The GMC Envoy, produced from 2002 to 2009, represents a rugged mid-size SUV that has earned a reputation for durability when properly maintained.
While many vehicles struggle to reach the 200,000-mile mark, achieving 300,000 miles with a GMC Envoy is entirely possible with the right maintenance approach and preventive care strategies. This comprehensive guide reveals the essential tricks that separate high-mileage survivors from vehicles that fail prematurely.
The key to GMC Envoy longevity lies in understanding its most vulnerable systems and addressing them proactively. The 4.2-liter inline-six engine, while generally reliable, requires specific maintenance intervals to prevent costly failures.
The 4L60E automatic transmission, a known weak point in these vehicles, demands particular attention to fluid quality and cooling system integrity. Additionally, the transfer case, differential, and suspension components need regular inspection and service to maintain optimal performance throughout the vehicle’s extended lifespan.
Successful high-mileage GMC Envoy ownership requires more than following the basic maintenance schedule. It demands understanding the vehicle’s engineering quirks, recognizing early warning signs of potential problems, and implementing preventive measures before minor issues become major repairs.
This proactive approach, combined with quality parts and proper procedures, transforms what could be a maintenance nightmare into a reliable, long-lasting vehicle capable of serving faithfully for decades.
The investment in preventive maintenance pays dividends in reduced repair costs, improved reliability, and extended vehicle life well beyond typical expectations.
1. Master the Transmission Maintenance Schedule
The 4L60E automatic transmission in the GMC Envoy is arguably the most critical component requiring meticulous maintenance for achieving 300,000 miles.
This transmission, while capable of reliable service, has specific vulnerabilities that must be addressed through proper fluid maintenance, thermal management, and operational practices.
The key to transmission longevity lies in maintaining optimal fluid quality and preventing overheating, which can quickly destroy internal components.
Begin with establishing a strict fluid change schedule every 30,000 miles, regardless of what the owner’s manual suggests for “normal” driving conditions.
The reality is that most driving patterns involve stop-and-go traffic, towing, or temperature extremes that qualify as “severe service.” Use only genuine GM Dexron VI transmission fluid, as aftermarket alternatives may not provide the same level of protection for the transmission’s delicate internal components.
During each service, replace the transmission filter and inspect the pan for metal particles that could indicate internal wear. Temperature management proves crucial for transmission survival. Install an auxiliary transmission cooler if your Envoy regularly tows trailers or operates in hot climates.

Monitor transmission fluid temperatures using an aftermarket gauge, keeping operating temperatures below 200°F whenever possible. Temperatures above 220°F dramatically accelerate fluid degradation and internal component wear.
Additionally, avoid aggressive driving habits like rapid acceleration from stops or prolonged high-speed operation, which generate excessive heat and stress transmission components.
Pay attention to early warning signs of transmission problems, including delayed engagement when shifting from park to drive, harsh or erratic shifting patterns, or unusual noises during operation. Address these symptoms immediately rather than hoping they’ll resolve themselves.
Regular inspection of the transmission cooler lines for leaks and the cooling system’s health ensures adequate heat dissipation. Remember that transmission repairs become exponentially more expensive as problems progress, making early intervention essential for long-term reliability.
Keep software updates current and address any diagnostic trouble codes promptly. This integrated approach to transmission maintenance, combining mechanical care with electronic system health, provides the foundation for achieving exceptional mileage from your GMC Envoy’s drivetrain.
2. Implement Advanced Engine Oil Management
Engine oil management extends far beyond simple oil changes every 3,000 miles. Achieving 300,000 miles from a GMC Envoy’s 4.2-liter inline-six engine requires understanding oil chemistry, filtration systems, and contamination sources that can significantly impact engine longevity.
The key lies in maintaining optimal oil quality while addressing the unique challenges this engine presents over its extended service life. Start by selecting the appropriate oil viscosity and quality level for your driving conditions and climate.
While 5W-30 is typically specified, high-mileage vehicles may benefit from slightly thicker oil, like 5W-40 or 10W-30 in warmer climates to maintain adequate oil pressure as engine clearances increase with wear.
Choose high-quality synthetic or synthetic blend oils that provide better thermal stability and additive packages designed for extended drain intervals. These oils resist breakdown better than conventional oils and provide superior protection against sludge formation and bearing wear.

