Timing belts play a vital role in the operation of many internal combustion engines, particularly those with overhead camshafts.
Their job is to synchronize the crankshaft and camshaft rotation so that the engine’s valves open and close at exactly the right times during each cylinder’s intake and exhaust strokes.
This coordination is crucial because even a slight misalignment can lead to poor engine performance, increased emissions, or catastrophic engine damage.
When a timing belt breaks, especially in interference engines where the pistons and valves share overlapping space, the consequences can be severe, often requiring extensive repairs or even a full engine rebuild. This has made timing belt maintenance a top priority for vehicle owners and mechanics worldwide.
The reliability of timing belts depends on several factors, including the materials used in manufacturing, the engine’s design, and the engineering of the belt tensioning system.
While timing belts are generally considered durable components, they are also subject to wear and tear over time. Heat, oil contamination, misalignment, and general mileage contribute to their degradation.
That said, not all engines experience timing belt failure with the same frequency. Certain engines are known for their robust timing belt systems, which can withstand long-term use without breaking, sometimes well beyond their recommended replacement intervals.
These engines tend to benefit from higher-quality materials, better tensioning mechanisms, and design choices that minimize stress on the belt.
For car enthusiasts, mechanics, and prospective buyers, knowing which engines rarely suffer timing belt failure can inform purchasing decisions and maintenance strategies. It can help avoid unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs, while also improving vehicle longevity.
This article discusses eight engines that have developed strong reputations for timing belt durability, focusing on the engineering and material choices that contribute to their resilience.
These examples demonstrate how thoughtful design and proper maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan of critical engine components like timing belts.
While it is never advisable to neglect timing belt replacement altogether, understanding which engines provide more forgiveness in this area offers valuable insight into the automotive engineering landscape.
From compact four-cylinders to turbocharged powerplants, these engines showcase the combination of innovation and practical design needed to reduce the likelihood of timing belt failures.
As we look at each engine, we’ll explore the specific reasons behind its success, including material composition, belt routing, tensioning technology, and maintenance practices.
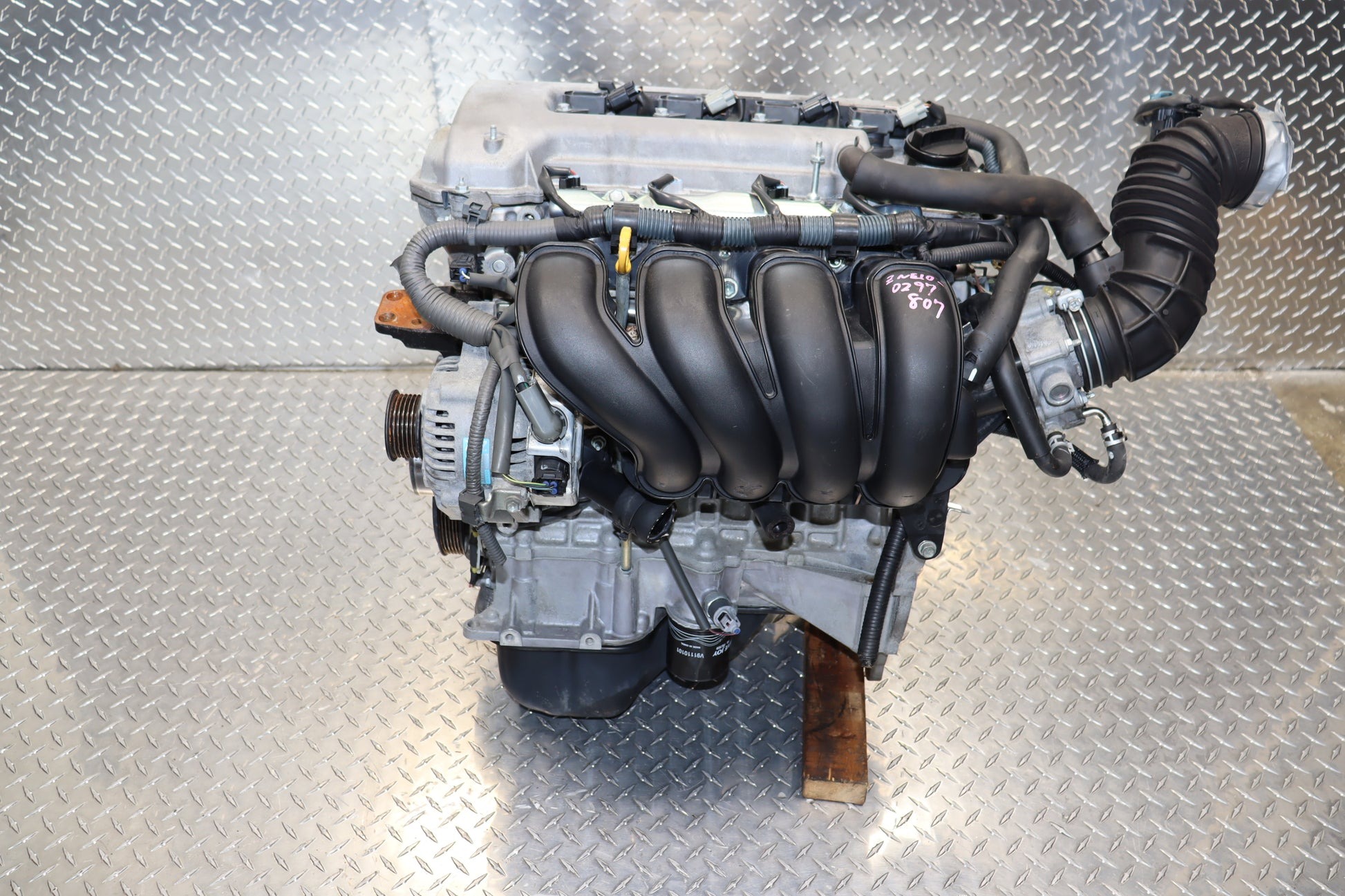
1. Toyota 1ZZ-FE Engine
The Toyota 1ZZ-FE is a 1.8-liter inline-four engine that earned a reputation for durability and particularly for timing belt longevity.
