sizing ensures adequate torque capacity for even aggressive shifting techniques. This robust synchronizer design enables the 420G to provide consistent shift quality from the first mile to well beyond 200,000 miles.
The shift mechanism design demonstrates Getrag’s commitment to driver satisfaction, featuring a short-throw shifter with precise gate definition and positive engagement.
The shifter mechanism utilizes high-quality bushings and joints that maintain tight tolerances throughout their service life, preventing the development of play or imprecise shifting characteristics that plague lesser transmissions. The shift effort remains consistent and appropriate across all gears, providing driver confidence during both casual driving and performance situations.
Internal lubrication systems within the 420G are designed for longevity, featuring strategically placed oil passages that ensure adequate lubrication reaches all critical components regardless of operating angle or acceleration forces.
The oil pump design provides consistent pressure throughout the operating range, while the filtration system prevents contamination from causing premature wear. This comprehensive lubrication approach contributes significantly to the transmission’s exceptional durability.
Maintenance requirements for the 420G are minimal, typically requiring only periodic fluid changes with specified synthetic gear oil. The transmission’s robust design and high-quality components mean that properly maintained examples regularly exceed 250,000 miles without significant issues.
Many owners report that their 420G transmissions continue to shift smoothly and operate quietly even after decades of service, testament to the quality of German engineering and manufacturing.
The 420G’s reputation extends beyond BMW applications, with the transmission becoming sought after for engine swaps and performance builds due to its exceptional durability and refined operation.
The transmission’s ability to handle increased torque loads while maintaining smooth operation makes it an ideal choice for modified vehicles where reliability remains paramount.
Performance applications have further demonstrated the 420G’s capabilities, with examples serving in various motorsports applications without modification.
The transmission’s robust construction and conservative ratings provide substantial safety margins that allow for performance use without concerns about premature failure, making it a favorite among enthusiasts who demand both performance and reliability.
4. Aisin AZ6 6-Speed Manual Transmission
The Aisin AZ6 6-speed manual transmission represents the culmination of Japanese precision manufacturing and engineering excellence, designed to provide decades of trouble-free service while delivering refined operation that befits premium automotive applications.
Developed by Aisin, one of Japan’s premier transmission manufacturers, the AZ6 incorporates advanced design elements and manufacturing techniques that ensure exceptional durability and smooth operation throughout its extended service life.
Aisin’s reputation for quality stems from its position as a tier-one supplier to major automotive manufacturers, requiring adherence to the strictest quality standards and reliability requirements.
The AZ6 reflects this commitment to excellence, featuring construction techniques and materials that exceed typical automotive transmission standards. Every component undergoes rigorous testing and quality control procedures that ensure consistent performance and longevity across production runs.
The transmission case construction utilizes high-strength aluminum alloy with precision-cast bearing supports that maintain exact tolerances throughout the transmission’s service life.
The case design incorporates extensive ribbing and reinforcement that provides exceptional rigidity while minimizing weight, ensuring that gear alignment remains precise even under extreme operating conditions. The bearing supports feature generous sizing with proper preload specifications that prevent deflection and maintain smooth operation.
Internal components showcase Aisin’s expertise in gear design and manufacturing, with each gear precisely machined from high-quality steel alloys that undergo advanced heat treatment processes.
The gear tooth profiles are optimized for smooth power transfer while minimizing noise and vibration, creating a refined driving experience that remains consistent throughout the transmission’s service life. The manufacturing tolerances are held to extremely tight specifications that ensure proper meshing and load distribution.

The synchronizer system represents one of the AZ6’s most impressive features, utilizing large-diameter synchronizer rings with advanced friction materials that provide smooth engagement under all operating conditions.
The synchronizers are generously sized to handle substantial torque loads while maintaining effectiveness throughout their service life. The cone angles and surface treatments are optimized to provide positive engagement while minimizing wear, ensuring consistent shift quality over hundreds of thousands of miles.
Lubrication system design within the AZ6 demonstrates Aisin’s attention to detail, featuring strategically positioned oil passages that ensure adequate lubrication reaches all critical components regardless of operating conditions.
The system includes provisions for splash lubrication as well as positive oil delivery to high-stress components, preventing premature wear and ensuring smooth operation. The oil capacity is generous, providing thermal mass that helps regulate operating temperatures.
The shift mechanism design emphasizes precision and durability, featuring a short-throw shifter with clearly defined gates and positive engagement characteristics.
The shifter components utilize high-quality materials and tight manufacturing tolerances that prevent the development of play or imprecise operation over time. The shift effort is carefully calibrated to provide appropriate feedback while remaining comfortable during extended driving sessions.
Maintenance procedures for the AZ6 are straightforward and infrequent, typically requiring only periodic fluid changes with Aisin’s specified synthetic gear oil.
The transmission’s robust design and high-quality components result in exceptionally long service intervals, with many examples operating trouble-free for over 200,000 miles with basic maintenance. The accessibility of service points makes routine maintenance simple for both professional technicians and dedicated enthusiasts.
The AZ6’s versatility extends beyond its original applications, with the transmission proving adaptable to various performance and specialty vehicle builds.
The robust construction and conservative ratings provide substantial safety margins that allow for increased power applications without concerns about premature failure. This over-engineering approach ensures that the AZ6 remains reliable even when used in applications that exceed its original design parameters.
Quality control procedures during manufacturing ensure consistency across production runs, with each transmission receiving comprehensive testing before shipment.
This attention to detail results in extremely low failure rates and consistent performance characteristics that make the AZ6 a preferred choice for applications where reliability is paramount.