Implement oil analysis programs to monitor engine health and optimize change intervals. Used oil analysis reveals metal wear patterns, contamination levels, and additive depletion rates, allowing you to identify potential problems before they become failures.
This data helps establish optimal drain intervals based on actual operating conditions rather than arbitrary mileage recommendations. Many high-mileage engines can safely extend oil change intervals with synthetic oils while maintaining superior protection.
Address oil consumption issues proactively as the engine accumulates miles. The 4.2-liter engine may develop slight oil consumption through valve guides or ring wear over time.
Monitor oil levels religiously and maintain proper levels to prevent bearing damage from oil starvation. Consider using high-mileage oil formulations that contain seal conditioners to reduce minor leaks and oil consumption.
Clean the filter mounting surface thoroughly and apply a thin coat of oil to the filter gasket to ensure proper sealing. This comprehensive approach to oil management provides the foundation for exceptional engine longevity in your GMC Envoy.
3. Prioritize Cooling System Integrity
The cooling system serves as the lifeblood of engine longevity, and maintaining its integrity becomes increasingly critical as a GMC Envoy approaches high mileage.
The 4.2-liter engine generates substantial heat, and any cooling system deficiency can quickly lead to catastrophic engine damage. A comprehensive cooling system maintenance program addresses not only the obvious components like the radiator and thermostat, but also the subtle factors that influence cooling efficiency over time.
Begin with establishing a complete cooling system flush schedule every 30,000 miles or three years, whichever comes first. Use only GM-approved coolant (Dex-Cool) and maintain the proper 50/50 mixture ratio for optimal heat transfer and corrosion protection.
However, be aware that Dex-Cool has specific compatibility requirements and can cause problems when mixed with other coolant types. If previous owners used non-Dex-Cool coolants, perform a thorough system flush to remove all traces before introducing the proper coolant.
Thermostats gradually lose their calibration over time, potentially allowing the engine to run too hot or too cool. Either condition reduces efficiency and accelerates wear.

Use genuine GM thermostats with the correct opening temperature for your specific engine configuration. Additionally, replace the radiator cap every time you service the cooling system, as cap seals deteriorate and lose their ability to maintain proper system pressure.
Pay particular attention to the water pump, which typically begins showing signs of wear around 100,000 miles. Listen for bearing noise, check for coolant leaks from the weep hole, and monitor for play in the pump shaft.
Replace the water pump proactively rather than waiting for complete failure, which can leave you stranded and potentially cause engine overheating damage.
When replacing the water pump, also replace the drive belt tensioner and any associated pulleys to ensure reliable operation. Monitor cooling system pressure regularly using a cooling system pressure tester.
Remember that cooling system hoses deteriorate from the inside out, so external appearance may not reflect actual condition. This proactive approach to cooling system maintenance prevents the overheating incidents that frequently end high-mileage vehicle careers prematurely.
4. Master Differential and Transfer Case Service
The GMC Envoy’s four-wheel-drive system includes both a transfer case and front and rear differentials that require specific maintenance attention to achieve 300,000-mile reliability.
These components operate under severe stress and contamination conditions, yet they’re often overlooked until catastrophic failure occurs. Proper maintenance of these drivetrain components ensures smooth operation, prevents costly repairs, and maintains the vehicle’s off-road capability throughout its extended service life.
Establish a differential service schedule every 30,000 miles for both front and rear units. The rear differential, in particular, operates under constant load and generates significant heat during highway driving.
Use the manufacturer-specified gear oil viscosity (typically 75W-90 synthetic gear oil) and add limited-slip additives if equipped with a locking differential.
During service, inspect the magnetic drain plug for metal particles that indicate gear wear. Small amounts of fine metal particles are normal, but large chunks or excessive buildup suggest internal damage requiring immediate attention.
The transfer case requires even more frequent attention due to its complex internal mechanisms and chain-drive operation. Service the transfer case every 25,000 miles using GM-approved transfer case fluid (AutoTrac II fluid for most Envoys).