Introduced in the late 1990s, it powered many popular Toyota models such as the Corolla, Celica, and Matrix. One critical factor in the 1ZZ-FE’s timing belt reliability is Toyota’s focus on quality control and material selection.
The belt itself is made from durable synthetic rubber compounds reinforced with strong fibers that resist stretching, cracking, and wear.
This combination allows the belt to maintain its integrity under varying operating conditions, including changes in temperature and mechanical load.
Beyond the belt material, Toyota engineered the timing system to reduce unnecessary stress on the belt. For instance, the belt tensioners and guides are designed to apply consistent tension and maintain precise alignment, ensuring the belt doesn’t slip or experience uneven wear.
The use of hydraulic tensioners in some models provides automatic adjustment, which reduces manual error during installation or maintenance.
This feature is crucial in preventing premature failure because it eliminates belt slack or over-tightening, both of which can shorten the belt’s lifespan. These carefully calibrated components work in harmony to keep the timing belt functioning smoothly over thousands of miles.
The engine design itself also contributes to the timing belt’s endurance. The 1ZZ-FE operates with a relatively modest compression ratio and moderate valve timing profiles, reducing peak stresses that might otherwise accelerate belt wear. This moderate mechanical load on the timing belt system helps prevent fatigue and cracking.
Additionally, the engine’s valves and pistons are designed with some tolerance for minor timing variances, which lowers the risk of catastrophic engine damage should timing belt tension fluctuate temporarily. This engineering balance means the belt does not need to cope with extreme forces.
Many Toyota owners report that, when they adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended timing belt replacement intervals, usually between 90,000 to 100,000 miles, the belts often last well beyond these figures without signs of failure.
This experience further strengthens the 1ZZ-FE’s reputation as an engine with a timing belt system that rarely breaks. The combination of high-quality materials, thoughtful mechanical design, and clear maintenance schedules makes the Toyota 1ZZ-FE an excellent example of timing belt reliability.
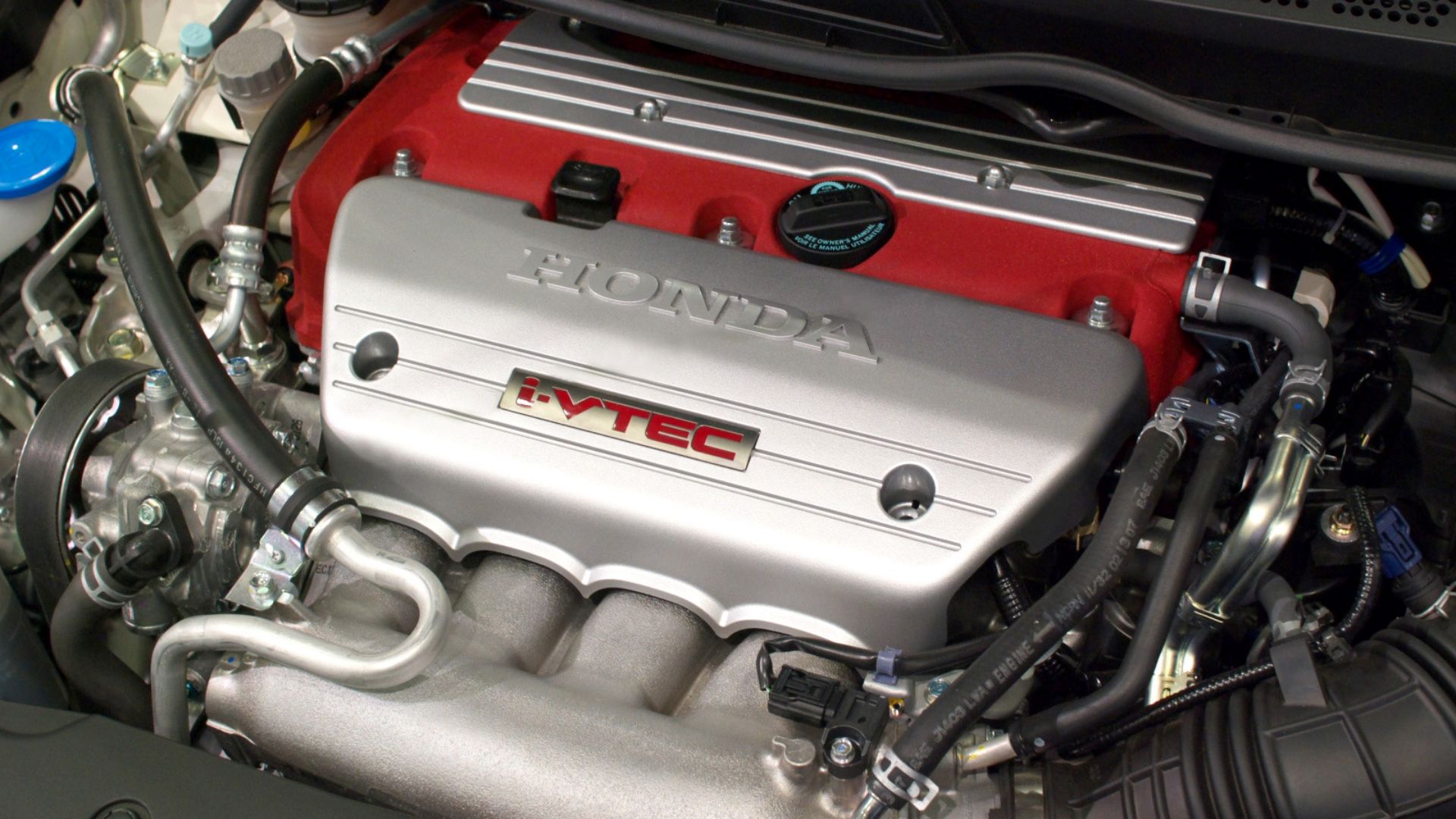

2. Honda D Series Engines
Honda’s D series engines, particularly the D15 and D16 variants, have been widely praised for their reliability and longevity, including the performance of their timing belts. These engines were common in compact cars such as the Honda Civic and CRX during the 1990s and early 2000s.
