The Nissan 240SX stands as one of the most beloved rear-wheel-drive sports cars of the 1990s, cherished by enthusiasts for its balanced chassis, responsive handling, and tremendous modification potential.
However, as these iconic machines age into their third decade, reaching the coveted 200,000-mile milestone requires more than just regular oil changes and wishful thinking.
The SR20DET and KA24DE engines, while robust in design, demand specific attention to detail and proactive maintenance strategies to maintain their reliability and performance.
Achieving high mileage with a 240SX isn’t just about preserving a vehicle it’s about maintaining a piece of automotive history that continues to influence car culture today.
These cars have become increasingly valuable, not just monetarily but as platforms for learning mechanical skills and experiencing pure driving pleasure.
The key to longevity lies in understanding the unique characteristics and common failure points of these vehicles, then implementing a systematic approach to maintenance that addresses both preventive care and performance preservation.
The following ten steps represent a comprehensive strategy developed through decades of collective experience from mechanics, enthusiasts, and long-term owners who have successfully guided their 240SX vehicles well beyond the 200,000-mile threshold while maintaining their spirited character and reliability.
1. Master the Art of Oil Change Intervals and Quality Selection
The foundation of any high-mileage engine program begins with understanding that oil is the lifeblood of your 240SX’s powerplant. Both the naturally aspirated KA24DE and the turbocharged SR20DET engines have specific lubrication needs that become increasingly critical as mileage accumulates.
The key lies not just in changing oil regularly, but in selecting the right oil grade, understanding optimal change intervals, and monitoring oil condition between services.
For the KA24DE engine, synthetic blend or full synthetic oil in 5W-30 viscosity provides the best balance of protection and performance in most climates.
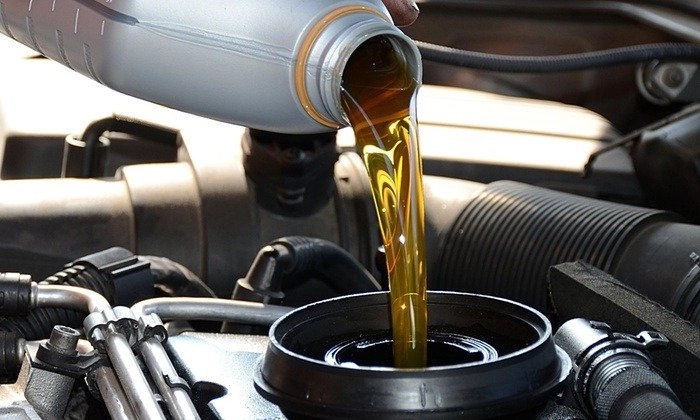

The larger displacement and iron block construction of this engine benefit from the consistent viscosity characteristics that synthetic oils provide, especially during cold starts and high-temperature operation.
Full synthetic oils also resist breakdown under stress better than conventional oils, which becomes crucial as engine components develop normal wear patterns over time.
The oil filter selection is equally important and often overlooked. OEM Nissan filters or equivalent quality aftermarket options from reputable manufacturers provide the best filtration efficiency and bypass valve operation.
Cheap filters can actually harm your engine by allowing contaminants to circulate or by restricting flow when the filter element becomes loaded with particles. Investing in quality filtration pays dividends in engine longevity, especially as internal clearances increase with age.
2. Implement a Comprehensive Cooling System Maintenance Program
The cooling system in a 240SX is the unsung hero of engine longevity, and its proper maintenance becomes absolutely critical as these vehicles age.
Both the KA24DE and SR20DET engines generate substantial heat, and the cooling system must operate flawlessly to prevent the thermal damage that can quickly end an engine’s life.
A comprehensive approach to cooling system maintenance involves understanding the entire system as an interconnected network rather than focusing on individual components. Start with the radiator, which in many 240SX vehicles may still be the original unit from the 1990s.
Aluminum radiators suffer from internal corrosion and external damage over time, leading to reduced heat transfer efficiency and potential leaks. Upgrading to a quality aluminum radiator with an improved core design not only increases cooling capacity but also reduces weight.

Companies like Koyo, Mishimoto, and ISR offer direct-fit replacements that provide superior cooling performance compared to aging factory units. The water pump requires particular attention as these vehicles age.
The OEM water pumps use impellers that can experience cavitation damage or corrosion over time, reducing coolant flow and causing hot spots within the engine.