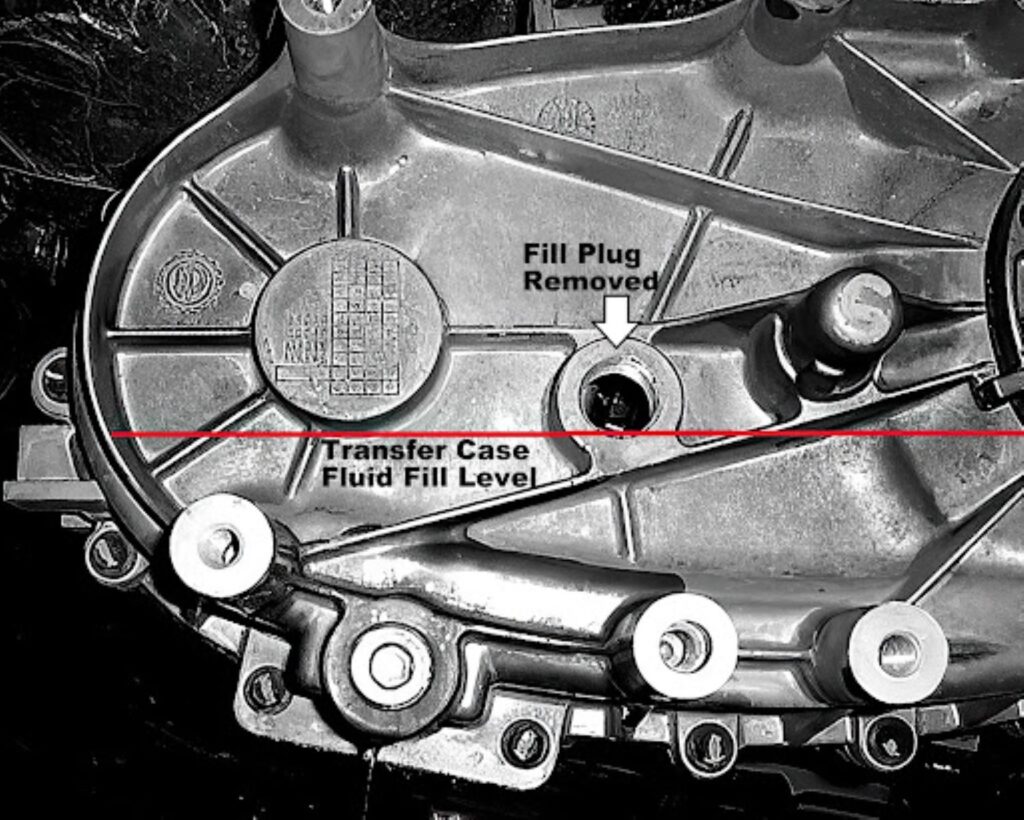
This specialized fluid provides the proper friction characteristics for the clutch packs while protecting chains and gears from wear. Never substitute automatic transmission fluid or other alternatives, as they lack the specific additives required for transfer case operation.
Monitor these components for leaks, unusual noises, or operational problems. Differential leaks often occur at the pinion seal or axle seals and should be repaired immediately to prevent contamination and fluid loss.
Transfer case problems typically manifest as grinding noises during engagement, difficulty shifting between ranges, or binding during turns. Address these symptoms promptly, as continued operation can cause expensive internal damage.
Consider upgrading to synthetic fluids in all drivetrain components for improved protection and extended service life. Synthetic gear oils provide better thermal stability, reduced friction, and improved flow characteristics at temperature extremes.
While more expensive initially, synthetic fluids often allow extended service intervals and provide superior protection against wear. This investment pays dividends in reduced maintenance frequency and improved component longevity, essential factors for achieving 300,000-mile reliability from your GMC Envoy’s drivetrain.
Also Read: 5 Lexuses With Long Engine Life vs. 5 Models With Early Oil Consumption
5. Implement Comprehensive Suspension Maintenance
Suspension system maintenance becomes increasingly important as a GMC Envoy accumulates miles, directly affecting vehicle safety, handling, and component longevity throughout the drivetrain.
The Envoy’s independent front suspension and solid rear axle configuration require specific maintenance approaches to maintain optimal performance and prevent premature wear of expensive components like tires, steering components, and the vehicle’s structure itself.
Begin with regular inspection of all suspension components every 15,000 miles or during routine oil changes. Focus on ball joints, which bear significant loads in the Envoy’s suspension design and tend to wear prematurely under normal operating conditions.