One reason for their timing belt durability is Honda’s deliberate choice of materials and belt reinforcement. The belts contain strong cords made from fiberglass or Kevlar, which provide excellent resistance to stretching and degradation over time, even under the strain of daily driving or light spirited use.
The D series engines also utilize a relatively simple yet effective tensioning mechanism that keeps the belt tight and aligned with minimal friction.
Honda designed these tensioners to maintain consistent belt pressure, avoiding the common issues of slack belts or overtensioned belts that can lead to premature wear or snapping.
The tensioner’s reliability is supported by periodic maintenance, where changing the tensioner at recommended intervals ensures continued optimal operation. Honda’s maintenance manuals clearly emphasize these replacement points, contributing to the engine’s timing belt resilience.
Additionally, many D-series engines feature a non-interference design, meaning the pistons and valves do not occupy the same space within the combustion chamber at any point in the engine cycle.
While this doesn’t prevent the timing belt from wearing out or breaking, it significantly reduces the risk of internal engine damage in the event of failure.
This design choice lowers repair costs and encourages owners to follow maintenance intervals without the anxiety of catastrophic engine damage looming over timing belt issues. As a result, many owners find their D series engines both forgiving and reliable when it comes to timing belt maintenance.
Moreover, the timing belt path in D-series engines is relatively straightforward, minimizing sharp bends and complex routing that can increase wear.
This simple path, combined with good material quality and consistent tensioning, results in a belt system that can often last well beyond the expected mileage if properly maintained.
Drivers who stick to Honda’s recommended replacement schedules usually enjoy years of trouble-free operation, solidifying the D series engines’ place among those with timing belts that rarely break.

3. Subaru EJ25 Engine (Certain Years)
The Subaru EJ25 engine, a 2.5-liter flat-four boxer engine, is well-known for powering various Subaru models such as the Impreza, Forester, and Outback.
While the EJ series as a whole has had mixed reviews regarding timing belt reliability, specific years and versions of the EJ25 have earned praise for their timing belt durability.
This can be attributed to a combination of improved materials, belt tensioning technology, and the inherent advantages of the flat boxer engine layout.
One of the standout features of the EJ25’s timing belt system is the use of hydraulic tensioners in many models. These tensioners automatically adjust the belt tension according to engine speed, temperature, and wear, ensuring the timing belt maintains optimal tension without manual intervention.
This reduces the chances of slack developing or the belt becoming overly tight, two common causes of premature timing belt failure. Hydraulic tensioners help compensate for natural belt stretch over time, making the system more reliable under various driving conditions.
The boxer engine configuration itself contributes positively to the timing belt’s durability. The horizontally opposed pistons and cylinders create a balanced engine with fewer vibrations and reduced stress on the timing components compared to inline engines.
This layout also allows for a shorter and more direct timing belt route with fewer sharp bends and idlers, minimizing wear caused by friction or misalignment. The relatively compact timing system reduces the belt’s exposure to heat and contaminants, further extending its lifespan.
When properly maintained, with timing belt replacements generally recommended every 100,000 miles, many owners have reported minimal issues with belt failure.
Adhering to Subaru’s maintenance guidelines is key, as neglecting the timing belt can lead to significant engine damage due to the interference nature of many EJ engines.
However, in the well-engineered EJ25 variants, the combination of hydraulic tensioning, boxer layout, and quality materials results in timing belts that are less prone to breaking unexpectedly, contributing to the engine’s reputation for reliability.

4. Volkswagen 1.8T 20V Engine
The Volkswagen 1.8T 20-valve turbocharged engine has become a favorite among enthusiasts for its balance of power and reliability. Found in many VW and Audi models during the late 1990s and early 2000s, this engine also stands out for its durable timing belt system.
Despite the extra stresses introduced by turbocharging, which increases engine torque and heat, Volkswagen engineered the timing belt and its components to endure these conditions without frequent failure.
One key aspect of the 1.8T’s timing belt durability is the construction of the belt itself. Volkswagen used reinforcement cords made from high-strength materials such as Kevlar or fiberglass, which resist stretching and tearing even under the intense torque spikes produced by the turbocharger.
These cords maintain the belt’s structural integrity and prevent elongation, which is essential for accurate timing and engine performance. The belt’s rubber compound is also formulated to resist heat and chemical degradation caused by exposure to oil or coolant.
The timing belt system design is another factor that contributes to its resilience. Volkswagen’s engineers minimized the number of sharp bends and idler pulleys in the belt path, reducing friction points and uneven wear.
The belt tensioner, often spring-loaded or hydraulic depending on the model year, maintains consistent tension, preventing slack or overtightening that could cause premature failure. These components work together to keep the belt running smoothly even during extended high-RPM operation.
Furthermore, the timing belt system benefits from regular maintenance as specified in Volkswagen’s service intervals, generally around 80,000 to 100,000 miles.
Owners who follow these schedules typically experience trouble-free belt operation, with many belts lasting well beyond the recommended replacement mileages.
This combination of advanced materials, thoughtful design, and proper upkeep makes the Volkswagen 1.8T 20V engine a solid example of timing belt reliability, even in a turbocharged application.

5. Mitsubishi 4G63 Engine (Non-Turbo Versions)
The Mitsubishi 4G63 engine, particularly its naturally aspirated non-turbo versions, is recognized for robust timing belt durability. This 2.0-liter inline-four powered a range of Mitsubishi Lancer and Eclipse models during the 1990s and early 2000s.