When replacing the water pump, it’s wise to upgrade to an improved design or, at a minimum, use genuine OEM parts rather than cheap aftermarket alternatives. The timing of water pump replacement often coincides with timing belt service, making it a logical time to address both components simultaneously.
Coolant selection and maintenance intervals deserve special consideration in aging vehicles. Use high-quality extended-life coolants that provide superior corrosion protection for the mixed metals found in the cooling system.
Flush the system completely every 30,000 to 50,000 miles, ensuring that all old coolant and accumulated deposits are removed. Adding a quality coolant additive like Water Wetter can improve heat transfer characteristics and provide additional corrosion protection.
3. Prioritize Timing Belt and Drive Belt System Reliability
The timing belt system in 240SX vehicles equipped with the KA24DE engine represents one of the most critical maintenance items that can determine whether your engine reaches 200,000 miles or suffers catastrophic failure.
Unlike timing chains, timing belts are wear items that must be replaced at specific intervals, and failure can result in significant engine damage due to the interference design of these engines.
Understanding the interference nature of the KA24DE is crucial for appreciating the importance of timing belt maintenance. When the timing belt breaks, the pistons can collide with the valves, resulting in bent valves, damaged pistons, and potentially cracked cylinder heads.
This type of failure can easily cost more than the vehicle’s value to repair, making preventive timing belt replacement one of the most important investments in your 240SX’s longevity.
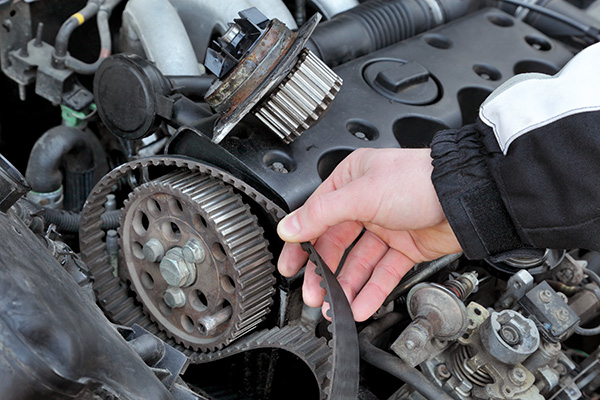

The recommended replacement interval for the timing belt is typically 105,000 miles under normal conditions, but many experienced mechanics and long-term owners recommend a more conservative approach of 80,000 to 90,000 miles, especially on vehicles that have experienced severe service conditions.
Age is as important as mileage timing belts deteriorate over time, even with low mileage, so belts older than seven years should be considered for replacement regardless of mileage.
Quality components make a significant difference in timing belt system reliability. Use OEM belts and tensioners when possible, as they’re engineered specifically for the application and tested under the conditions your engine will experience.
Aftermarket alternatives can be acceptable if they meet or exceed OEM specifications, but avoid bargain-basement components that may fail prematurely and cause expensive engine damage.
4. Execute Strategic Transmission and Differential Maintenance
The drivetrain components of the 240SX are generally robust and capable of handling high mileage when properly maintained, but they require specific attention to fluid changes, component wear patterns, and potential upgrade paths that can extend service life significantly.
Both manual and automatic transmissions have unique maintenance requirements that become increasingly important as these vehicles age and accumulate miles.
For manual transmission-equipped 240SX vehicles, the five-speed transmission is generally reliable but benefits greatly from regular fluid changes and attention to synchronizer wear patterns.
The factory fill was typically conventional gear oil, but modern synthetic gear oils provide superior protection and can extend transmission life significantly.
Redline MT-90 or similar synthetic gear oils designed for synchronizer-equipped transmissions offer excellent protection while maintaining smooth shifting characteristics even as synchronizers begin to show wear.
Manual transmission fluid should be changed every 30,000 to 50,000 miles, or more frequently if the vehicle is driven aggressively or used for track events.
The fluid serves multiple purposes in a manual transmission, lubricating gears and bearings while also protecting synchronizers during gear changes.
As transmission components wear, metal particles accumulate in the fluid, potentially causing accelerated wear if not removed regularly through fluid changes.
Clutch system maintenance becomes increasingly important as mileage accumulates. The hydraulic clutch system uses brake fluid, which absorbs moisture over time and can cause corrosion in the master and slave cylinders.