Signs of ball joint wear include clicking noises during turns, uneven tire wear, or play detectable during physical inspection. Replace worn ball joints immediately, as failure can cause loss of vehicle control and potentially catastrophic accidents.
Use high-quality replacement parts with grease fittings when possible to enable future lubrication. Shock absorbers and struts require replacement approximately every 75,000 miles, though this interval may vary based on driving conditions and load carrying.

Worn shock absorbers don’t just affect ride quality; they accelerate tire wear, reduce braking effectiveness, and place additional stress on other suspension components.
Test shock absorber condition by pushing down firmly on each corner of the vehicle and observing the rebound behavior. The vehicle should return to its normal position with minimal oscillation. Replace shocks and struts as complete axle sets to maintain balanced handling characteristics.
Pay special attention to suspension bushings, which deteriorate over time and allow excessive movement between components. Polyurethane bushings offer improved durability compared to rubber alternatives and maintain their dimensional stability longer under stress.
However, they may transmit more noise and vibration to the passenger compartment. Inspect control arm bushings, sway bar bushings, and shock absorber mounts regularly for cracking, tearing, or excessive deformation.
This comprehensive approach to suspension maintenance ensures your GMC Envoy maintains its intended handling characteristics while protecting expensive components throughout its extended service life.
6. Execute Strategic Fuel System Maintenance
Fuel system maintenance becomes increasingly critical as vehicles age, with contamination, component wear, and system deposits threatening engine performance and longevity.
The GMC Envoy’s fuel injection system requires specific maintenance approaches to ensure clean fuel delivery, proper combustion, and emissions compliance throughout the vehicle’s extended service life.
Neglecting fuel system maintenance can lead to expensive injector replacement, fuel pump failure, and catalytic converter damage. Start with fuel filter replacement every 30,000 miles, regardless of manufacturer recommendations for extended intervals.
The fuel filter represents the last line of defense against contamination reaching expensive injection components. A partially restricted filter forces the fuel pump to work harder, potentially reducing its lifespan and affecting fuel pressure regulation.
Use genuine GM fuel filters or high-quality aftermarket alternatives that meet or exceed original equipment specifications. During filter replacement, inspect the fuel lines for signs of deterioration, particularly near heat sources or areas exposed to road salt.
Implement regular fuel system cleaning procedures using high-quality additives designed specifically for gasoline direct injection systems. Add fuel system cleaner every 15,000 miles to prevent deposit buildup on injectors, intake valves, and combustion chambers.

These deposits reduce fuel flow, alter spray patterns, and can cause rough idle, hesitation, and reduced power output. Professional fuel system cleaning services may be necessary every 60,000 miles for vehicles operating in dusty conditions or using lower-quality fuels regularly.
Monitor fuel pump operation and replace proactively around 150,000 miles. Fuel pumps in the GMC Envoy are located inside the fuel tank, making replacement labor-intensive and expensive.
Signs of fuel pump wear include difficulty starting, loss of power under acceleration, or fuel pressure readings outside specification. Don’t wait for complete pump failure, which can leave you stranded and potentially damage other fuel system components. When replacing the fuel pump, also replace the fuel strainer and inspect the tank for contamination.
Pay attention to fuel quality and storage practices, particularly if the vehicle sits unused for extended periods. Use top-tier gasoline brands that contain enhanced detergent packages to prevent deposit formation.
Add fuel stabilizer if the vehicle will be stored for more than 30 days to prevent fuel degradation and gum formation. Keep the fuel tank at least half full to minimize condensation formation, which can cause water contamination and corrosion problems.
This comprehensive approach to fuel system maintenance ensures clean combustion and optimal engine performance throughout your GMC Envoy’s extended service life.
7. Maintain Electrical System Reliability
Electrical system maintenance becomes increasingly challenging as vehicles age, with wire insulation deterioration, connector corrosion, and component failures threatening reliability.
The GMC Envoy’s complex electrical systems control everything from engine management to comfort features, making systematic electrical maintenance essential for achieving 300,000-mile reliability.
A proactive approach to electrical system care prevents the intermittent problems that can be difficult to diagnose and expensive to repair. Begin with battery and charging system maintenance, the foundation of electrical system reliability.