While the turbocharged versions of this engine tend to put more stress on the timing belt, the non-turbo variants benefit from a more moderate mechanical load, which enhances belt longevity.
Mitsubishi’s timing belts are made from advanced synthetic materials reinforced with fiberglass cords, providing excellent resistance to heat, cracking, and stretching.
These materials allow the belts to maintain their strength and elasticity even after prolonged exposure to the harsh environment inside the engine bay. The belt’s compound is designed to resist oil and coolant contamination, which can be a common cause of premature belt failure in some engines.
The timing belt tensioners in the 4G63 non-turbo engines are designed to provide consistent and reliable tension throughout the belt’s service life.
Proper tensioning ensures that the belt remains in firm contact with the camshaft and crankshaft pulleys, reducing slippage and wear. These tensioners are often mechanical springs that maintain steady pressure, reducing the risk of sudden tension loss or overtightening.
Owners who adhere to Mitsubishi’s recommended timing belt replacement intervals, which generally fall between 60,000 and 90,000 miles, often report that the belts last well beyond this mileage without problems.
The engine’s moderate operating conditions, combined with high-quality belt materials and reliable tensioning mechanisms, make the non-turbo 4G63 a prime example of an engine with timing belts that rarely fail unexpectedly.

6. Ford 1.8L Zetec Engine
The Ford Zetec 1.8-liter inline-four engine, introduced in the early 1990s and used in models such as the Ford Focus and Escort, is widely regarded for its balance of performance, efficiency, and durability, including timing belt reliability.
Despite being a mass-produced engine, the Zetec’s timing belt system reflects careful design choices to ensure long service life under typical driving conditions.
Ford used durable synthetic rubber compounds for the timing belt, reinforced with fiberglass or aramid fibers, to resist cracking, stretching, and abrasion. This construction allows the belt to endure the cyclical stresses of engine operation without degrading prematurely.
Additionally, the timing belt tensioners and guides are engineered for precise belt alignment and consistent tension, reducing the risk of belt slippage or uneven wear, which are common causes of failure.
The timing system layout in the Zetec engine is relatively straightforward, featuring a simple belt path with minimal pulleys and tensioners.
This simplicity reduces the number of components that can fail and lessens friction points, contributing to smoother belt operation and extended life.
The engine itself operates under moderate mechanical stress, with smooth power delivery that does not place excessive load on the timing belt system.
When owners follow Ford’s maintenance recommendations, typically replacing the timing belt every 60,000 to 90,000 miles, they generally experience trouble-free operation.
The engine’s design, combined with quality belt materials and components, results in a timing belt system that rarely breaks unexpectedly, making the Zetec a dependable choice for drivers seeking reliability without sacrificing performance.
Also read: 9 Maintenance Oversights That Kill a Dodge Viper’s Longevity
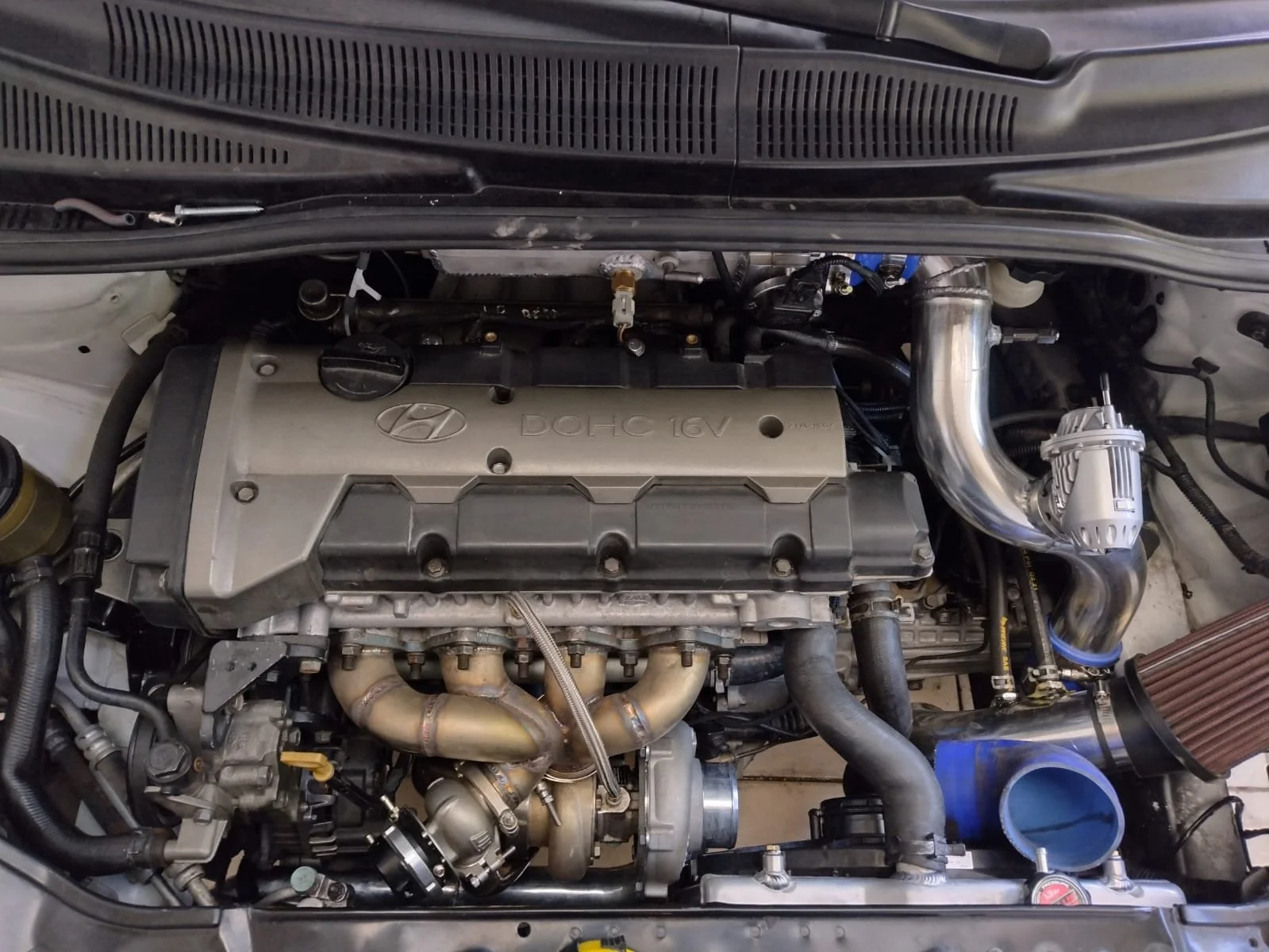

7. Hyundai Beta II 2.0L Engine
The Hyundai Beta II 2.0-liter inline-four engine, prevalent in Hyundai models from the late 1990s and early 2000s, is another solid example of timing belt durability. Hyundai invested in engineering a timing belt system that combines strong materials with a robust tensioning setup, contributing to the belt’s long service life.