Flush the clutch hydraulic system every two years or 30,000 miles using high-quality DOT 3 or DOT 4 brake fluid. Pay attention to clutch pedal feel and engagement characteristics changes in pedal feel often indicate developing problems in the hydraulic system or clutch components.
Driveshaft maintenance often involves the universal joints and center support bearing. These components can develop wear over time, leading to vibration and eventual failure. Lubricate universal joints if they have grease fittings, and replace them if excessive play is detected.
The center support bearing should be replaced if it develops noise or excessive play, as failure can cause driveshaft damage and create safety hazards.
Also Read: 9 Worst Moves That Kill a Ford Probes Longevity
5. Develop a Proactive Fuel System Cleaning and Maintenance Strategy
The fuel system in aging 240SX vehicles presents unique challenges that can significantly impact engine performance, reliability, and longevity. As these vehicles approach or exceed 200,000 miles, fuel system components that were designed for a 15-year service life are now operating well beyond their intended lifespan.
A proactive approach to fuel system maintenance can prevent performance problems and protect expensive engine components from damage caused by contaminated or inadequate fuel delivery.
Fuel injectors are precision components that play a critical role in engine performance and emissions. Over time, injectors can become clogged with deposits from fuel additives, combustion byproducts, and contamination.
Dirty injectors cause uneven fuel distribution between cylinders, leading to rough idle, reduced power, increased emissions, and potential engine damage from lean conditions.
Professional ultrasonic injector cleaning every 60,000 to 80,000 miles can restore proper spray patterns and flow characteristics, often dramatically improving engine performance and fuel economy.
The fuel pump and fuel filter work together to ensure clean fuel reaches the injectors at the proper pressure. Original fuel pumps in these vehicles may be operating with reduced output due to internal wear, contamination, or electrical resistance in aging wiring.

Fuel pressure testing should be performed annually on high-mileage vehicles to ensure the pump can maintain proper pressure under all operating conditions.
Many enthusiasts upgrade to high-performance fuel pumps during maintenance, which can provide improved reliability and support for future engine modifications.
Fuel filter replacement is often neglected, but becomes increasingly important as vehicles age. The fuel filter protects the injectors and fuel rail from contamination, but as it becomes loaded with debris, it can restrict fuel flow and cause fuel starvation problems.
Replace the fuel filter every 30,000 to 50,000 miles, or more frequently if fuel quality in your area is questionable. Some owners install additional inline filters for extra protection, particularly if they frequently use fuel from questionable sources.
The evaporative emissions system, while not directly related to fuel delivery, affects fuel system health and emissions compliance. Components like the charcoal canister and purge valves can fail over time, leading to fuel vapor problems and potential emissions test failures.
Regular inspection and replacement of these components, as needed, helps maintain proper fuel system operation and environmental compliance.
6. Maintain Electrical System Integrity Through Preventive Care
The electrical system in aging 240SX vehicles represents one of the most complex and potentially problematic areas that can significantly impact reliability and longevity.
As vehicles approach 200,000 miles, electrical components that were designed for 15-20 years of service are operating well beyond their intended lifespan, often in harsh under-hood environments that accelerate deterioration.
A systematic approach to electrical system maintenance can prevent the frustrating intermittent problems and component failures that often sideline high-mileage vehicles.
Battery and charging system maintenance forms the foundation of electrical system reliability. The alternator in these vehicles typically produces 80-90 amps when new, but output can decrease significantly as internal components wear.
Annual testing of the charging system output under load conditions can identify developing problems before they leave you stranded. Clean battery terminals regularly and apply dielectric grease to prevent corrosion, which can cause voltage drop problems that affect sensitive electronic components.
Ground connections throughout the vehicle deserve special attention, as poor grounds are responsible for a significant percentage of electrical problems in aging vehicles.

The main engine ground strap, body ground points, and individual component grounds can develop resistance over time due to corrosion or loose connections.
Cleaning and tightening ground connections annually, along with applying dielectric grease for protection, can prevent many mysterious electrical problems.
Wiring harnesses under the hood face particularly harsh conditions from heat, vibration, and contamination. Inspect harnesses regularly for signs of deterioration, paying particular attention to areas near heat sources like the exhaust manifold or areas where harnesses contact sharp edges.
Replace or repair damaged sections promptly, as electrical problems often cascade one failing component can cause problems throughout the electrical system.