Test battery capacity annually and replace batteries proactively every four to five years, regardless of apparent condition. High-mileage vehicles benefit from slightly larger capacity batteries that provide reserve power during high electrical demand situations.
Clean battery terminals regularly and apply terminal protector spray to prevent corrosion. Inspect the alternator belt for proper tension and condition, as a loose or worn belt can cause charging system problems that damage electrical components.
Address ground connections systematically, as poor grounds cause more electrical problems than any other single factor. Clean and tighten all major ground connections annually, paying particular attention to the engine-to-frame ground strap and body ground points.

Apply dielectric grease to prevent corrosion after cleaning. Many intermittent electrical problems stem from corroded or loose ground connections that create voltage drops and erratic system operation.
Protect wiring harnesses from environmental damage by inspecting routing and securing loose wires away from heat sources, moving parts, and sharp edges. Replace any wire loom or protective covering that shows signs of deterioration.
Pay special attention to areas where wires pass through firewalls or frame members, as these locations are prone to chafing damage. Use proper electrical tape or heat-shrink tubing when making repairs, and avoid using wire nuts or other non-automotive connectors that can cause reliability problems.
Implement preventive replacement schedules for high-failure electrical components like ignition coils, oxygen sensors, and mass airflow sensors. These components typically begin showing signs of wear around 100,000 miles and can cause drivability problems or emissions failures if not replaced proactively.
Use original equipment or high-quality aftermarket replacements that meet OEM specifications. This systematic approach to electrical system maintenance prevents the cascade failures that often occur when one electrical problem causes stress on related components.
8. Optimize Brake System Performance and Longevity
Brake system maintenance extends far beyond simple pad replacement and requires a comprehensive approach to ensure safety and prevent expensive component damage.
The GMC Envoy’s brake system must cope with the vehicle’s substantial weight and potentially heavy towing loads, making systematic maintenance essential for achieving 300,000-mile reliability.
Proper brake maintenance also protects other vehicle systems from the stress of emergency stops and maintains consistent stopping performance throughout the vehicle’s extended service life.
Establish a complete brake fluid flush schedule every two years, regardless of mileage. Brake fluid is hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture from the atmosphere over time.
This moisture lowers the fluid’s boiling point and promotes corrosion within the hydraulic system. Use only DOT 3 brake fluid that meets GM specifications, and never mix different fluid types.
During fluid changes, inspect all brake lines, hoses, and fittings for signs of leakage or deterioration. Replace any rubber brake hoses that show signs of cracking, swelling, or age deterioration.