The timing belts used in the Beta II engine are manufactured from durable synthetic rubber with embedded reinforcing fibers, typically fiberglass or Kevlar, providing excellent resistance to wear and stretching.
These belts can endure significant heat and mechanical stress, which is essential given the engine bay’s hot environment and the cyclic forces imposed by engine operation.
Hyundai also designed the timing belt tensioners and guides to maintain steady, accurate belt tension and alignment. This reduces the likelihood of belt slip, premature wear, or sudden failure due to improper tension.
The belt routing in the Beta II is straightforward, minimizing unnecessary bends or idlers that could increase friction and wear. This design simplicity contributes to the timing belt’s long life.
Adhering to Hyundai’s recommended timing belt replacement intervals, typically between 60,000 and 90,000 miles, helps ensure that the belt remains in optimal condition.
Many owners report belts lasting beyond these intervals when proper maintenance is performed, making the Beta II a reliable engine for those seeking a timing belt system that is less prone to failure.
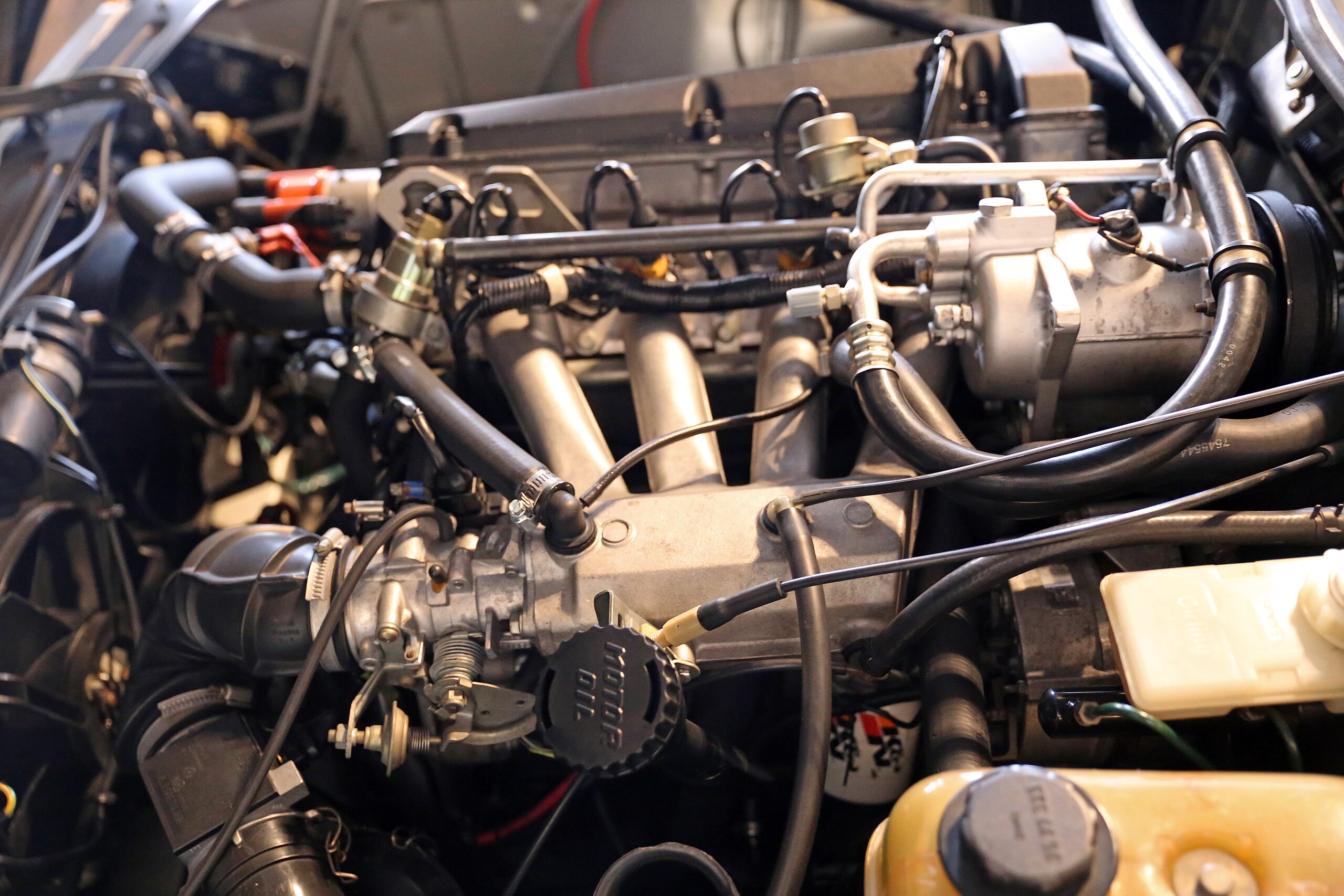
8. Saab B205 Engine
The Saab B205 engine, a 2.0-liter inline-four, was used in various Saab models, including the 9-3 and 900 during the late 1990s and early 2000s.