The ignition system requires particular attention in high-mileage vehicles, especially those equipped with distributors. Distributor caps and rotors deteriorate over time, causing misfires and poor performance.
Replace these components every 30,000 to 50,000 miles, and inspect the distributor advance mechanisms for proper operation. Spark plug wires should be replaced when resistance exceeds specifications or when physical deterioration is evident.
The engine control module (ECM) and related components represent some of the most expensive electrical components in the vehicle. Protect the ECM from moisture and vibration, and ensure that all connections are clean and secure.
Consider having the ECM tested if you experience intermittent performance problems that cannot be traced to other components, as internal failures can occur in aging electronic modules.
7. Implement Advanced Engine Management and Performance Monitoring
Modern engine management strategies become increasingly important as 240SX vehicles age and accumulate high mileage, not necessarily for increased performance, but for enhanced monitoring capabilities and protection against the component failures that can occur in aging engines.
Installing quality aftermarket engine management systems or enhancing the factory systems with additional monitoring capabilities can provide early warning of developing problems while optimizing engine operation for longevity.
Engine monitoring systems allow owners to track critical parameters in real-time, providing insights into engine health that are impossible to obtain through traditional gauges alone.
Air-fuel ratio monitoring through wideband oxygen sensors gives immediate feedback on fuel system performance and can detect problems like failing injectors, fuel pump issues, or intake leaks before they cause engine damage.
Exhaust gas temperature monitoring, particularly important for turbocharged SR20DET engines, can prevent turbocharger damage from over-temperature conditions. Oil pressure and temperature monitoring become increasingly critical as engine bearings and oil pumps wear with age.

Installing quality oil pressure and temperature gauges provides real-time feedback on lubrication system performance and can provide early warning of developing problems. Many high-mileage engine failures could be prevented if owners had warning of dropping oil pressure or excessive oil temperatures.
Coolant temperature monitoring beyond the factory gauge can provide more precise information about engine thermal conditions. Factory gauges are often designed to show “normal” across a wide temperature range, potentially missing temperature excursions that could indicate developing problems.
Precision coolant temperature monitoring can help optimize thermostat selection and identify cooling system problems before they cause overheating damage.
Knock detection systems, whether integrated into aftermarket engine management or added as standalone units, provide crucial protection for aging engines that may be more susceptible to detonation due to carbon buildup or component wear.
Advanced knock detection can automatically adjust ignition timing to prevent damaging detonation while maintaining optimal performance under safe conditions.
Regular data analysis becomes part of the maintenance routine when advanced monitoring systems are installed. Reviewing logged data can reveal trends that indicate developing problems, allowing for proactive maintenance before failures occur.
This approach transforms maintenance from reactive problem-solving to predictive problem prevention, significantly improving the likelihood of reaching high mileage without major component failures.
8. Execute Comprehensive Suspension and Steering System Rehabilitation
The suspension and steering systems in high-mileage 240SX vehicles play crucial roles not only in handling and comfort but also in vehicle safety and component longevity.
As these vehicles age, suspension components experience wear that can affect tire wear patterns, handling characteristics, and the stress placed on other vehicle systems.
A systematic approach to suspension maintenance and rehabilitation can restore proper geometry and function while extending the service life of related components.
Suspension bushings throughout the vehicle deteriorate over time, particularly the rubber bushings used in factory applications. Worn bushings allow excessive movement and misalignment of suspension components, leading to poor handling, irregular tire wear, and increased stress on other suspension parts.
Polyurethane bushing upgrades offer superior longevity compared to rubber replacements, though they may transmit more road noise and vibration into the cabin. Shock absorbers and struts are wear items that gradually lose their damping effectiveness over time.
While complete failure is obvious, gradual degradation can be difficult to detect without careful testing. Worn dampers affect not only ride comfort but also tire contact with the road surface, potentially reducing traction and increasing tire wear.

Quality replacement dampers appropriate for the vehicle’s intended use can significantly improve both safety and component longevity. Ball joints and tie rod ends are critical safety components that require regular inspection and replacement when wear limits are exceeded.
These components support the vehicle’s weight while allowing for steering and suspension movement, making them subject to significant wear over time.
Failed ball joints or tie rod ends can cause loss of vehicle control, making their maintenance a critical safety issue rather than just a performance concern.
Steering system components, including the steering rack, power steering pump, and associated hoses, require attention as vehicles age. Power steering fluid should be changed every 50,000 to 75,000 miles to prevent component damage from contaminated fluid.