Monitor brake pad and rotor condition regularly rather than waiting for wear indicators to signal replacement time. Replace brake pads when they reach approximately 30% of their original thickness to prevent rotor damage and maintain optimal stopping performance.
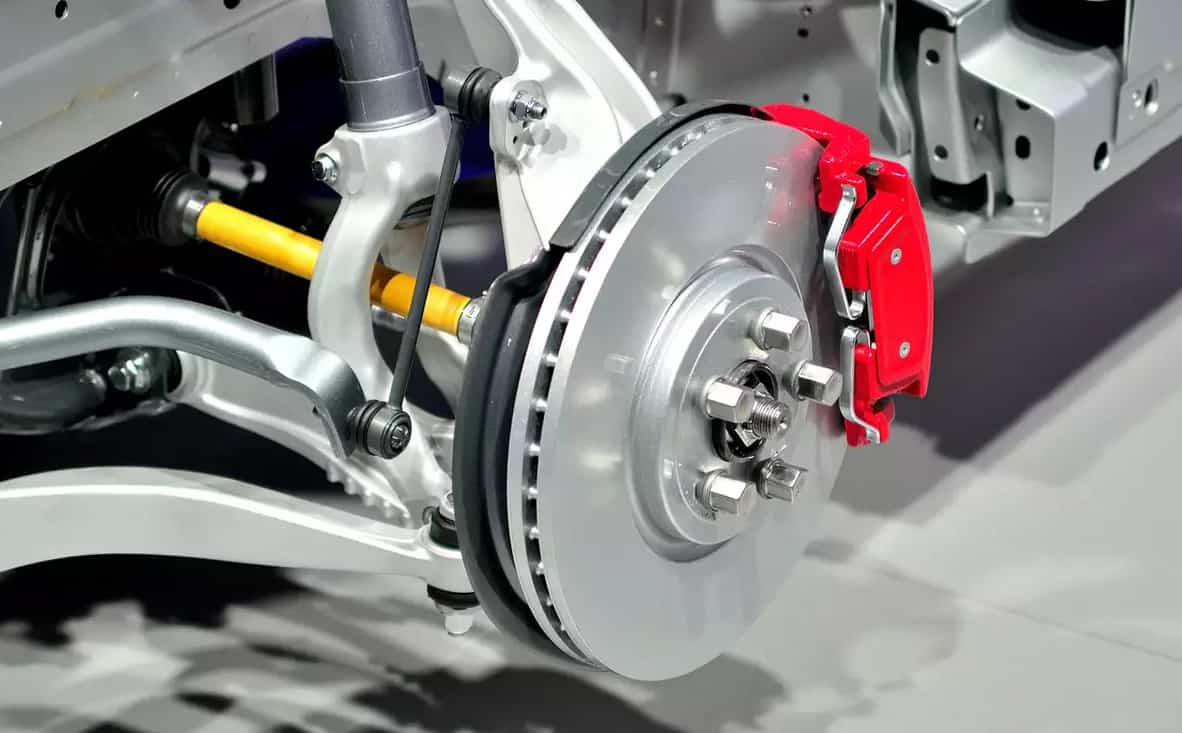

When replacing pads, always resurface or replace rotors to ensure proper pad-to-rotor contact and prevent premature pad wear. Use high-quality brake pads appropriate for your driving style and conditions, avoiding both the cheapest economy pads and unnecessarily expensive racing compounds.
Pay particular attention to the brake caliper operation and maintenance. Lubricate caliper slide pins annually with high-temperature brake grease to ensure even pad wear and prevent caliper binding. Inspect caliper boots for tears or damage that could allow contamination to enter the sliding mechanism.
Replace calipers if they show signs of leakage, binding, or uneven operation. A binding caliper not only reduces braking effectiveness but can also cause rapid pad wear, rotor damage, and potential brake fade during heavy use.
Address parking brake adjustment and maintenance regularly, as this system is often neglected until complete failure occurs. Adjust parking brake cables to maintain proper holding force without dragging during normal operation. Lubricate cable pivot points and inspect cables for fraying or corrosion.
Replace parking brake shoes or pads according to manufacturer recommendations, typically every 75,000 miles. This comprehensive approach to brake system maintenance ensures consistent stopping performance while preventing the expensive repairs that result from deferred brake maintenance.
9. Implement Proactive Timing Chain Maintenance
The GMC Envoy’s 4.2-liter inline-six engine uses a timing chain system that requires specific maintenance attention to prevent catastrophic engine damage.
Unlike timing belts that have specific replacement intervals, timing chains are designed to last the engine’s lifetime under ideal conditions. However, achieving 300,000-mile reliability requires understanding timing chain wear patterns, maintaining proper lubrication, and recognizing early warning signs of potential problems before they become expensive failures.
Monitor timing chain stretch and tensioner operation regularly, particularly after 150,000 miles when wear becomes more noticeable. Signs of timing chain problems include rattling noises during startup, rough idle conditions, or diagnostic trouble codes related to camshaft/crankshaft correlation.
These symptoms indicate that the chain has stretched beyond the tensioner’s ability to maintain proper timing, potentially causing valve-to-piston interference and catastrophic engine damage. Address timing chain noise immediately rather than hoping it will improve with continued operation.
Maintain exceptional oil change intervals and quality to ensure proper timing chain lubrication. The timing chain and tensioners depend entirely on engine oil pressure for proper operation, making oil quality and change intervals critical for long-term reliability.