Also Read: 5 SUVs With Lowest NVH (Noise/Vibration/Harshness) and 5 Rattlers
5. ZF S5-31 5-Speed Manual Transmission
The ZF S5-31 5-speed manual transmission stands as a testament to German engineering excellence and robust construction, designed to provide decades of reliable service in demanding truck and SUV applications while maintaining the refinement expected from premium automotive components.
Developed by ZF, one of the world’s leading transmission manufacturers, the S5-31 incorporates heavy-duty design elements and manufacturing techniques that ensure exceptional durability under the most challenging operating conditions.
ZF’s engineering philosophy emphasizes robust construction and long-term reliability, characteristics that define every aspect of the S5-31’s design and manufacturing.
The transmission was specifically developed for high-torque applications where durability and reliability take precedence over weight considerations, resulting in a gearbox that can handle extreme loads while maintaining smooth, precise operation throughout its extended service life.
The transmission case represents a masterpiece of casting and machining technology, utilizing high-strength aluminum alloy with thick walls and extensive internal ribbing that provides exceptional rigidity.
The case design incorporates multiple mounting points with reinforced areas that distribute loads evenly, preventing stress concentrations that could lead to cracking or distortion. The bearing supports are generously sized and precisely machined to maintain proper preload and alignment throughout the transmission’s service life.
Internal components showcase ZF’s expertise in heavy-duty transmission design, featuring gear sets manufactured from premium steel alloys that undergo extensive heat treatment processes to achieve optimal hardness and toughness characteristics.
The gear teeth are precision-cut with profiles optimized for maximum strength while maintaining smooth operation and minimal noise generation. The manufacturing tolerances are held to extremely tight specifications that ensure proper load distribution and extended service life.
The synchronizer system within the S5-31 utilizes advanced multi-cone designs with large-diameter synchronizer rings that provide smooth engagement even under high-torque conditions.
The synchronizers feature aggressive cone angles and advanced friction materials that maintain effectiveness throughout their service life, enabling smooth shifts regardless of load conditions or operating temperature. The generous sizing ensures adequate torque capacity for even the most demanding applications.
Differential construction reflects ZF’s commitment to durability, featuring robust side gears and differential case assembly that can handle extreme torque loads without premature wear.
The ring and pinion gears are precision-manufactured with optimized tooth contact patterns that ensure smooth operation and long service life. The differential assembly is designed to accommodate both open and limited-slip configurations, providing versatility for various applications.
The shift mechanism design emphasizes durability and precision, featuring a rugged shifter assembly with clearly defined gates and positive engagement characteristics.
The shifter components are manufactured from high-strength materials with generous sizing that prevents wear and maintains precise operation throughout the transmission’s service life. The shift effort is calibrated to provide appropriate feedback while remaining manageable during extended operation.
Lubrication system design demonstrates ZF’s attention to critical details, incorporating strategically positioned oil passages that ensure adequate lubrication reaches all components regardless of operating angle or load conditions.
The system features provisions for both splash and pressure lubrication, with oil pumps and passages designed to maintain consistent flow under extreme operating conditions. The generous oil capacity provides thermal mass that helps regulate operating temperatures.
Maintenance requirements for the S5-31 reflect its heavy-duty design philosophy, with extended service intervals that reduce operating costs while maintaining reliability.
The transmission typically requires only periodic fluid changes with ZF’s specified heavy-duty gear oil, with many examples operating trouble-free for over 300,000 miles with basic maintenance. The robust construction and high-quality components result in exceptional longevity even under severe service conditions.
The S5-31’s reputation extends far beyond its original applications, with the transmission becoming a popular choice for custom builds and conversions where ultimate durability is required.
The transmission’s ability to handle extreme torque loads while maintaining smooth operation makes it ideal for high-performance diesel applications and heavy-duty commercial use where reliability is paramount.
Performance testing has demonstrated the S5-31’s exceptional capabilities in both commercial and performance applications, with examples regularly handling torque loads that would destroy lesser transmissions.
The conservative ratings and robust construction provide substantial safety margins that ensure reliable operation even under extreme conditions, making the S5-31 a preferred choice for applications where failure is not acceptable.
5 Manual Transmissions That Grind Constantly
These problematic gearboxes suffer from persistent grinding issues due to inadequate synchronizer design, poor manufacturing tolerances, and insufficient lubrication systems that create constant shifting difficulties and accelerated component wear throughout normal driving operations and maintenance cycles.
Their troublesome engineering includes weak synchro rings, basic gear metallurgy, and problematic shift linkage designs that amplify the grinding symptoms typically associated with premature wear or inadequate fluid protection during temperature cycling.
From second gear grinding that makes smooth acceleration impossible to reverse gear conflicts that require excessive force during parking maneuvers, these transmissions demand careful shifting techniques and frequent repairs.
Owners discover that while these vehicles may offer attractive pricing and performance potential, their transmission reliability creates persistent driving frustration and requires expensive rebuilding procedures or replacement components to achieve acceptable shifting quality and maintain safe operation.