Steering racks can develop internal wear, leading to loose steering feel or fluid leaks, while power steering pumps can lose pressure output or develop noise problems. Anti-roll bars and their associated bushings and links also require attention as vehicles age.
Worn anti-roll bar bushings can cause clunking noises and affect handling, while damaged end links can create safety hazards. Regular inspection and replacement of these components maintains proper suspension geometry and function.
9. Establish a Systematic Preventive Maintenance Schedule and Documentation System
The difference between 240SX vehicles that reach 200,000 miles and beyond versus those that suffer premature failures often comes down to the consistency and thoroughness of preventive maintenance programs.
Establishing a systematic approach to maintenance scheduling and documentation creates a framework for staying ahead of potential problems while building a comprehensive history that can guide future maintenance decisions and support resale value.
Developing a maintenance schedule that goes beyond basic manufacturer recommendations requires understanding the unique characteristics and common failure points of your specific vehicle.
Create different maintenance intervals for different systems engine oil changes every 3,000-5,000 miles, transmission services every 30,000-50,000 miles, and timing belt replacement every 80,000-100,000 miles.
Tailor these intervals to your driving conditions, with more frequent service for severe conditions like frequent short trips, extreme temperatures, or spirited driving.
Documentation systems serve multiple purposes beyond simple record-keeping. Comprehensive maintenance records help identify patterns in component failures, track the effectiveness of different maintenance approaches, and provide valuable information for diagnosing intermittent problems.
Digital documentation systems using smartphone apps or cloud-based services ensure records are preserved and easily accessible, while traditional paper logs provide backup documentation that doesn’t depend on technology.
Parts quality tracking becomes increasingly important as vehicles age and require more frequent component replacements. Document not only what was replaced and when, but also the brand, part number, and supplier information for each component.
Performance modifications may require more frequent oil changes, upgraded cooling systems, or specialized components that aren’t available at typical auto parts stores. Plan maintenance schedules and parts availability around any modifications to ensure they don’t compromise reliability.
10. Plan for Strategic Component Upgrades and Preventive Replacements
The final strategy for extending a 240SX past 200,000 miles involves making strategic decisions about when to upgrade or replace components before they fail, rather than waiting for breakdowns that can cause collateral damage or leave you stranded.
This approach requires understanding the typical failure modes and service lives of various components, then making calculated decisions about when preventive replacement provides better value than waiting for failure.
Engine internals present some of the most critical upgrade opportunities for high-mileage vehicles. While complete engine rebuilds may not be cost-effective for all vehicles, strategic upgrades like improved head gaskets, timing chain guides (for SR20DET), or upgraded engine mounts can prevent failures that would otherwise require extensive repairs.
Consider the vehicle’s condition and value when deciding whether internal engine upgrades are justified. Turbocharger rebuilds or upgrades become relevant for SR20DET-equipped vehicles as original turbos approach the end of their service lives.
Rather than waiting for turbo failure which can cause engine damage from oil starvation or debris ingestion consider proactive turbo service or upgrade when the original unit shows signs of bearing wear or reduced performance. Modern turbocharger designs often offer improved reliability and performance compared to original equipment.
Cooling system upgrades provide excellent value for high-mileage vehicles, as improved cooling capacity can prevent overheating damage that would be far more expensive to repair.
Aluminum radiator upgrades, improved water pumps, and enhanced cooling fans can provide better protection for aging engines while often reducing weight compared to original components.
Fuel system upgrades can prevent fuel delivery problems while providing capacity for future modifications. Upgrading to higher-capacity fuel pumps, larger fuel injectors, or improved fuel management systems can prevent fuel starvation problems while supporting any future engine modifications that might be considered.
Electrical system upgrades focus on reliability improvements rather than performance enhancements. Consider upgrades like improved alternators for vehicles with audio system modifications, enhanced grounding systems for better electrical stability, or engine management system upgrades that provide better monitoring and protection capabilities.
Cost-benefit analysis for each potential upgrade helps ensure that modification spending provides appropriate value. Consider not only the initial cost but also the potential savings from prevented failures, improved reliability, and extended service life when evaluating upgrade options. Sometimes spending money proactively on upgrades provides better value than reactive repairs after component failures.
Also Read: 8 Driving Habits That Kill a Honda Accord Coupe Too Early