Known for combining turbocharged performance with reliability, the B205 also features a timing belt system that is highly regarded for its durability and longevity, provided that regular maintenance is followed.
Saab engineers selected high-quality materials for the timing belt, incorporating strong reinforcement cords designed to resist stretching and degradation caused by heat and contaminants.
The belt’s rubber compound is formulated for durability, maintaining flexibility and strength over long service periods. This ensures that the timing belt remains reliable even under the increased thermal loads common in turbocharged engines.
The B205’s timing belt system also benefits from precision tensioning components that maintain consistent belt tension, reducing the risk of slack or over-tightening.
The tensioners, often spring-loaded or hydraulic, help absorb vibrations and maintain belt alignment. This careful engineering prevents many of the common causes of timing belt failure, such as slipping or uneven wear.
Owners who replace the timing belt according to Saab’s recommended intervals, often around 90,000 miles, generally experience long-lasting belt performance without unexpected breakage.
The combination of strong materials, precise tensioning, and routine maintenance makes the B205 a standout engine when it comes to timing belt durability in turbocharged vehicles.
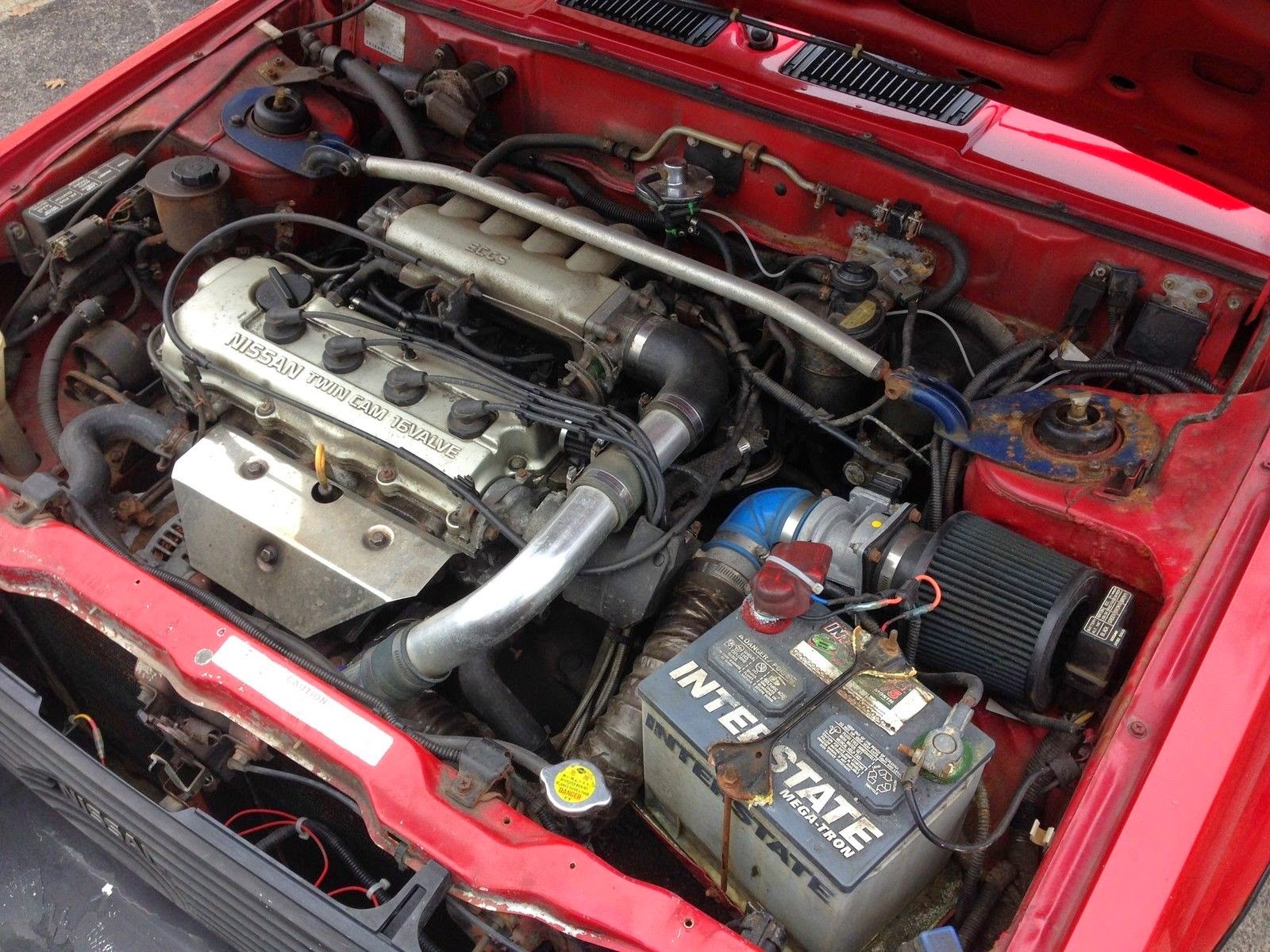

9. Nissan GA16DE Engine
The Nissan GA16DE is a 1.6-liter inline-four engine widely used in models such as the Nissan Sentra and NX during the 1990s. This engine is recognized for its simplicity, durability, and reliable timing belt system.
One of the core reasons behind its timing belt longevity is Nissan’s use of reinforced rubber belts combined with high-quality tensioning components designed to endure years of operation under various driving conditions. The belt features fiberglass cords that resist stretching and fatigue, helping it maintain precise timing over long distances.
