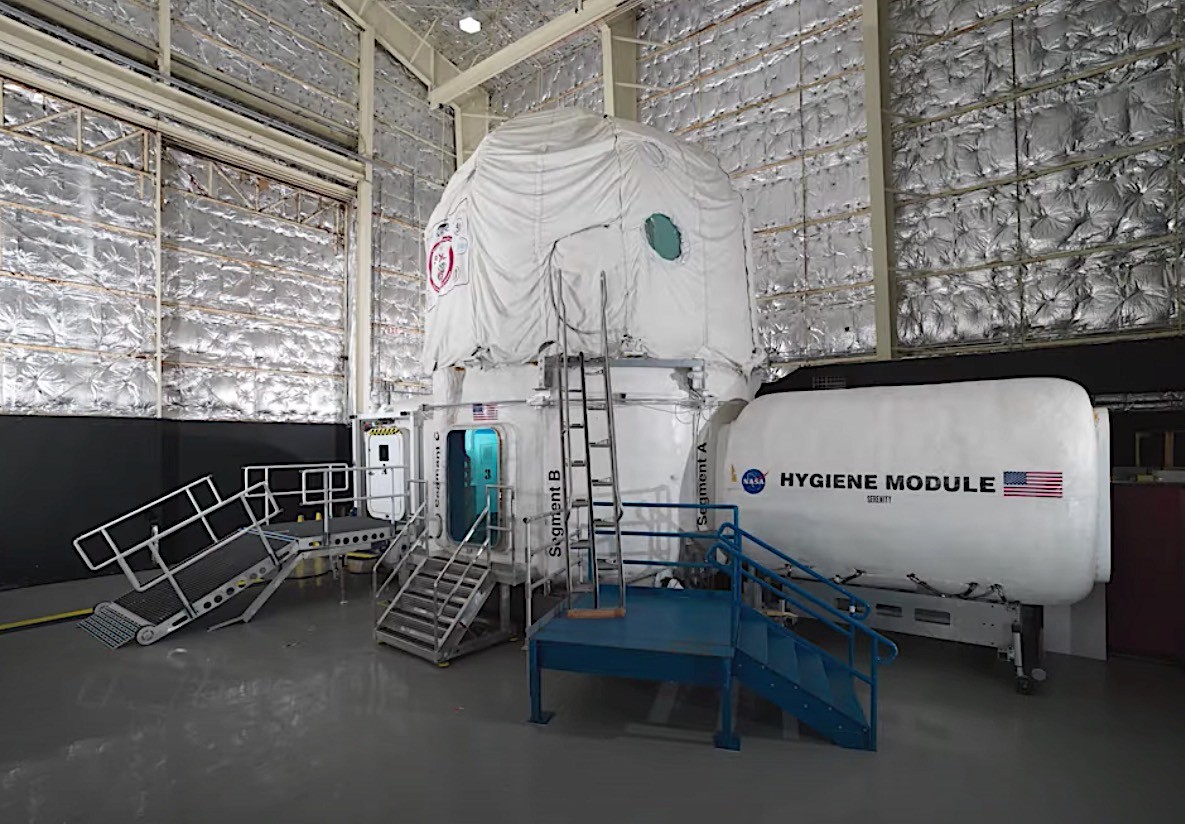
While NASA’s lunar ambitions often steal the spotlight, the agency is quietly but determinedly preparing for a journey to Mars. While specific mission details and hardware may remain under wraps, NASA is diligently practicing the intricacies of astronaut life on the Red Planet.
One of the key elements of this training is the Human Exploration Research Analog (HERA), a 650 square foot habitat at the Johnson Space Center that simulates the conditions of a Martian mission.

Volunteers spend up to 45 days isolated within HERA, replicating the challenges of living alone on Mars. This year alone, three crews of four have participated in these simulated missions. NASA recently announced the final HERA mission of 2024, which will take place from November 1 to December 16.
The crew includes Obaid Alsuwaidi, Kristen Magas, Tiffany Snyder, and Anderson Wilder. The upcoming mission to simulate a Mars journey will be a grueling test of human endurance. The crew will be isolated in a confined space for six weeks, experiencing communication delays and limited resources.
They will conduct scientific research, including virtual reality Mars walks and human health studies. Additionally, the crew will experiment with food production, growing vegetables and raising shrimp. The primary goal of this mission is to understand the challenges of long duration space travel and assess human adaptability to such extreme conditions.
The crew will face a number of challenges during the mission. They will be isolated from the outside world for six weeks, which can be mentally and emotionally taxing. They will also have to deal with communication delays, which can make it difficult to coordinate tasks and solve problems.
Finally, they will have to conserve resources, which will require them to be mindful of their consumption of food, water, and energy. The mission is expected to provide valuable insights into the challenges of long-duration space travel.
By studying the crew’s experiences, scientists will be able to better understand the physical and psychological demands of a mission to Mars. This information will be used to develop strategies for mitigating the risks associated with such a mission.

