As the world searches for sustainable solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change, the debate over synthetic fuels versus electric vehicles (EVs) has gained momentum.
Both technologies offer pathways to a greener future, but they come with distinct advantages and challenges. This article explores the arguments on both sides of the debate and examines the potential of synthetic fuels as an alternative to EVs.
What Are Synthetic Fuels?
Synthetic fuels, also known as e-fuels, are produced by combining hydrogen with carbon dioxide captured from the atmosphere or industrial processes.
The resulting fuel can be used in internal combustion engines (ICEs) much like conventional fossil fuels but with significantly lower carbon emissions. Proponents of synthetic fuels argue that they offer several advantages over EVs.
Advantages of Synthetic Fuels
One of the main benefits of synthetic fuels is their compatibility with existing infrastructure. Synthetic fuels can be used in current ICE vehicles without requiring significant modifications to engines or fueling systems.
This means that the vast network of refueling stations and the millions of ICE vehicles on the road today could continue to operate with minimal changes. This compatibility makes synthetic fuels an attractive option for sectors that are difficult to electrify, such as aviation, shipping, and heavy-duty transport.
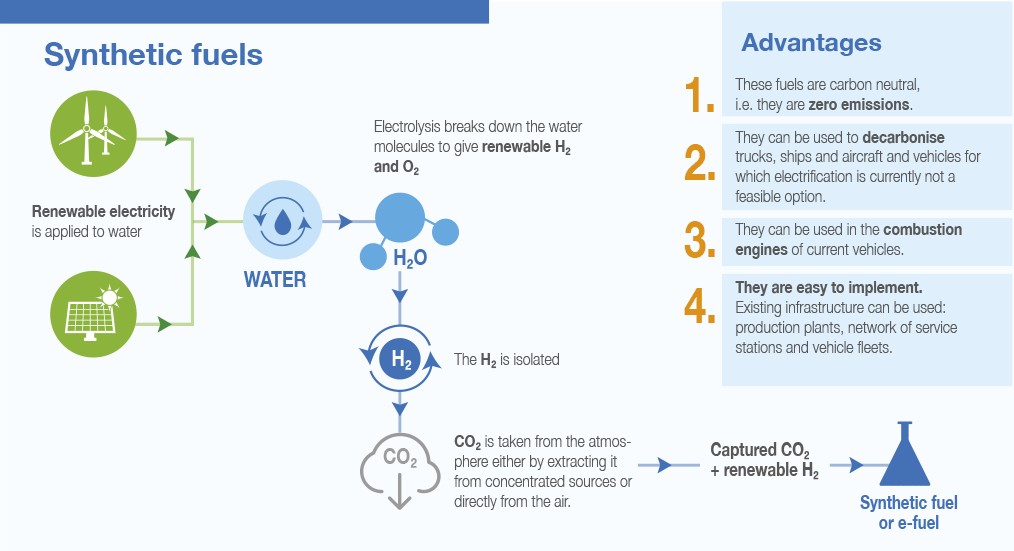
Another advantage is the potential for synthetic fuels to achieve carbon neutrality. When produced using renewable energy sources, the hydrogen and carbon dioxide used to create synthetic fuels can result in a closed carbon loop.
The carbon dioxide emitted during combustion is offset by the carbon dioxide captured during production, making synthetic fuels a climate-friendly option. This potential for carbon neutrality is a key selling point for synthetic fuels.
Challenges of Synthetic Fuels
However, critics of synthetic fuels point to several challenges that must be addressed. One of the primary concerns is the energy efficiency of producing synthetic fuels.
The process of synthesizing hydrogen and combining it with carbon dioxide is energy-intensive and currently less efficient than directly using electricity to power EVs. This inefficiency can result in higher energy costs and reduced sustainability compared to EVs.
Another challenge is the scalability of synthetic fuel production. While the technology exists, producing synthetic fuels at a scale sufficient to meet global energy demands remains a significant hurdle. Large-scale production requires substantial investments in renewable energy infrastructure and carbon capture technology, which may take years to develop.
Advantages of Electric Vehicles
On the other hand, electric vehicles offer several compelling advantages. EVs are highly efficient, converting a larger percentage of energy from the battery to power the wheels compared to ICE vehicles. This efficiency translates to lower operating costs and reduced emissions. Additionally, the rapidly growing network of charging stations and advancements in battery technology are making EVs more accessible and convenient for consumers.