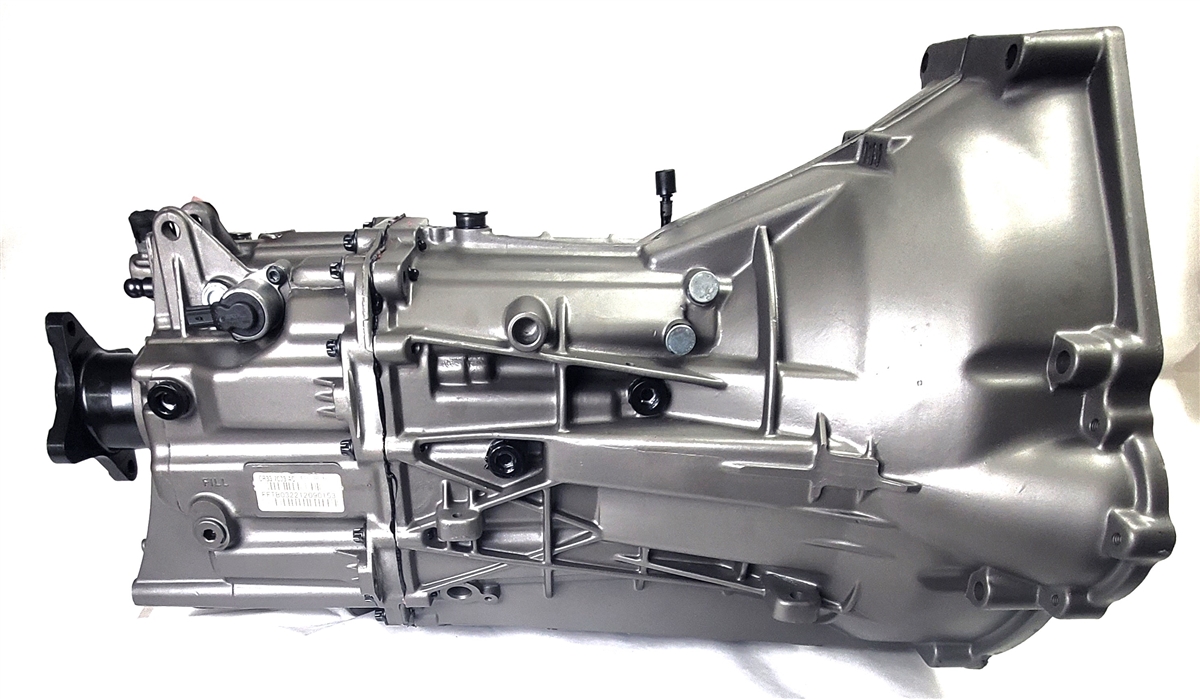
1. Ford MT-82 6-Speed Manual Transmission
The Ford MT-82 6-speed manual transmission represents one of the most problematic manual gearboxes in recent automotive history, plaguing Ford Mustang owners with a litany of issues that range from annoying to downright dangerous.
Introduced in 2011 as the standard transmission for the Mustang GT, the MT-82 was intended to provide improved fuel economy and performance compared to its predecessor, but instead delivered years of frustration for owners and substantial warranty costs for Ford Motor Company.
The fundamental problems with the MT-82 stem from cost-cutting measures and inadequate development testing that resulted in numerous design flaws and manufacturing defects.
Ford’s decision to outsource the transmission’s development and manufacturing to Getrag while imposing strict cost targets led to compromises in materials quality and design robustness that would plague the transmission throughout its production run. The rushed development schedule prevented adequate real-world testing that might have identified these issues before production began.
Synchronizer problems represent the most common and frustrating issue with the MT-82, with countless owners reporting grinding noises during shifts, particularly when shifting into second and third gears.
The synchronizer rings are inadequately sized for the transmission’s torque capacity and feature friction materials that wear rapidly under normal driving conditions. The cone angles are poorly optimized, resulting in inadequate engagement force and premature wear that leads to grinding and difficult shifting within relatively few miles.
The shift mechanism design compounds the synchronizer problems, featuring a poorly designed shifter assembly with excessive play and imprecise gate definition.
The shifter bushings are undersized and manufactured from inferior materials that wear rapidly, creating additional play that makes precise shifting difficult. The shift cables feature inadequate support and routing that allows them to bind and stretch over time, further degrading shift quality and contributing to synchronizer wear.
Internal component quality represents another major issue with the MT-82, with numerous reports of premature gear wear, bearing failures, and case cracking. The gear teeth feature inadequate surface hardness and poor heat treatment that results in accelerated wear under normal operating conditions.
The bearing assemblies are undersized for the loads they must support, leading to premature failure and costly repairs that often occur well before warranty expiration.
Manufacturing quality control appears inconsistent across production runs, with some transmissions exhibiting problems from delivery while others develop issues gradually over time.
The assembly tolerances vary significantly between units, resulting in inconsistent shift quality and reliability even among identical vehicles. This inconsistency suggests inadequate quality control procedures and insufficient testing during the manufacturing process.
The lubrication system design contributes to premature wear and component failure, with inadequate oil flow to critical components and poor thermal management that allows temperatures to reach damaging levels.
The oil passages are poorly positioned and inadequately sized, preventing proper lubrication during aggressive driving or extended operation. The oil capacity is insufficient for the transmission’s heat generation, leading to accelerated degradation of lubricant properties.
Warranty claims for the MT-82 reached epidemic proportions, with Ford ultimately extending warranty coverage and issuing multiple technical service bulletins addressing various issues.
Many owners experienced multiple transmission replacements under warranty, only to have replacement units develop similar problems within thousands of miles. The warranty extensions and replacement costs represented a significant financial burden for Ford and a major source of customer dissatisfaction.
Attempted fixes and updates proved largely ineffective, with Ford releasing multiple software updates, revised synchronizer designs, and modified lubricants that failed to address the fundamental design flaws.
Many owners resorted to aftermarket solutions including short-throw shifters, modified bushings, and alternative lubricants in attempts to improve reliability and shift quality, often with limited success.
The MT-82’s problems extend beyond mere inconvenience, with numerous reports of complete transmission failures that left owners stranded and facing expensive repairs.
The unpredictable nature of these failures, combined with the transmission’s poor reputation, significantly impacted resale values and owner satisfaction with affected vehicles. Many enthusiasts specifically avoided Mustangs equipped with the MT-82, preferring automatic-equipped models or seeking earlier vehicles with different transmissions.