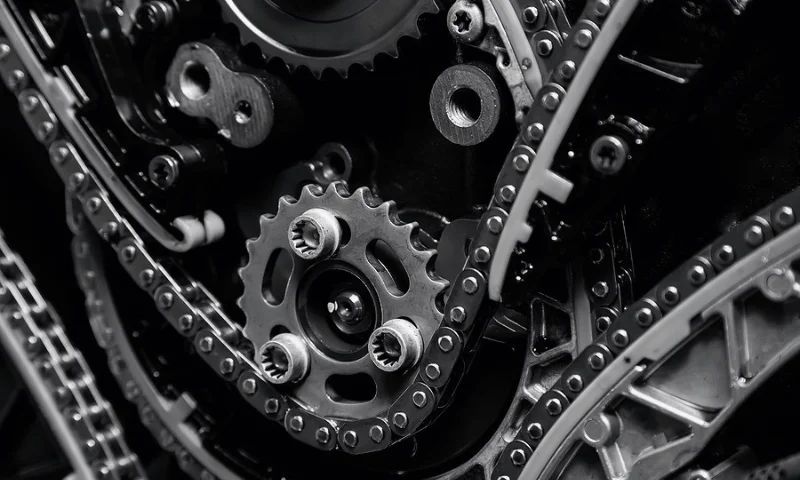

Use high-quality oils with appropriate viscosity ratings and avoid extended drain intervals that could compromise chain lubrication. Monitor oil pressure regularly and address any pressure loss immediately, as inadequate oil pressure can cause rapid timing chain wear and tensioner failure.
Consider proactive timing chain replacement around 200,000 miles if the vehicle shows any signs of chain wear or if you plan to keep the vehicle significantly longer.
While this represents a substantial maintenance investment, it’s considerably less expensive than rebuilding an engine after timing chain failure. When replacing the timing chain, also replace the tensioners, guides, and related components to ensure reliable operation for the next 200,000 miles.
Use genuine GM parts or high-quality aftermarket alternatives that meet OEM specifications. Implement additional monitoring procedures for high-mileage engines, including regular valve adjustment checks and compression testing to verify proper valve timing and sealing.
These tests can reveal timing chain problems before they become critical and help establish optimal replacement timing. Pay attention to fuel economy and power output changes that might indicate timing chain stretch affecting engine performance.
This proactive approach to timing chain maintenance protects your engine investment and ensures reliable operation throughout the vehicle’s extended service life.
10. Master Preventive Component Replacement Strategy
Achieving 300,000-mile reliability requires transitioning from reactive maintenance to a proactive component replacement strategy that addresses wear items before they fail and cause secondary damage.
This approach minimizes roadside breakdowns, prevents cascade failures, and maintains optimal vehicle performance throughout its extended service life.
The key lies in understanding component lifecycles, recognizing interdependencies, and timing replacements to maximize both reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Develop a comprehensive replacement schedule based on component lifecycles rather than arbitrary mileage intervals. Items like water pumps, alternators, and power steering pumps typically begin showing wear around 125,000 miles and should be replaced proactively rather than waiting for failure.
When replacing these components, also service related systems, for example, replace the serpentine belt, tensioner, and idler pulleys when installing a new alternator. This approach reduces labor costs and ensures all related components have similar remaining service life.
Implement strategic component upgrading during replacement cycles to improve long-term reliability. When replacing original equipment parts, consider upgraded alternatives that offer improved durability or performance characteristics.

Examples include using synthetic transmission fluid instead of conventional fluids, installing heavy-duty alternators for improved electrical system capacity, or upgrading to performance-oriented spark plugs for better combustion characteristics.
These upgrades often provide better long-term value than simply replacing worn components with identical parts. Maintain detailed maintenance records that track component replacement dates, mileages, and remaining service life expectations.
This information helps optimize future maintenance timing and identifies patterns that might indicate underlying problems. For example, premature alternator failure might indicate charging system problems that need addressing to prevent repeated failures.
Use this data to refine your maintenance strategy and identify the most cost-effective replacement intervals for your specific driving conditions. Plan major maintenance events to coincide with natural service intervals, minimizing labor costs and vehicle downtime.
For example, schedule timing chain replacement to coincide with a major engine service that requires similar disassembly procedures. This approach maximizes the value of maintenance investments and ensures that related components receive attention when they’re easily accessible.
This investment in preventive maintenance pays dividends in reduced repair costs, improved reliability, and the satisfaction of keeping a well-engineered vehicle performing optimally throughout its extended service life.
Also Read: 5 EV Chargers That Are Easy to Fix vs 5 That Fail in Winter