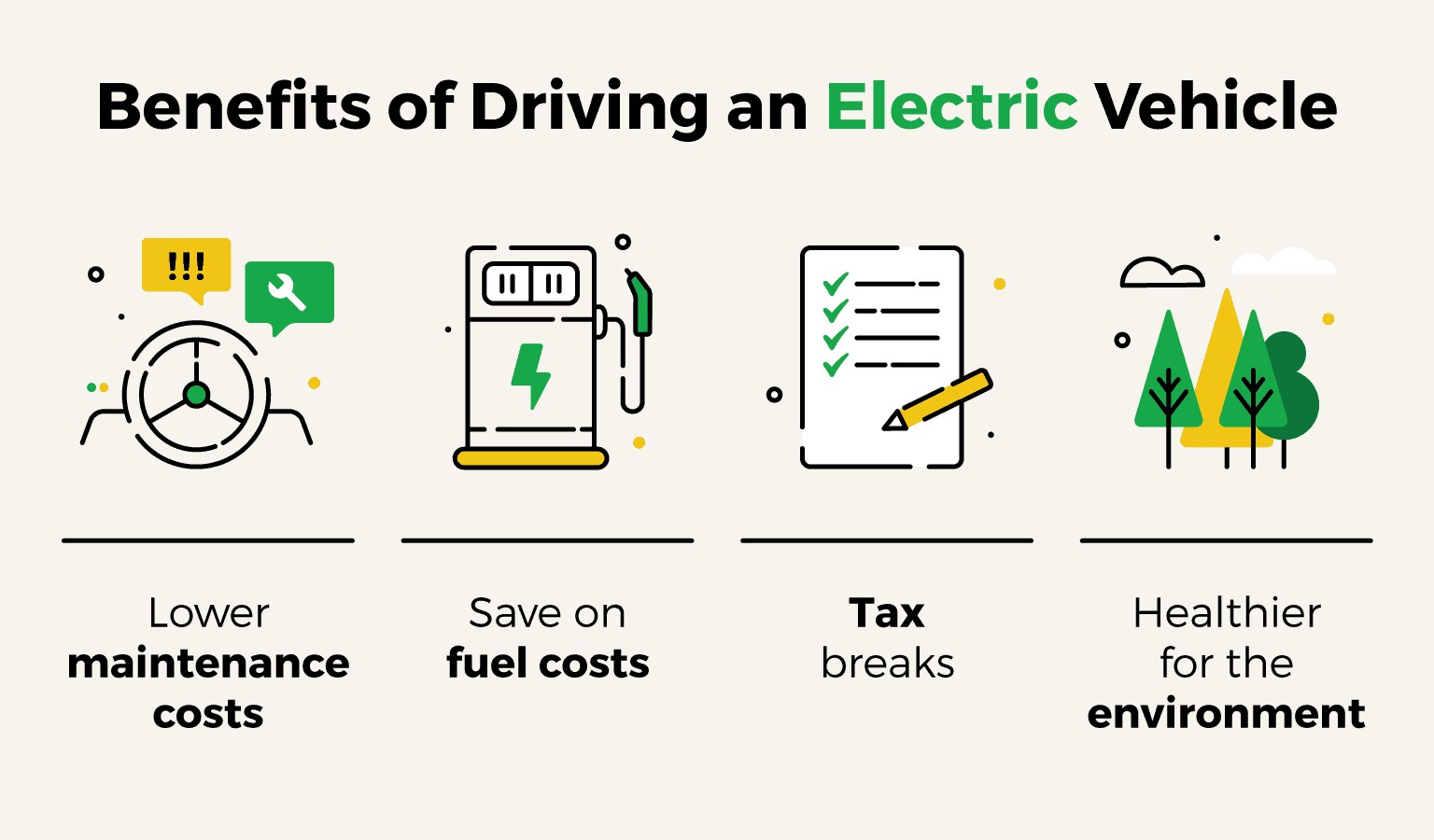
Moreover, the transition to EVs aligns with broader efforts to decarbonize the energy grid. As renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power become more prevalent, the electricity used to charge EVs will increasingly come from clean sources, further reducing their carbon footprint.
Challenges of Electric Vehicles
Despite these advantages, EVs also face challenges, particularly in terms of range anxiety, charging infrastructure, and the environmental impact of battery production and disposal. Addressing these issues is crucial to accelerating the adoption of EVs and realizing their full potential as a sustainable transportation solution.
The debate over synthetic fuels versus electric vehicles reflects the complexity of achieving a sustainable future. While synthetic fuels offer the promise of compatibility with existing infrastructure and carbon neutrality, their energy efficiency and scalability remain significant challenges.
EVs, on the other hand, provide high efficiency and align with the transition to renewable energy but face their own set of hurdles.
Ultimately, a diverse approach that includes both technologies may be necessary to address the varied needs of different sectors and regions in the global effort to reduce emissions and combat climate change.
Also Read: Government Incentives for EVs, Who Really Benefits From The Tax Cuts?