Performance applications proved particularly problematic for the MT-82, with modified vehicles experiencing accelerated failure rates and more severe symptoms.
The transmission’s marginal design provides little safety margin for increased power levels, making it unsuitable for performance modifications that are common among Mustang owners. This limitation further damaged the transmission’s reputation among the enthusiast community that represents a significant portion of Mustang buyers.
2. Chrysler NV3500 5-Speed Manual Transmission
The Chrysler NV3500 5-speed manual transmission stands as one of the most problematic and frustrating gearboxes ever installed in American trucks and SUVs, earning a reputation for premature failure and expensive repairs that plagued Dodge and Jeep owners throughout the 1990s and early 2000s.
Originally developed as a cost-effective solution for light truck applications, the NV3500 instead became synonymous with reliability problems and poor durability that made it one of the most dreaded transmissions in automotive history.
The fundamental issues with the NV3500 stem from a combination of inadequate design and poor manufacturing quality that resulted in numerous failure modes affecting virtually every major component.
Chrysler’s decision to develop the transmission in-house while maintaining aggressive cost targets led to compromises in materials quality and design robustness that would prove catastrophic in real-world applications.
The transmission’s problems were so widespread that entire online communities developed around troubleshooting and replacing failed NV3500 units.
Fifth gear failure represents the most notorious and common problem with the NV3500, with countless owners experiencing complete fifth gear destruction that leaves metal debris throughout the transmission case.
The fifth gear design features inadequate support and insufficient material thickness that cannot handle the loads imposed during highway driving. The gear teeth are poorly designed with stress concentrations that lead to rapid crack propagation and catastrophic failure, often without warning.
The synchronizer system design represents another major weakness, with undersized synchronizer rings and inadequate friction materials that wear rapidly under normal operating conditions.
The synchronizers are particularly problematic in third and fourth gears, where inadequate cone angles and poor surface treatments result in grinding and difficult shifting within relatively few miles. The synchronizer assembly lacks adequate support structure, allowing deflection that accelerates wear and reduces effectiveness.

Bearing failures plague the NV3500 throughout its service life, with numerous reports of premature bearing collapse that leads to gear misalignment and accelerated wear.
The bearing assemblies are undersized for the loads they must support, while the bearing races feature inadequate surface hardness that allows rapid wear development. The bearing lubrication is inadequate due to poor oil flow design, exacerbating wear rates and reducing service life significantly below acceptable levels.
The shift mechanism represents another source of constant problems, featuring a poorly designed shifter assembly with excessive play and imprecise operation.
The shift forks are manufactured from inadequate materials with insufficient strength for the loads imposed during gear changes. The detent system is poorly designed, featuring weak springs and improper geometry that allow gears to pop out of engagement during operation, creating hazardous driving conditions.
Case integrity problems affect many NV3500 transmissions, with reports of cracking around bearing supports and mounting points that compromise structural integrity.
The aluminum case features inadequate wall thickness in critical areas, while the casting quality varies significantly between production runs. The case design lacks adequate ribbing and reinforcement, allowing deflection under load that accelerates bearing wear and gear misalignment.
Manufacturing quality control appears to have been inconsistent throughout the NV3500’s production run, with significant variations in component quality and assembly tolerances between individual units.
Many transmissions exhibited problems from delivery, while others developed issues gradually over time. This inconsistency suggests inadequate quality control procedures and insufficient testing during development and production phases.
The lubrication system design contributes significantly to the transmission’s reliability problems, with inadequate oil flow to critical components and poor thermal management that allows damaging temperatures to develop.
The oil passages are poorly positioned and inadequately sized, preventing proper lubrication during normal operation. The oil pump design is marginal, providing insufficient flow under high-load conditions when lubrication is most critical.
Repair attempts often prove futile due to the transmission’s fundamental design weaknesses, with rebuilt units frequently developing the same problems as original equipment.
The replacement parts market features numerous quality issues, with many aftermarket components failing to address the root causes of failure. Complete transmission replacement often represents the only viable solution, resulting in expensive repairs that frequently exceed the vehicle’s value.
The NV3500’s problems created significant financial burdens for owners, with repair costs often reaching thousands of dollars for transmissions that failed well before reasonable service life expectations.
The unpredictable nature of failures meant that owners could face sudden, expensive repairs without warning, while the transmission’s poor reputation significantly impacted the resale values of affected vehicles.
Performance applications proved particularly problematic for the NV3500, with any increase in power or torque leading to accelerated failure rates and more severe damage
The transmission’s marginal design provides no safety margin for modifications, making it completely unsuitable for performance applications. Many owners of modified vehicles experienced catastrophic failures within thousands of miles of installation.