Nissan designed the timing belt system on the GA16DE with careful attention to minimizing stress points. The belt routing is straightforward, with minimal bends and pulleys, which reduces friction and uneven wear.
The tensioner itself uses a spring-loaded design that automatically compensates for belt stretch, ensuring the proper tension remains constant without manual adjustment. This reduces the likelihood of slack, which can cause misalignment or premature failure.
The engine’s moderate operating parameters also contribute to the timing belt’s longevity. The GA16DE operates with conservative valve timing and compression ratios, resulting in smoother operation and less mechanical strain on the timing belt.
Moreover, the engine features a non-interference valve design in many models, reducing the risk of catastrophic damage if the timing belt ever does fail, making the system more forgiving.
Routine maintenance aligned with Nissan’s recommended timing belt replacement intervals, usually around 60,000 to 90,000 miles, typically results in trouble-free belt operation.
Many owners have reported belts lasting well beyond the suggested service life when properly maintained, reinforcing the GA16DE’s reputation as an engine with a timing belt system that rarely breaks.

10. Renault F4P Engine
The Renault F4P is a 1.8-liter inline-four engine used in various Renault models from the 1990s and early 2000s. This engine is well-regarded for its robust timing belt system, which benefits from Renault’s focus on reliability and cost-effective engineering.
The timing belt is constructed from durable synthetic rubber reinforced with fiberglass cords, providing excellent resistance to wear, heat, and stretching. This reinforcement ensures the belt maintains its integrity over extended periods without cracking or elongating prematurely.
The timing belt system on the F4P engine is designed to minimize unnecessary mechanical stresses.
Renault engineers employed a simple belt path with few idler pulleys and a reliable tensioner that uses a spring mechanism to maintain constant tension.
This design avoids belt slack or excessive tightness, which are primary contributors to early belt wear or failure. Furthermore, the tensioner’s durability means it requires less frequent replacement, supporting the belt’s longevity.
Renault’s F4P engine also operates with relatively mild valve timing and compression ratios, which places less stress on the timing components. The engine’s design emphasizes smooth power delivery and balanced mechanical loads, reducing vibrations and potential belt fatigue.
In addition, the engine’s timing belt covers provide good protection from contaminants such as oil and debris, which can deteriorate belt material over time.
Many owners following Renault’s timing belt replacement recommendations, often set between 60,000 and 90,000 miles, experience long-lasting belts that rarely break unexpectedly.
The combination of strong materials, well-engineered tensioning, and straightforward design has helped make the F4P a reliable example of timing belt durability in European compact cars.
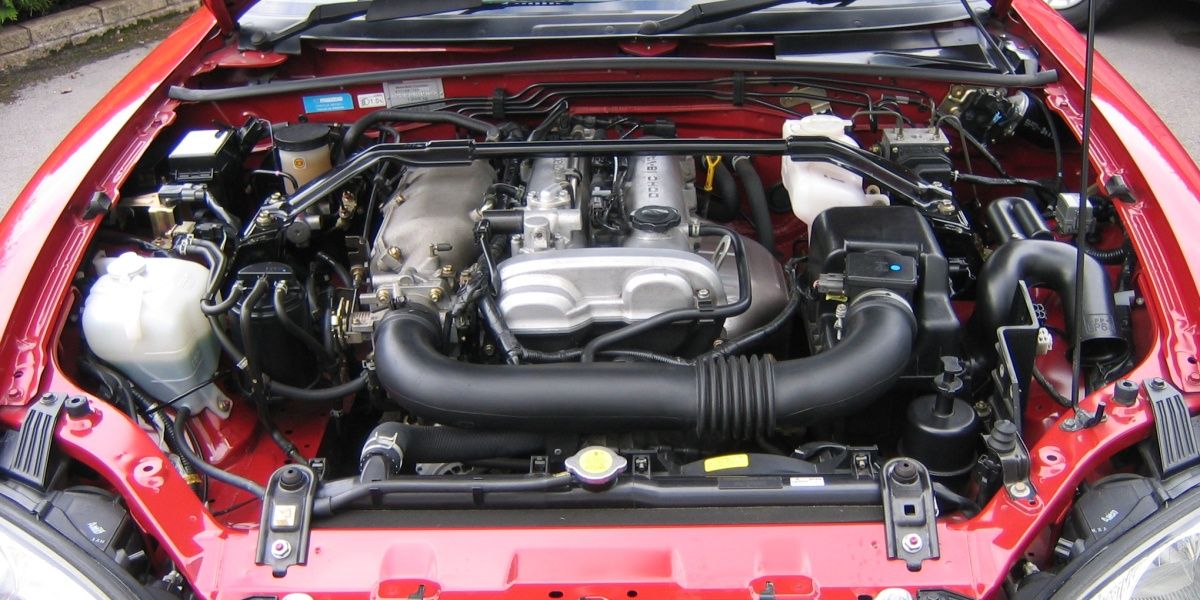

11. Mazda BP-ZE Engine
The Mazda BP-ZE, a 1.8-liter inline-four engine, is well-known for powering the popular Mazda MX-5 Miata from the 1990s. This engine is praised for its lively performance and exceptional reliability, including its timing belt system.
Mazda employed high-quality timing belts reinforced with fiberglass cords, which provide excellent tensile strength and resistance to heat and wear. This reinforcement allows the timing belt to maintain precise synchronization between the crankshaft and camshaft even after prolonged use.
Mazda’s design of the BP-ZE’s timing belt system focuses on maintaining proper tension and alignment. The engine utilizes a spring-loaded tensioner that consistently adjusts for belt stretch, minimizing the risk of slack or overtightening.
The timing belt routing is relatively straightforward, reducing friction points and wear caused by complex belt paths. Additionally, Mazda engineered the timing covers to protect the belt from oil leaks and dirt ingress, further extending the belt’s useful life.
The BP-ZE engine is a non-interference engine, which means that even if the timing belt were to fail unexpectedly, the risk of internal engine damage is minimal.