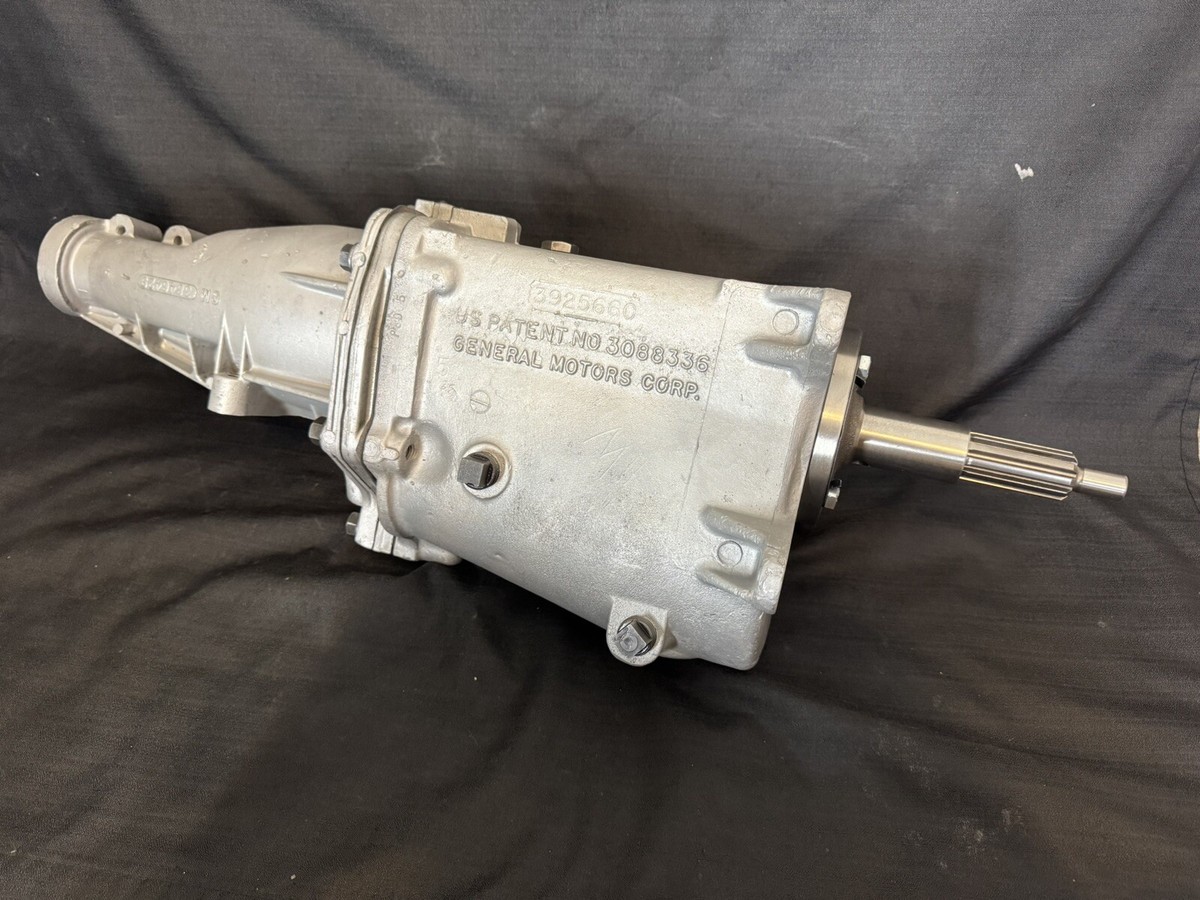
3. General Motors Muncie M22 “Rock Crusher” 4-Speed Manual Transmission
The General Motors Muncie M22 “Rock Crusher” 4-speed manual transmission, while legendary for its strength in high-performance applications, earned its notorious nickname due to the excessive noise it generated during operation, making it one of the most unpleasant transmissions to live with on a daily basis.
Originally designed for high-performance muscle cars of the late 1960s and early 1970s, the M22’s straight-cut gear design created a constant whining noise that made normal conversation difficult and contributed to driver fatigue during extended operation.
The fundamental issue with the M22 stems from General Motors’ decision to use straight-cut gears throughout the transmission to maximize strength for drag racing applications.
While this design choice provided exceptional durability under extreme loads, it resulted in excessive noise generation that made the transmission unsuitable for street driving.
The straight-cut gears create constant mesh contact that generates harmonic vibrations and noise that resonates throughout the vehicle structure, creating an unpleasant driving experience.
Synchronizer design represents another major weakness of the M22, with inadequate synchronizer rings and poor friction materials that provided minimal assistance during gear changes.
The synchronizers were sized more for durability than smooth operation, resulting in difficult shifts that required careful throttle matching and precise timing.
The brass synchronizer rings wore rapidly under normal driving conditions, leading to grinding and clashing during gear changes that could damage gear teeth over time.
The shift mechanism design prioritized strength over refinement, featuring heavy-duty components that required substantial effort to operate effectively.
The shifter mechanism featured wide gate spacing and long throws that made rapid gear changes difficult and tiring during extended driving sessions.
The detent system was designed for positive engagement rather than smooth operation, resulting in notchy shifts that lacked the refinement expected in street applications. Lubrication challenges plagued the M22 due to the high-speed operation of straight-cut gears that created excessive heat and churning losses.
The transmission required frequent oil changes with expensive racing lubricants to maintain adequate protection for the gear teeth and bearings. The oil capacity was insufficient for extended highway operation, leading to overheating and accelerated wear during normal driving conditions.

The noise characteristics of the M22 extended beyond mere inconvenience, with the constant whining creating driver fatigue and making radio or conversation impossible at highway speeds.
The harmonic vibrations transmitted through the drivetrain and chassis structure created sympathetic vibrations in body panels and interior components that added to the overall noise level. Many owners resorted to extensive sound deadening modifications with limited effectiveness.
Gear ratio spacing in the M22 was optimized for drag racing rather than street driving, resulting in large gaps between gears that made smooth acceleration difficult.
The wide ratio spreads required frequent shifting during normal driving conditions, while the lack of an overdrive gear resulted in high engine speeds during highway cruising. This poor ratio selection contributed to increased fuel consumption and engine wear during street driving.
Manufacturing tolerances in the M22 were held to racing standards rather than production requirements, resulting in inconsistent build quality and performance between individual units.
Some transmissions exhibited acceptable noise levels while others were nearly unbearable, depending on assembly tolerances and individual component variations. This inconsistency made it impossible to predict the characteristics of any particular transmission.
The M22’s reputation for strength came at the cost of everyday usability, with the transmission requiring specialized knowledge and techniques for smooth operation.
The heavy shift effort and difficult synchronization made the transmission challenging for inexperienced drivers, while the constant noise made it unsuitable for family use or daily driving. Many owners eventually replaced their M22 transmissions with more civilized alternatives despite the strength advantages.
Maintenance requirements for the M22 exceeded typical transmission service intervals due to the high-stress operating conditions created by the straight-cut gear design.
The transmission required frequent inspections and oil changes with expensive racing lubricants to maintain reliability. The aggressive gear design created metal particles that contaminated the oil rapidly, requiring more frequent service than conventional helical-gear transmissions.
Cost considerations made the M22 impractical for most applications, with the transmission commanding premium prices both new and in the current collector market.
The specialized nature of the transmission meant that service and repair required experienced technicians familiar with racing transmission requirements. Replacement parts were expensive and often difficult to obtain, making maintenance costly and time-consuming.
The M22’s legacy remains complicated, with the transmission achieving legendary status among drag racers while being remembered as one of the most unpleasant street transmissions ever produced.
The “Rock Crusher” nickname perfectly captured the transmission’s dual nature: incredibly strong but nearly unbearable for normal driving. Modern enthusiasts often seek M22 transmissions for period-correct restorations while fully understanding the compromises involved in daily operation.
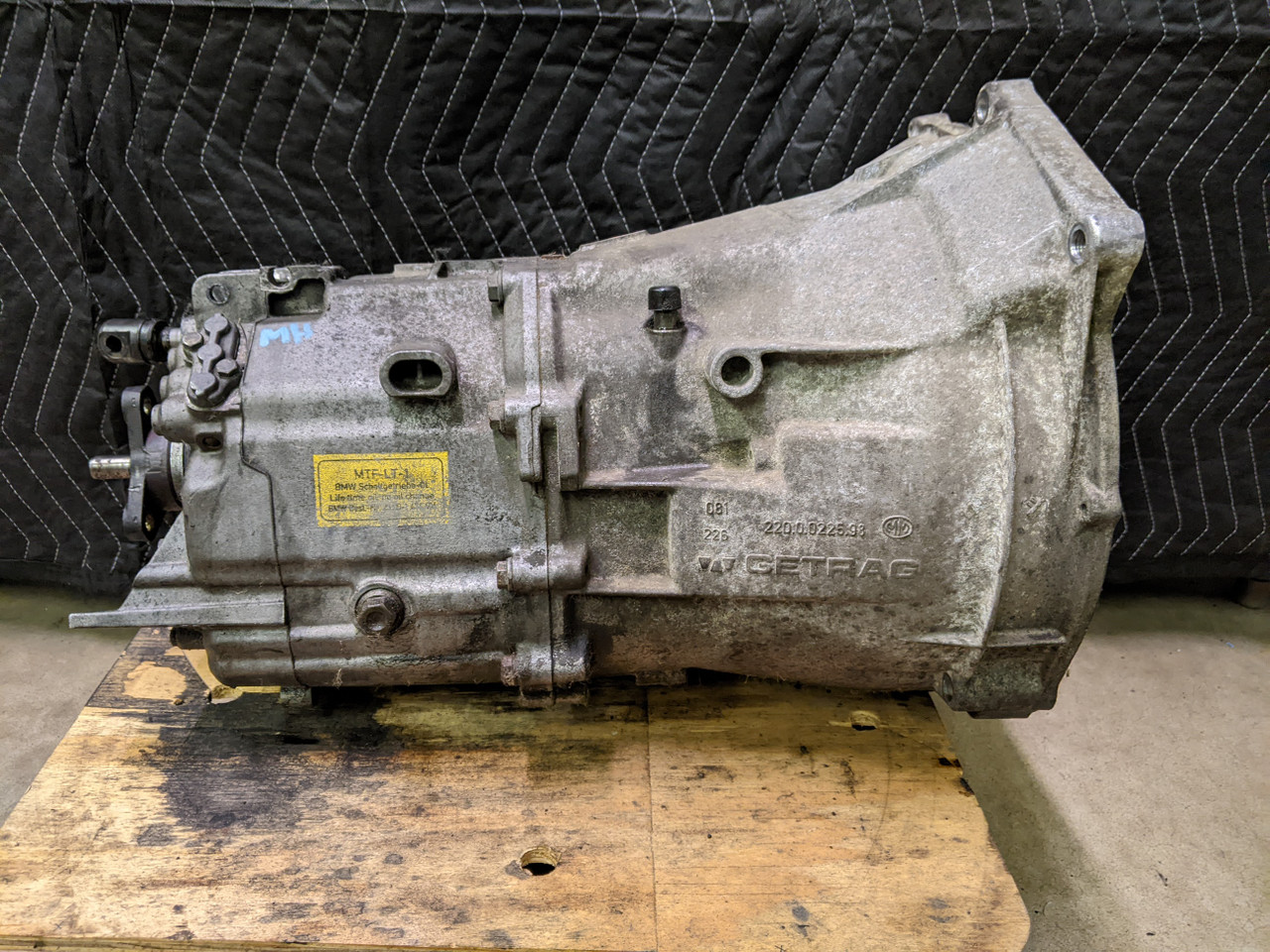
4. BMW Getrag 250G 5-Speed Manual Transmission
The BMW Getrag 250G 5-speed manual transmission represents one of the most problematic and short-lived collaborations between BMW and Getrag, suffering from fundamental design flaws and manufacturing defects that plagued BMW owners throughout the early 1990s.