This design consideration provides an additional layer of reliability, making the timing belt system more forgiving for owners who may occasionally exceed recommended maintenance intervals.
Furthermore, the engine’s balanced mechanical loads and smooth operation reduce stresses that can contribute to belt degradation.
Owners who follow Mazda’s maintenance schedule, which generally advises timing belt replacement around 60,000 to 90,000 miles, often report timing belts that last well beyond these intervals.
The BP-ZE’s combination of quality materials, intelligent design, and routine upkeep make it a prime example of an engine whose timing belt system rarely breaks unexpectedly, providing peace of mind for drivers and enthusiasts alike.
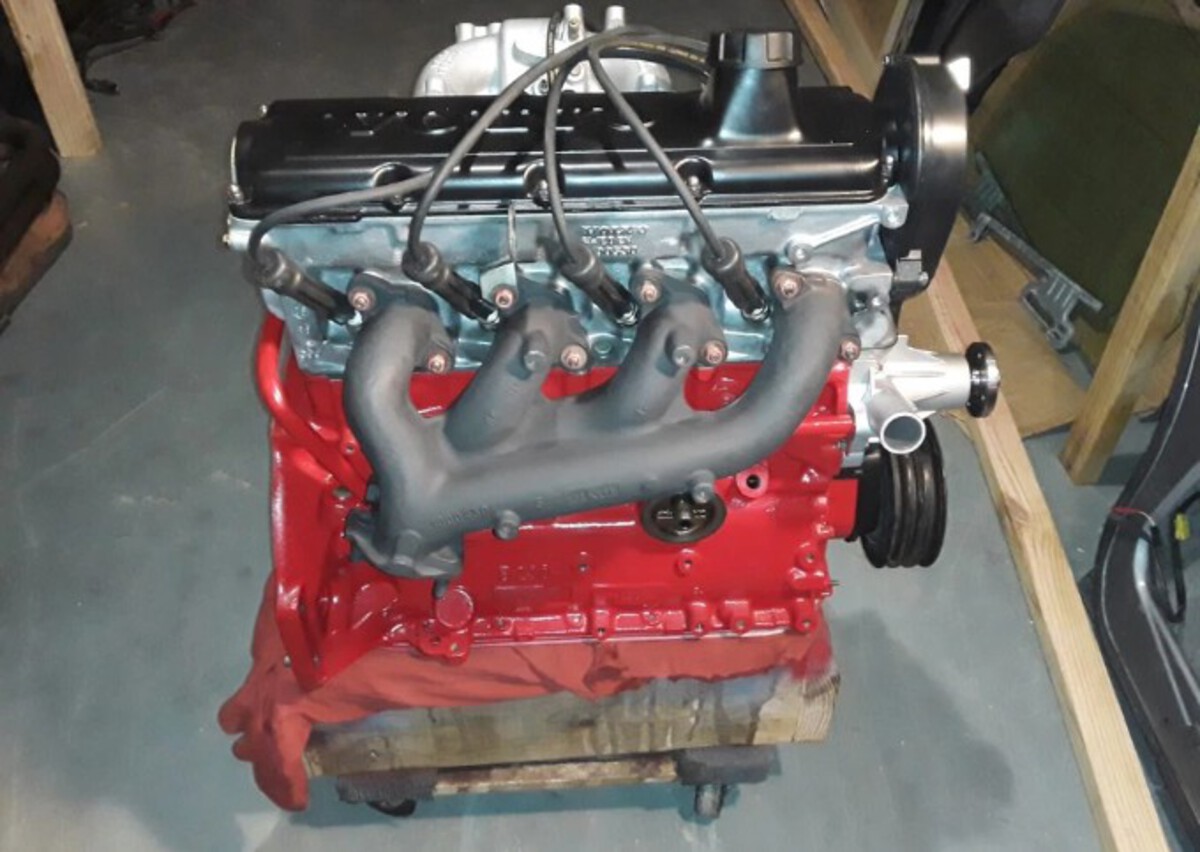

12. Volvo B230 Engine
The Volvo B230 engine, a 2.3-liter inline-four produced primarily in the 1980s and 1990s, has built a solid reputation for reliability, including its timing belt system.
Known for powering several Volvo models like the 240, 740, and 940 series, the B230 combines durability with straightforward engineering that contributes to the timing belt’s long-lasting performance.
One key factor is Volvo’s use of high-quality timing belts made from reinforced synthetic rubber materials that resist heat, oil contamination, and mechanical wear over time.
The belts include fiberglass or aramid fibers for added tensile strength, helping maintain precise timing over extended mileage.
Volvo’s design philosophy for the B230 engine includes a relatively simple and direct timing belt path, which reduces the number of pulleys and idlers that might cause friction and premature wear.
The tensioning system often employs a spring-loaded tensioner that maintains consistent pressure on the belt, automatically compensating for belt stretch as the engine ages.
This consistency prevents slack from developing and reduces the risk of belt misalignment, a common cause of failure in less robust timing belt setups.
The B230 is a non-interference engine in many variants, which means that in the event of a timing belt failure, the valves and pistons do not collide, significantly reducing the potential for catastrophic engine damage.
This engine design reduces anxiety for owners regarding timing belt maintenance, although regular replacement is still strongly recommended to avoid breakdowns. The mechanical loads and valve timing in the B230 are moderate, which minimizes stress on the timing belt compared to higher-performance engines.
Owners and enthusiasts who maintain their B230 engines according to Volvo’s service guidelines, typically replacing the timing belt around 60,000 to 90,000 miles, report few timing belt failures.
The combination of quality materials, effective tensioning mechanisms, simple routing, and engine design choices makes the B230 a classic example of a timing belt system that rarely breaks, even after many years of use.
This reliability has helped the B230 remain a favorite among Volvo fans and classic car collectors who value long-term durability.