Originally intended to provide improved refinement and durability compared to earlier transmissions, the 250G instead delivered years of frustration through premature failures and expensive repairs that tarnished both BMW’s and Getrag’s reputations for engineering excellence.
The primary issues with the 250G stem from inadequate development testing and a rushed introduction that failed to identify critical design weaknesses before production began.
BMW’s pressure to reduce costs while improving performance led to compromises in materials quality and design robustness that would prove catastrophic in real-world applications.
The transmission’s problems were so severe that BMW quietly discontinued its use and reverted to earlier designs while working on replacement solutions.
Synchronizer failure represents the most common and frustrating problem with the 250G, with owners reporting grinding noises and difficult shifting within relatively low mileage.
The synchronizer rings feature inadequate friction materials and poor cone geometry that provides insufficient engagement force for smooth operation.
The synchronizers are undersized for the transmission’s torque capacity, leading to rapid wear and premature failure that requires expensive repair or replacement.
The input shaft design represents a fundamental flaw that affects the transmission’s reliability and durability throughout its service life. The input shaft features an inadequate diameter and an insufficient support bearing arrangement that allows excessive deflection under load.
This deflection creates misalignment between gear sets that accelerates wear and reduces shift quality, while also creating stress concentrations that can lead to shaft failure in extreme cases.
Fifth gear problems plague many 250G transmissions, with reports of gear tooth chipping and complete gear failure that scatters metal debris throughout the transmission case.
The fifth gear design features inadequate material thickness and poor heat treatment that results in insufficient durability for highway driving conditions. The gear support arrangement allows excessive deflection that creates uneven loading and accelerated wear patterns.
The differential assembly represents another weak point in the 250G design, with numerous reports of premature side gear wear and differential case cracking.
The differential components are inadequately sized for the loads imposed by BMW’s increasingly powerful engines, while the materials quality appears inconsistent between production runs. The differential lubrication is marginal due to poor oil flow design, exacerbating wear rates and reducing service life.
Shift mechanism problems affect virtually all 250G transmissions as they accumulate mileage, with the shifter developing excessive play and imprecise operation.
The shift cables feature inadequate support and poor routing that allows binding and stretching over time, degrading shift quality and contributing to synchronizer wear. The shifter bushings are manufactured from inferior materials that wear rapidly, creating additional play that makes precise shifting difficult.
Manufacturing quality control appears to have been inadequate during the 250G’s production run, with significant variations in component quality and assembly tolerances between individual units.
Many transmissions exhibited problems from delivery, while others developed issues gradually over time as design weaknesses manifested themselves. This inconsistency suggests insufficient quality control procedures and inadequate testing protocols during development.
The lubrication system design contributes to many of the 250G’s reliability problems, with inadequate oil flow to critical components and poor thermal management that allows damaging temperatures to develop.
The oil passages are poorly positioned and inadequately sized, preventing proper lubrication during high-load operation when protection is most critical. The oil pump design is marginal, providing insufficient flow under demanding conditions.
Repair costs for the 250G often exceed the vehicle’s value, particularly for older BMW models where transmission replacement represents a significant financial burden.
The complexity of the transmission’s problems means that partial repairs are often unsuccessful, with rebuilt units frequently developing the same issues as original equipment. Many owners face the difficult decision between expensive transmission replacement and vehicle disposal.
The 250G’s problems significantly impacted BMW’s reputation for engineering excellence, with the transmission becoming a cautionary tale about rushed development and inadequate testing.
BMW’s decision to quietly discontinue the transmission while reverting to earlier designs demonstrated the severity of the issues and the company’s recognition that the 250G was fundamentally flawed beyond reasonable repair.
Performance applications proved particularly problematic for the 250G, with any increase in power or torque leading to accelerated failure rates and more severe damage.
The transmission’s marginal design provides no safety margin for modifications, making it completely unsuitable for performance applications that are common among BMW enthusiasts. Many owners of modified vehicles experienced catastrophic failures within thousands of miles.
5. Volkswagen 020 5-Speed Manual Transmission
The Volkswagen 020 5-speed manual transmission represents one of the most problematic and frustrating gearboxes in Volkswagen’s history, plaguing owners of various VW and Audi models throughout the 1980s and 1990s with a seemingly endless array of reliability issues and expensive repairs.
Originally designed as a cost-effective solution for front-wheel-drive applications, the 020 instead became synonymous with premature failure and poor durability that damaged Volkswagen’s reputation for engineering excellence.
The fundamental problems with the 020 stem from cost-cutting measures and inadequate development testing that resulted in numerous design compromises and manufacturing defects.
Volkswagen’s pressure to reduce production costs while meeting increasingly stringent fuel economy and emissions requirements led to decisions that prioritized short-term savings over long-term reliability. The transmission’s problems were so widespread that entire service industries developed around rebuilding and replacing failed 020 units.
Final drive failure represents the most catastrophic and expensive problem associated with the 020 transmission, with countless owners experiencing complete differential destruction that requires full transmission replacement.
The final drive assembly features inadequate bearing support and insufficient lubrication which leads to premature bearing failure and subsequent gear destruction.
The ring and pinion gears are undersized for the loads imposed by increasingly powerful engines, while the differential case lacks adequate reinforcement to prevent cracking under stress.
Synchronizer problems plague the 020 throughout its service life, with owners reporting grinding noises and difficult shifting that progressively worsen over time.
The synchronizer rings are manufactured from inferior materials with inadequate friction characteristics that wear rapidly under normal operating conditions.
The cone angles are poorly optimized, resulting in insufficient engagement force and accelerated wear that leads to grinding and clash during gear changes.
Input shaft bearing failure represents another common and expensive problem with the 020, often occurring without warning and resulting in complete transmission failure.
The input shaft bearing is undersized for the loads it must support, while the bearing race features inadequate surface hardness that allows rapid wear development. The bearing lubrication is marginal due to poor oil flow design, contributing to premature failure and catastrophic damage to surrounding components.
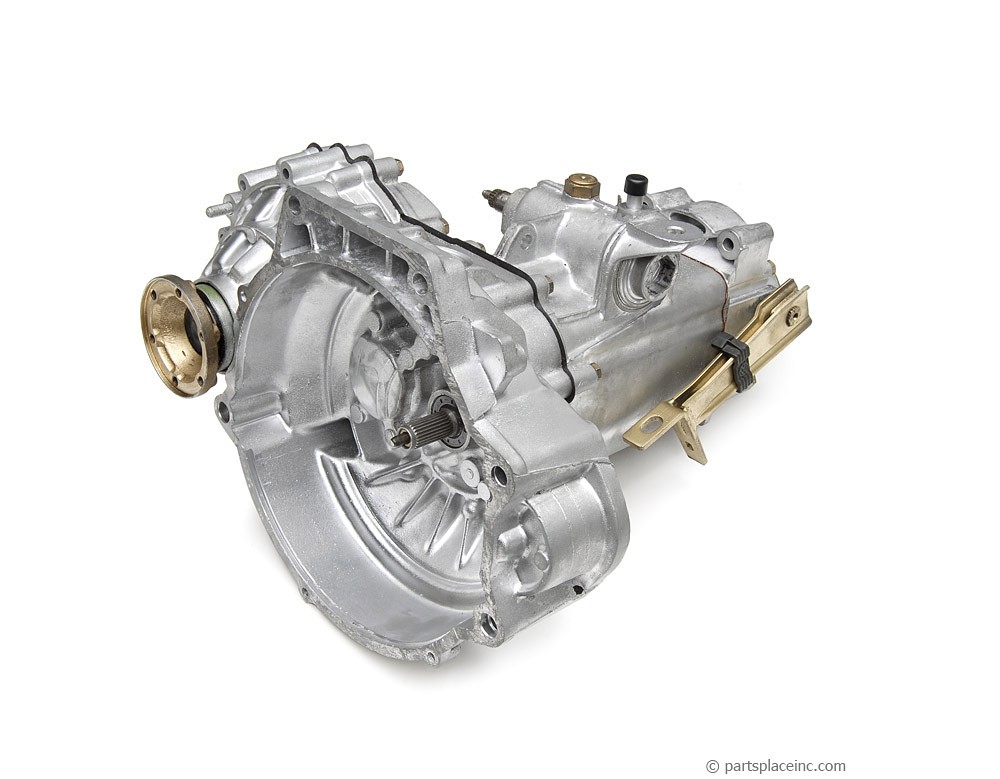

The case design represents a fundamental weakness in the 020’s construction, with numerous reports of cracking around bearing supports and mounting points that compromise structural integrity.
The aluminum case features inadequate wall thickness in critical areas, while the casting quality varies significantly between production runs. The case lacks adequate ribbing and reinforcement, allowing deflection under load that accelerates bearing wear and creates misalignment problems.
Shift mechanism design contributes to the 020’s reputation for poor operation, with a shifter assembly that develops excessive play and imprecise gate definition as mileage accumulates.
The shift cables feature inadequate support and poor routing that allows them to stretch and bind over time, degrading shift quality and contributing to synchronizer wear. The shifter bushings are manufactured from inferior materials that wear rapidly, creating additional play that makes precise shifting increasingly difficult.
Fifth gear problems affect many 020 transmissions, particularly those used in highway driving applications where the gear experiences constant loading. The fifth gear assembly features an inadequate support structure and insufficient material thickness that cannot handle sustained high-speed operation.
The gear teeth are poorly designed with stress concentrations that lead to crack initiation and propagation, often resulting in complete gear failure that scatters debris throughout the transmission.
Manufacturing quality control appears inconsistent throughout the 020’s production run, with significant variations in component quality and assembly tolerances between individual units and production facilities.
Many transmissions exhibited problems from delivery, while others developed issues gradually as design weaknesses manifested themselves under normal operating conditions. This inconsistency suggests inadequate quality control procedures and insufficient testing during both development and production phases.
The lubrication system design represents another source of reliability problems, with inadequate oil capacity and poor thermal management that allows damaging temperatures to develop during normal operation.
The oil passages are poorly positioned and inadequately sized, preventing proper lubrication of critical components during high-load conditions. The oil pump design is marginal, providing insufficient flow when protection is most needed.
Repair costs for the 020 often approach or exceed the value of affected vehicles, particularly for older models where transmission replacement represents a significant financial burden.
The complexity of the transmission’s problems means that partial repairs are often unsuccessful, with rebuilt units frequently developing similar issues within relatively short periods. Many owners face difficult decisions between expensive repairs and vehicle replacement.
The 020’s problems created significant warranty costs for Volkswagen and contributed to declining customer satisfaction scores throughout the 1980s and 1990s.
The transmission’s poor reputation became widely known among automotive enthusiasts and mechanics, leading many potential buyers to avoid affected models entirely. The reliability issues significantly impacted resale values and contributed to Volkswagen’s struggles in the North American market during this period.
Performance applications proved completely unsuitable for the 020, with even modest power increases leading to immediate and catastrophic failure.
The transmission’s marginal design provides no safety margin for modifications, making it one of the first components to fail in modified vehicles. Many enthusiasts learned to budget for immediate transmission replacement when planning performance modifications for 020-equipped vehicles.
Also Read: 5 Sedans With the Best Biometric Entry and 5 With Only Key Fobs